Mimesis vs. abstraction (truth vs. artifice)
Featured Artworks

The Broken Column
Frida Kahlo (1944)
The Broken Column presents a frontal self-image split open to expose a shattered classical spine, mapping <strong>chronic pain</strong> across the body with nails while a white <strong>medical corset</strong> both supports and imprisons. Against a cracked, barren landscape, Kahlo’s steady gaze transforms injury into <strong>endurance</strong> and self-possession <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
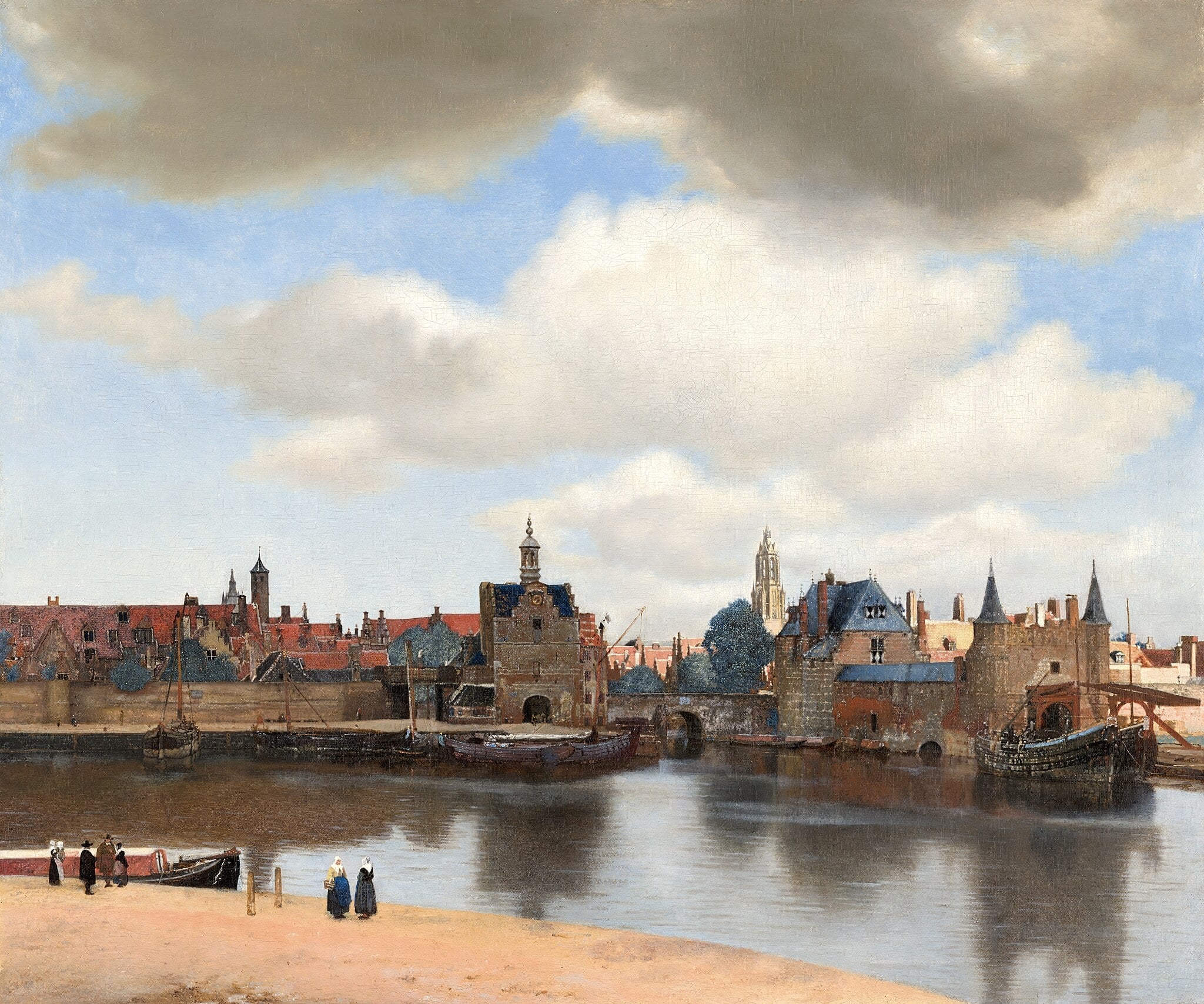

View of Delft
Johannes Vermeer (c. 1660–1661)
View of Delft turns a faithful city prospect into a meditation on <strong>civic order, resilience, and time</strong>. Beneath a low horizon, drifting clouds cast mobile shadows while shafts of sun ignite blue roofs and the bright spire of the <strong>Nieuwe Kerk</strong>, holding the scene’s moral center <sup>[1]</sup>. Small figures and moored boats ground prosperity in <strong>everyday community</strong> without breaking the hush.

The Descent from the Cross
Peter Paul Rubens (1611–1614)
At night beneath a black sky, The Descent from the Cross stages a solemn transfer of Christ’s body along a luminous <strong>white shroud</strong> that cuts diagonally across the scene. The flanking wings—<strong>The Visitation</strong> and <strong>The Presentation in the Temple</strong>—frame the central tragedy with beginnings and revelation, turning the triptych into a single arc from Incarnation to Redemption. Rubens fuses <strong>Baroque chiaroscuro</strong> with tender, communal gestures to make grief a shared act of devotion.

