Haystacks Series by Claude Monet | Light, Time & Atmosphere
by Claude Monet
Market Value
$90-140 million
How much is Haystacks Series by Claude Monet | Light, Time & Atmosphere worth?Fast Facts
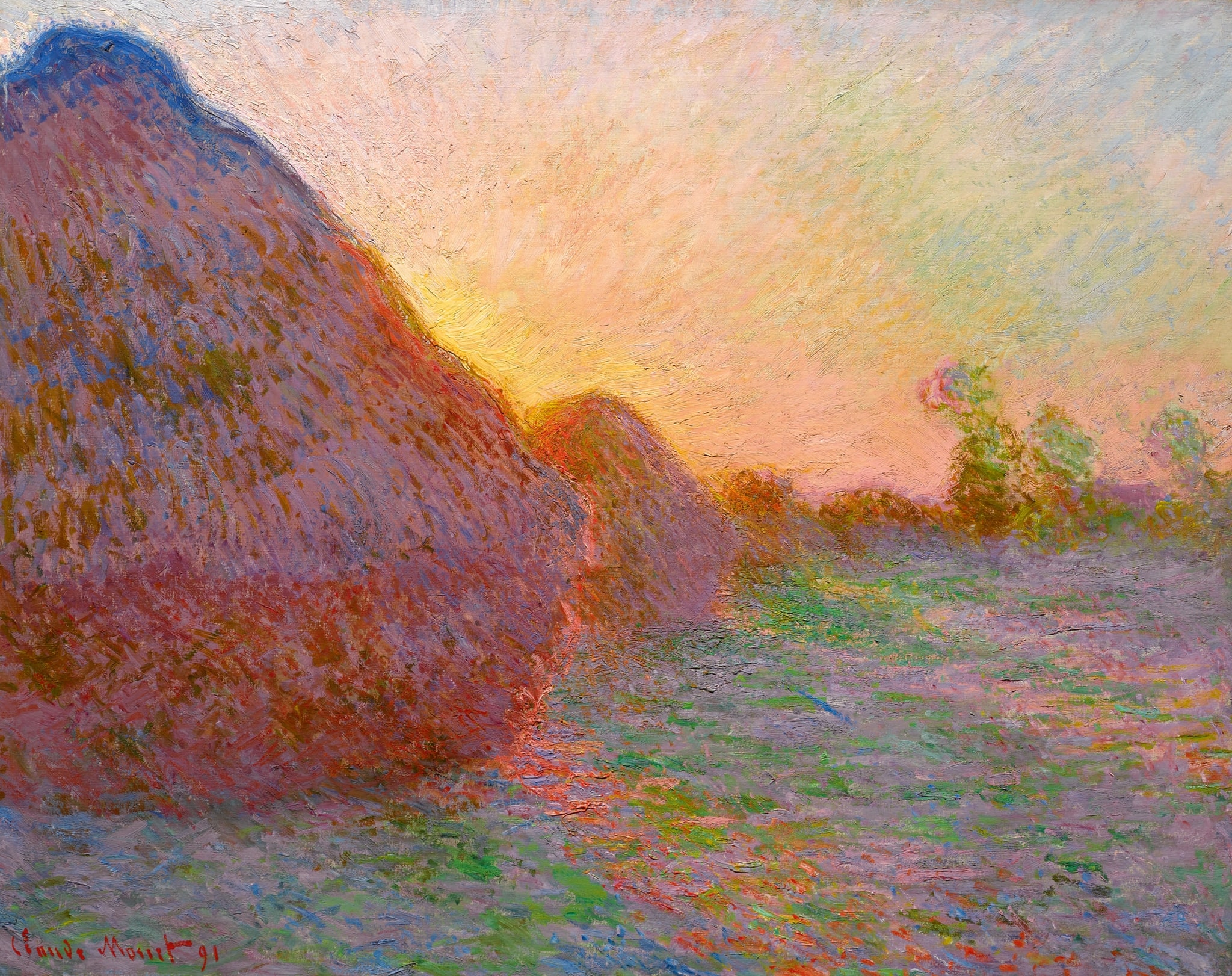
Click on any numbered symbol to learn more about its meaning
Meaning & Symbolism
Explore Deeper with AI
Ask questions about Haystacks Series by Claude Monet | Light, Time & Atmosphere
Popular questions:
Powered by AI • Get instant insights about this artwork
Related Themes
About Claude Monet
More by Claude Monet

La Japonaise (Camille Monet in Japanese Costume)
Claude Monet (1876)
Claude Monet’s La Japonaise (Camille Monet in Japanese Costume) (1876) stages a witty confrontation between <strong>Parisian modernity</strong> and the fashion for <strong>Japonisme</strong>. A fair-skinned model in a blazing red uchikake preens before a wall tiled with uchiwa fans, lifting a <strong>tricolor</strong> hand fan that asserts Frenchness amid the imported decor. The painting turns costume, props, and gaze into a performance about <strong>desire, display, and identity</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Boating
Claude Monet (1887)
Monet’s Boating crystallizes modern leisure as a drama of perception, setting a slim skiff and two pale dresses against a field of dark, mobile water. Bold cropping, a thrusting oar, and the complementary flash of hull and foliage convert a quiet outing into an experiment in <strong>modern vision</strong> and the <strong>materiality of water</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Thames below Westminster
Claude Monet (about 1871)
Claude Monet’s The Thames below Westminster turns London into <strong>light-made architecture</strong>, where Parliament’s mass dissolves into mist and the river shivers with <strong>industrial motion</strong>. Tugboats, a timber jetty with workers, and the rebuilt Westminster Bridge assert a modern city whose power is felt through atmosphere more than outline <sup>[1]</sup>.

Women in the Garden
Claude Monet (1866–1867)
Claude Monet’s Women in the Garden choreographs four figures in a sunlit bower to test how <strong>white dresses</strong> register <strong>dappled light</strong> and shadow. The path, parasol, and clipped flowers frame a modern ritual of leisure while turning fashion into an instrument of <strong>perception</strong>. The scene reads less as portraiture than as a manifesto for painting the <strong>momentary</strong> outdoors <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Impression, Sunrise
Claude Monet (1872)
In Impression, Sunrise, Claude Monet turns Le Havre’s fog-bound harbor into an experiment in <strong>immediacy</strong> and <strong>modernity</strong>. Cool blue-greens dissolve cranes, masts, and smoke, while a small skiff cuts the water beneath a blazing, <strong>equiluminant</strong> orange sun whose vertical reflection stitches the scene together <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The effect is a poised dawn where industry meets nature, a quiet <strong>awakening</strong> rendered through light rather than line.

The Train in the Snow (The Locomotive)
Claude Monet (1875)
Claude Monet’s The Train in the Snow (The Locomotive) (1875) turns a suburban winter platform into a study of <strong>modernity absorbed by atmosphere</strong>. The engine’s twin yellow headlights and a smear of red push through a world of greys and violets as steam fuses with the low sky, while the right-hand fence and bare trees drill depth and cadence into the scene <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. Monet fixes not an object but a <strong>moment of perception</strong>, where industry seems to dematerialize into weather <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.