La Japonaise (Camille Monet in Japanese Costume)
Claude Monet (1876)
Claude Monet’s La Japonaise (Camille Monet in Japanese Costume) (1876) stages a witty confrontation between <strong>Parisian modernity</strong> and the fashion for <strong>Japonisme</strong>. A fair-skinned model in a blazing red uchikake preens before a wall tiled with uchiwa fans, lifting a <strong>tricolor</strong> hand fan that asserts Frenchness amid the imported decor. The painting turns costume, props, and gaze into a performance about <strong>desire, display, and identity</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I
Gustav Klimt (1907)
Gustav Klimt’s Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I stages its sitter as a <strong>secular icon</strong>—a living presence suspended in a field of gold that converts space into <strong>pattern and power</strong>. The naturalistic face and hands emerge from a reliquary-like cascade of eyes, triangles, and tesserae, turning light, ornament, and status into the painting’s true subjects <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman with a Hat
Henri Matisse (1905)
In Woman with a Hat, Henri Matisse turns portraiture into a laboratory for <strong>pure color</strong> and <strong>modern identity</strong>. Jagged greens and violets carve the face; the hat detonates into a crown of brushstrokes; a fan slices the torso into bright planes. The result declares Fauvism’s credo: <strong>feeling over description</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Tea
Mary Cassatt (about 1880)
Mary Cassatt’s The Tea stages a poised, interior <strong>drama of manners</strong>: two women sit close yet feel apart, one thoughtful, the other raising a cup that <strong>veils her face</strong>. A gleaming, oversized <strong>silver tea service</strong> commands the foreground, its reflections turning ritual objects into actors in the scene <sup>[1]</sup>. The shallow, cropped room—striped wall, gilt mirror, marble mantel—compresses the atmosphere into <strong>intimacy edged by restraint</strong>.
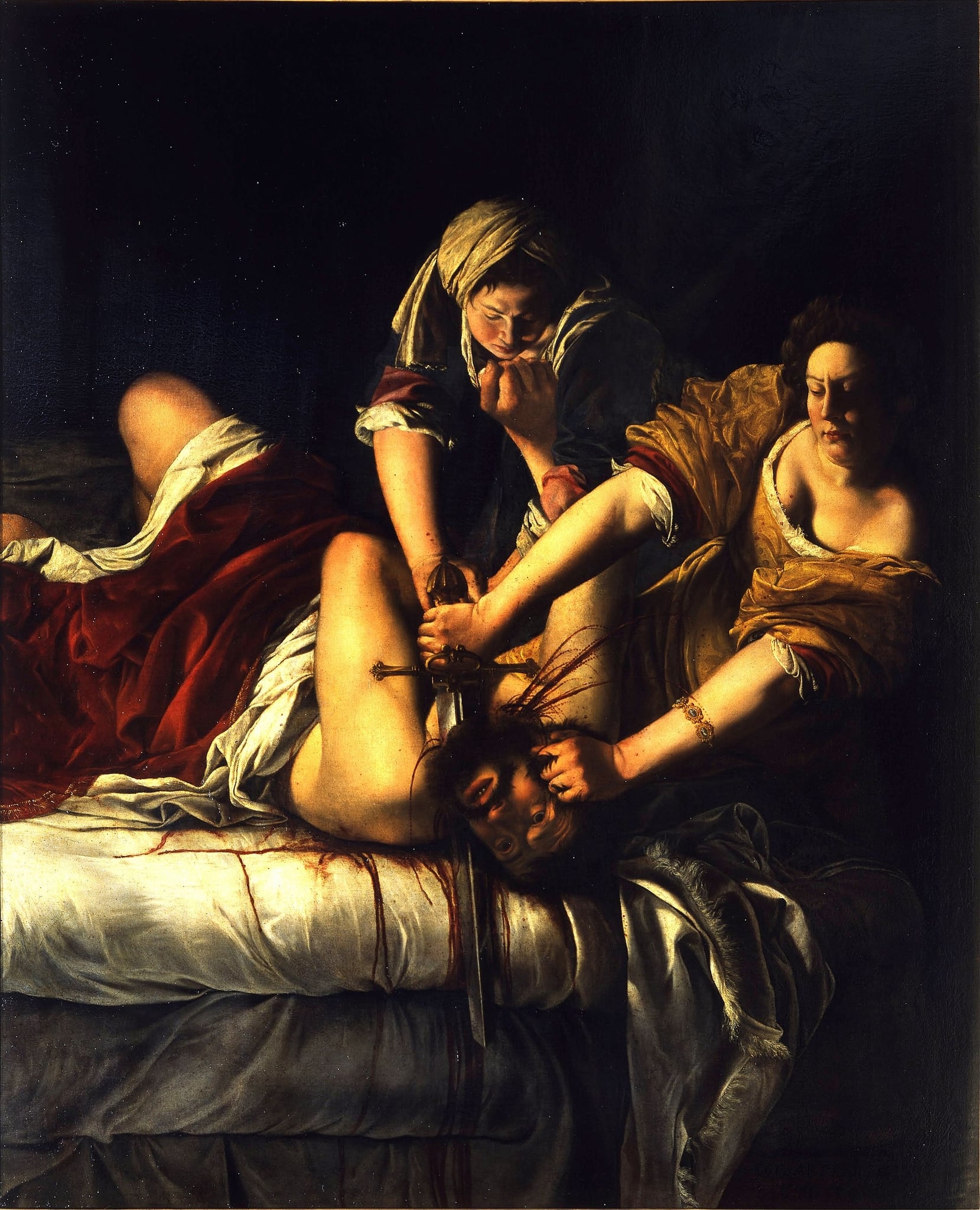

Judith Slaying Holofernes
Artemisia Gentileschi (c. 1612–13)
Artemisia Gentileschi’s Judith Slaying Holofernes hurls us into the fatal instant when Judith and her maid overpower the Assyrian general. In a void of darkness, a hard light chisels out straining arms, a heavy sword, and blood darkening the white sheets—an image of <strong>justice enacted through female collaboration</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Red Studio
Henri Matisse (1911)
Henri Matisse’s The Red Studio (1911) saturates the artist’s workspace in a continuous field of <strong>Venetian red</strong>, collapsing walls, floor, and furniture into a single chromatic plane. Objects and architecture appear as <strong>mustard-yellow reserve lines</strong> that read like drawing, while Matisse’s own paintings and sculptures retain full color, asserting art’s primacy within the room <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The result is a studio that feels like a <strong>mental map</strong> rather than a literal interior.

The Embroiderer
Johannes Vermeer (1669–1670)
In The Embroiderer, Johannes Vermeer condenses a world of work into a palm‑sized drama of <strong>attention</strong> and <strong>transformation</strong>. A young woman bends over a lace pillow as loose red and white threads spill in front, while a nascent pattern gathers under her poised fingers. Vermeer’s right‑hand light isolates the act of making and turns domestic labor into <strong>virtuous concentration</strong> <sup>[1]</sup>.

Boating
Claude Monet (1887)
Monet’s Boating crystallizes modern leisure as a drama of perception, setting a slim skiff and two pale dresses against a field of dark, mobile water. Bold cropping, a thrusting oar, and the complementary flash of hull and foliage convert a quiet outing into an experiment in <strong>modern vision</strong> and the <strong>materiality of water</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Sleeping Venus
Giorgione (c. 1508–1510)
In The Sleeping Venus, the goddess reclines across a rolling landscape, her body a serene diagonal that fuses human beauty with nature’s forms. Cool, <strong>silvery drapery</strong> and <strong>deep red cushions</strong> intensify her luminous flesh, while the right-hand <strong>Venus pudica</strong> gesture suspends desire between revelation and restraint. The painting crystallizes the Venetian ideal of poetic harmony (<strong>poesia</strong>) and inaugurates the fully realized reclining nude in Western art <sup>[2]</sup><sup>[4]</sup><sup>[6]</sup>.
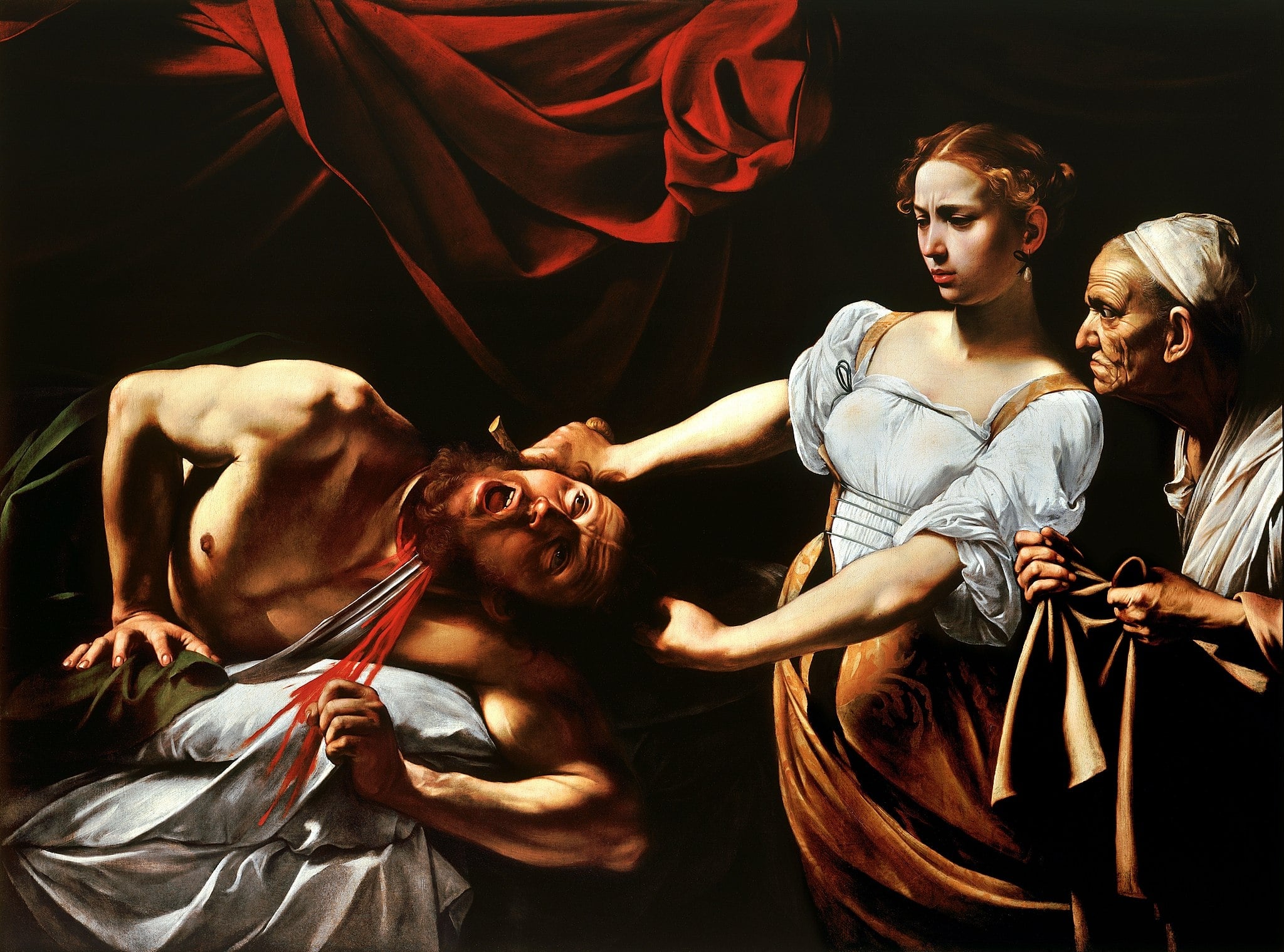

Judith Beheading Holofernes
Caravaggio (1599)
Caravaggio’s Judith Beheading Holofernes stages the biblical execution as a shocking present-tense event, lit by a raking beam that cuts figures from darkness. The <strong>red curtain</strong> frames a moral spectacle in which <strong>virtue overthrows tyranny</strong>, as Judith’s cool determination meets Holofernes’ convulsed resistance. Radical <strong>naturalism</strong>—from tendon strain to ribboning blood—makes deliverance feel material and irreversible.

The Thames below Westminster
Claude Monet (about 1871)
Claude Monet’s The Thames below Westminster turns London into <strong>light-made architecture</strong>, where Parliament’s mass dissolves into mist and the river shivers with <strong>industrial motion</strong>. Tugboats, a timber jetty with workers, and the rebuilt Westminster Bridge assert a modern city whose power is felt through atmosphere more than outline <sup>[1]</sup>.

Haystacks Series by Claude Monet | Light, Time & Atmosphere
Claude Monet
Claude Monet’s <strong>Haystacks Series</strong> transforms a routine rural subject into an inquiry into <strong>light, time, and perception</strong>. In this sunset view, the stacks swell at the left while the sun burns through the gap, making the field shimmer with <strong>apricot, lilac, and blue</strong> vibrations.

Venus of Urbino
Titian (1538)
Titian’s Venus of Urbino turns the mythic goddess into an ideal bride, merging frank <strong>eroticism</strong> with the codes of <strong>marital fidelity</strong>. In a Venetian bedroom, the nude’s direct gaze, roses, sleeping lapdog, and attendants at a cassone bind desire to domestic virtue and fertility <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Card Players by Paul Cézanne | Equilibrium and Form
Paul Cézanne
In The Card Players, Paul Cézanne turns a rural café game into a study of <strong>equilibrium</strong> and <strong>monumentality</strong>. Two hated peasants lean inward across an orange-brown table while a dark bottle stands upright between them, acting as a calm, vertical <strong>axis</strong> that stabilizes their mirrored focus <sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Silver Car Crash (Double Disaster)
Andy Warhol (1963)
Silver Car Crash (Double Disaster) pairs a grid of uneven, black‑and‑white silkscreened crash images with a vast, nearly blank field of metallic silver, staging a battle between <strong>relentless spectacle</strong> and <strong>mute void</strong>. Warhol’s industrial repetition converts tragedy into a consumable pattern while the reflective panel withholds detail, forcing viewers to face the limits of representation and the cold afterglow of modern media <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Bathers by Paul Cézanne: Geometry of the Modern Nude
Paul Cézanne
In Bathers, Paul Cézanne arranges a circle of generalized nudes beneath arching trees that meet like a <strong>natural vault</strong>, staging bathing as a timeless rite rather than a specific story. His <strong>constructive brushwork</strong> fuses bodies, water, and sky into one geometric order, balancing cool blues with warm ochres. The scene proposes a measured <strong>harmony between figure and landscape</strong>, a culmination of Cézanne’s search for enduring structure <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Women in the Garden
Claude Monet (1866–1867)
Claude Monet’s Women in the Garden choreographs four figures in a sunlit bower to test how <strong>white dresses</strong> register <strong>dappled light</strong> and shadow. The path, parasol, and clipped flowers frame a modern ritual of leisure while turning fashion into an instrument of <strong>perception</strong>. The scene reads less as portraiture than as a manifesto for painting the <strong>momentary</strong> outdoors <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Eight Elvises
Andy Warhol (1963)
A sweeping frieze of eight overlapping, gun‑drawn cowboys marches across a silver field, their forms slipping and ghosting as if frames of a film. Warhol converts a singular star into a <strong>serial commodity</strong>, where <strong>mechanical misregistration</strong> and life‑size scale turn bravado into spectacle <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Bacchus
Caravaggio (c. 1598)
Caravaggio’s Bacchus stages a human-scaled god who offers wine with disarming immediacy, yoking <strong>sensual invitation</strong> to <strong>vanitas</strong> warning. The tilted goblet, blemished fruit, and wilting leaves insist that abundance and youth are <strong>precarious</strong>. A private Roman milieu under Cardinal del Monte shaped this refined, provocative image <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

In the Garden
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1885)
In the Garden presents a charged pause in modern leisure: a young couple at a café table under a living arbor of leaves. Their lightly clasped hands and the bouquet on the tabletop signal courtship, while her calm, front-facing gaze checks his lean. Renoir’s flickering brushwork fuses figures and foliage, rendering love as a <strong>transitory, luminous sensation</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Girl Arranging Her Hair
Mary Cassatt (1886)
Mary Cassatt’s Girl Arranging Her Hair crystallizes a private rite of <strong>self‑regard</strong> into modern painting. Cool, broken strokes of the pale chemise meet the warm, patterned wall and bamboo furniture, staging a quiet drama of <strong>autonomy</strong> rather than display <sup>[1]</sup>. Exhibited in 1886, the work reframes the toilette as lived experience within Impressionism’s language of immediacy <sup>[2]</sup>.

Impression, Sunrise
Claude Monet (1872)
In Impression, Sunrise, Claude Monet turns Le Havre’s fog-bound harbor into an experiment in <strong>immediacy</strong> and <strong>modernity</strong>. Cool blue-greens dissolve cranes, masts, and smoke, while a small skiff cuts the water beneath a blazing, <strong>equiluminant</strong> orange sun whose vertical reflection stitches the scene together <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The effect is a poised dawn where industry meets nature, a quiet <strong>awakening</strong> rendered through light rather than line.

The Train in the Snow (The Locomotive)
Claude Monet (1875)
Claude Monet’s The Train in the Snow (The Locomotive) (1875) turns a suburban winter platform into a study of <strong>modernity absorbed by atmosphere</strong>. The engine’s twin yellow headlights and a smear of red push through a world of greys and violets as steam fuses with the low sky, while the right-hand fence and bare trees drill depth and cadence into the scene <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. Monet fixes not an object but a <strong>moment of perception</strong>, where industry seems to dematerialize into weather <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
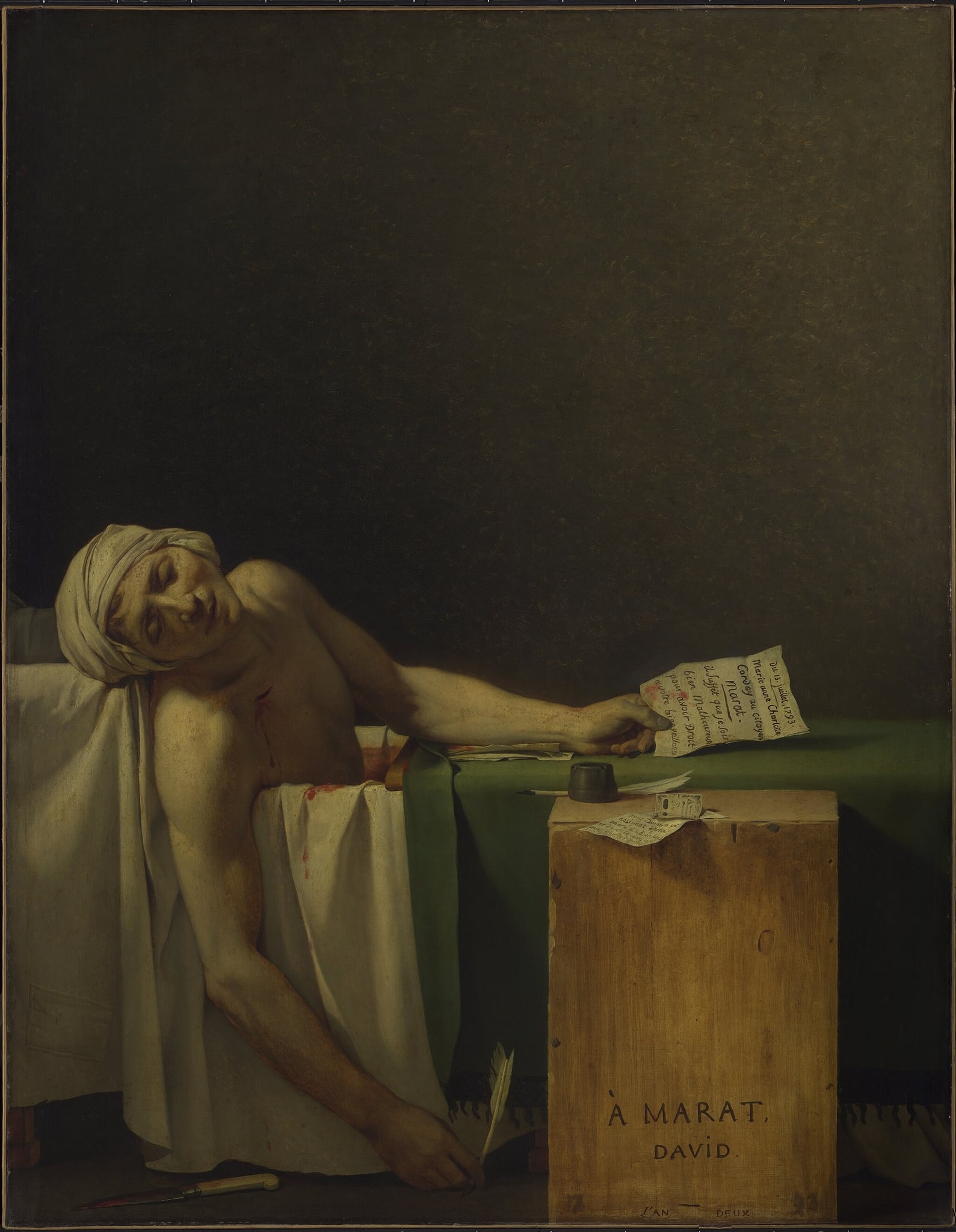

The Death of Marat
Jacques-Louis David (1793)
<strong>The Death of Marat</strong> turns a private murder into a <strong>secular martyrdom</strong>: Marat’s idealized body slumps in a bath, a pleading letter in his hand, a quill slipping from the other beside a bloodied knife and inkwell. Against a vast dark void, David’s calm light and austere geometry elevate humble objects—the green baize plank and the crate inscribed “À MARAT, DAVID, L’AN DEUX”—into civic emblems <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Artist's Garden at Giverny
Claude Monet (1900)
In The Artist's Garden at Giverny, Claude Monet turns his cultivated Clos Normand into a field of living color, where bands of violet <strong>irises</strong> surge toward a narrow, rose‑colored path. Broken, flickering strokes let greens, purples, and pinks mix optically so that light seems to tremble across the scene, while lilac‑toned tree trunks rhythmically guide the gaze inward <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Water Lilies
Claude Monet (1899)
<strong>Water Lilies</strong> centers on an arched <strong>Japanese bridge</strong> suspended over a pond where lilies and rippling reflections fuse into a single, vibrating surface. Monet turns the scene into a study of <strong>perception-in-flux</strong>, letting water, foliage, and light dissolve hard edges into atmospheric continuity <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Café Terrace at Night
Vincent van Gogh (1888)
In Café Terrace at Night, Vincent van Gogh turns nocturne into <strong>luminous color</strong>: a gas‑lit terrace glows in yellows and oranges against a deep <strong>ultramarine sky</strong> pricked with stars. By building night “<strong>without black</strong>,” he stages a vivid encounter between human sociability and the vastness overhead <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
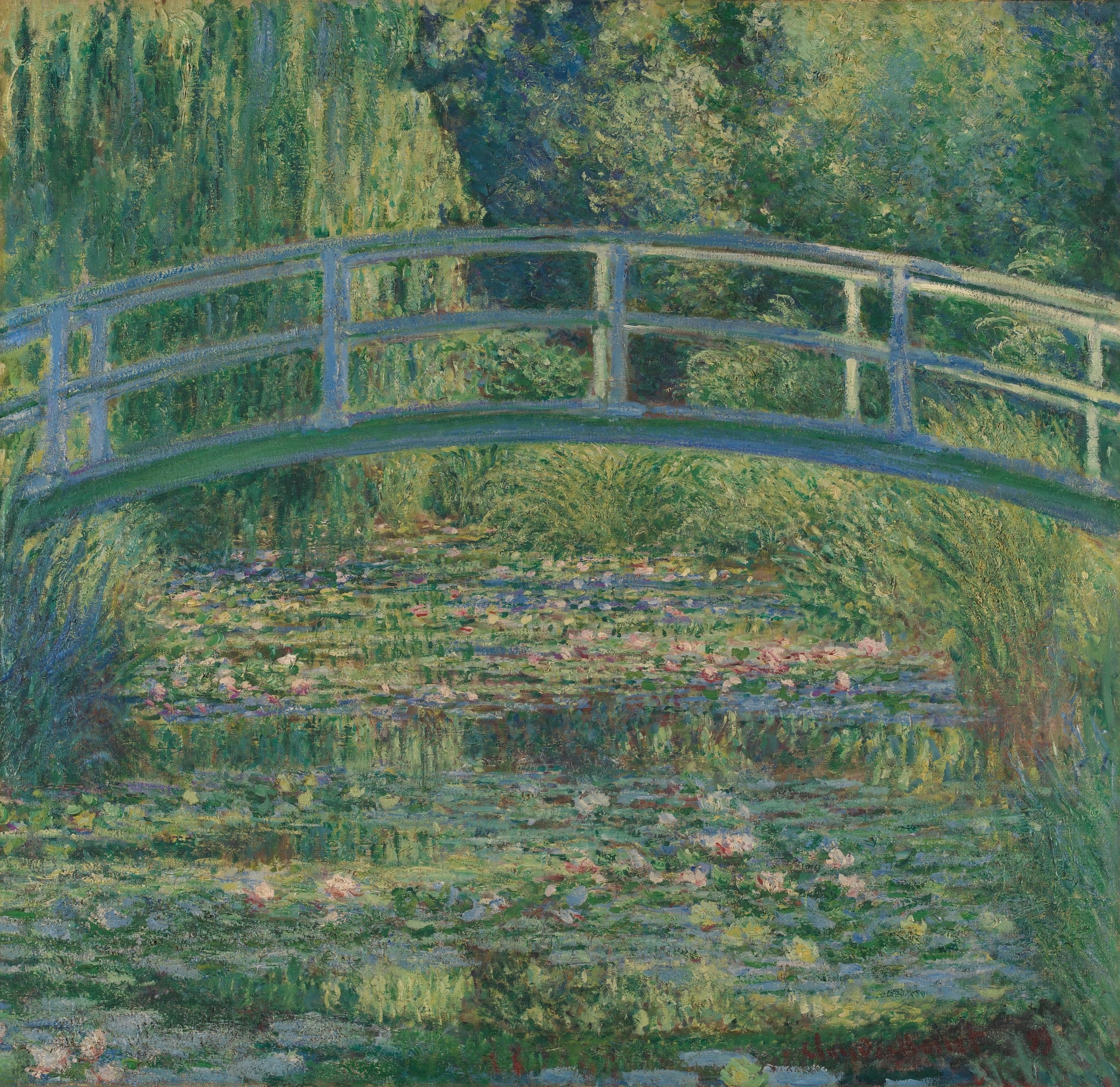

The Water Lily Pond
Claude Monet (1899)
Claude Monet’s The Water Lily Pond transforms a designed garden into a theater of <strong>perception and reflection</strong>. The pale, arched <strong>Japanese bridge</strong> hovers over a surface where lilies, reeds, and mirrored willow fronds dissolve boundaries between water and sky, proposing <strong>seeing itself</strong> as the subject <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
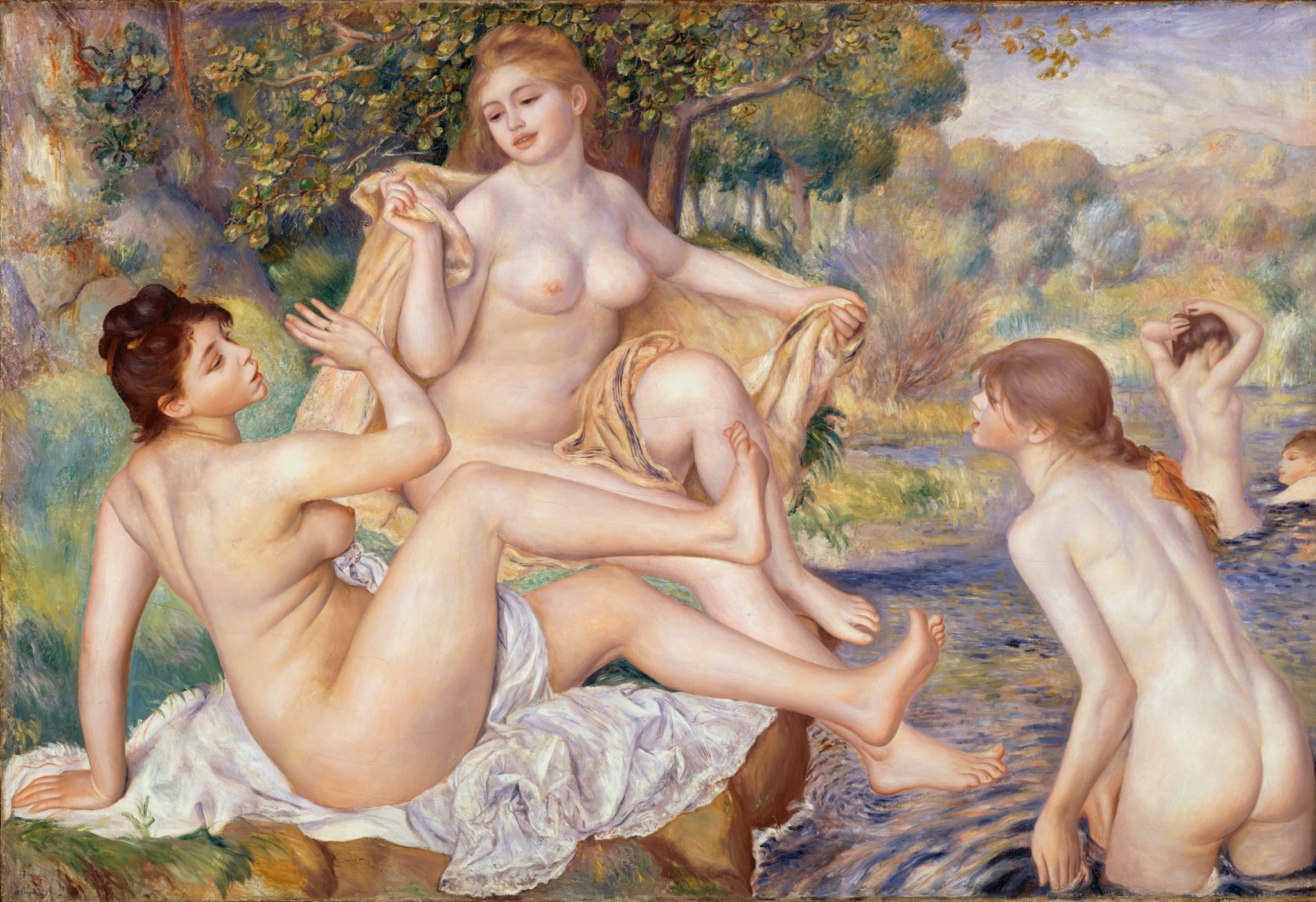

The Large Bathers
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1884–1887)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir’s The Large Bathers unites modern bodies with a pastoral grove to stage an <strong>Arcadian ideal</strong>. Three monumental nudes form interlocking curves and triangles while two background figures splash and groom, fusing <strong>sensual warmth</strong> with <strong>classical order</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Waterloo Bridge, Sunlight Effect
Claude Monet (1903 (begun 1900))
Claude Monet’s Waterloo Bridge, Sunlight Effect renders London as a <strong>lilac-blue atmosphere</strong> where form yields to light. The bridge’s stone arches persist as anchors, yet the span dissolves into mist while <strong>flecks of lemon and ember</strong> signal modern traffic crossing a city made weightless <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. Vertical hints of chimneys haunt the distance, binding industry to beauty as the Thames shimmers with the same notes as the sky <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
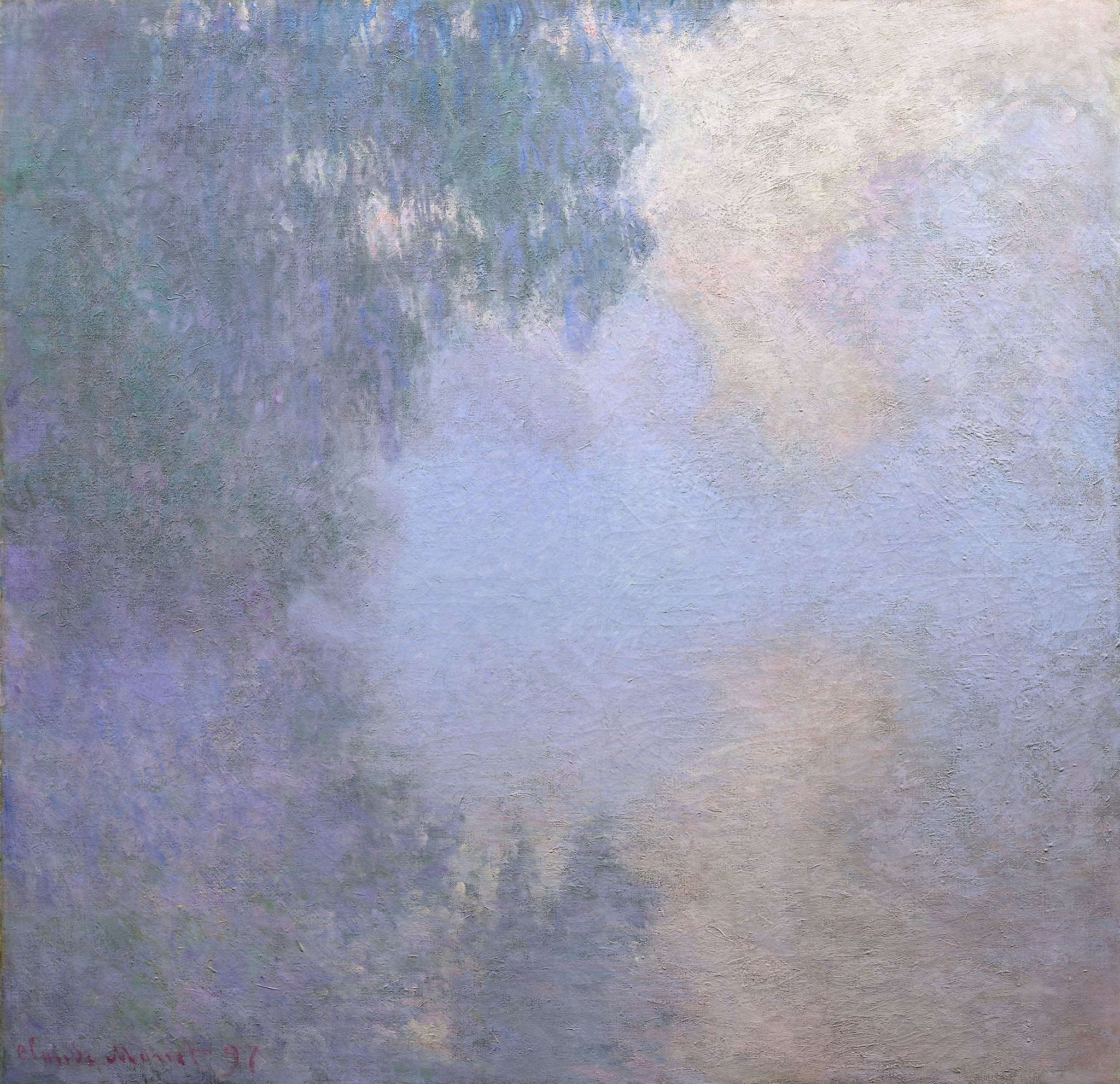

Morning on the Seine (series)
Claude Monet (1897)
Claude Monet’s Morning on the Seine (series) turns dawn into an inquiry about <strong>perception</strong> and <strong>time</strong>. In this canvas, the left bank’s shadowed foliage dissolves into lavender mist while a pale radiance opens at right, fusing sky and water into a single, reflective field <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Napoleon Crossing the Alps
Jacques-Louis David (1801–1805 (series of five versions))
Jacques-Louis David turns a difficult Alpine passage into a <strong>myth of command</strong>: a serene leader on a rearing charger, a <strong>billowing golden cloak</strong>, and names cut into stone that bind the crossing to Hannibal and Charlemagne. The painting manufactures <strong>political legitimacy</strong> by fusing modern uniform and classical gravitas into a single, upward-driving image <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

The Grand Canal
Claude Monet (1908)
Claude Monet’s The Grand Canal turns Venice into <strong>pure atmosphere</strong>: the domes of Santa Maria della Salute waver at right while a regiment of <strong>pali</strong> stands at left, their verticals reverberating in the water. The scene asserts <strong>light over architecture</strong>, transforming stone into memory and time into color <sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Supper at Emmaus
Caravaggio (1601)
Caravaggio’s The Supper at Emmaus captures the split-second when two disciples recognize Christ in the <strong>breaking of bread</strong>. A raking light isolates Christ’s calm blessing while the disciples erupt—one surging forward with a torn sleeve, the other flinging his arms wide—so the shock of revelation reads as bodily fact. The teetering <strong>basket of fruit</strong> and Eucharistic table amplify themes of abundance and fragility <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

The House of the Hanged Man
Paul Cézanne (1873)
Paul Cézanne’s The House of the Hanged Man turns a modest Auvers-sur-Oise lane into a scene of <strong>engineered unease</strong> and <strong>structural reflection</strong>. Jagged roofs, laddered trees, and a steep path funnel into a narrow, shadowed V that withholds a center, making absence the work’s gravitational force. Cool greens and slate blues, set in blocky, masoned strokes, build a world that feels both solid and precarious.

Wanderer above the Sea of Fog
Caspar David Friedrich (ca. 1817)
A solitary figure stands on a jagged crag above a churning <strong>sea of fog</strong>, his back turned in the classic <strong>Rückenfigur</strong> pose. Caspar David Friedrich transforms the landscape into an inner stage where <strong>awe, uncertainty, and resolve</strong> meet at the edge of perception <sup>[3]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

Portrait of Alexander J. Cassatt and His Son Robert Kelso Cassatt
Mary Cassatt (1884)
A quiet, domestic tableau becomes a study in <strong>authority tempered by affection</strong>. In Portrait of Alexander J. Cassatt and His Son Robert Kelso Cassatt, Mary Cassatt fuses father and child into a single dark silhouette against a luminous, brushed interior, their shared gaze fixed beyond the frame. The <strong>newspaper</strong>, <strong>linked hands</strong>, and <strong>cropped closeness</strong> transform a routine moment into a symbol of generational continuity and modern attentiveness.

The Hermitage at Pontoise
Camille Pissarro (ca. 1867)
Camille Pissarro’s The Hermitage at Pontoise shows a hillside village interlaced with <strong>kitchen gardens</strong>, stone houses, and workers bent to their tasks under a <strong>low, cloud-laden sky</strong>. The painting binds human labor to place, staging a quiet counterpoint between <strong>architectural permanence</strong> and the <strong>seasonal flux</strong> of fields and weather <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Laundresses Carrying Linen in Town
Camille Pissarro (1879)
In Laundresses Carrying Linen in Town, two working women strain under <strong>white bundles</strong> that flare against a <strong>flat yellow ground</strong> and a <strong>dark brown band</strong>. The abrupt cropping and opposing diagonals turn anonymous labor into a <strong>monumental, modern frieze</strong> of effort and motion.
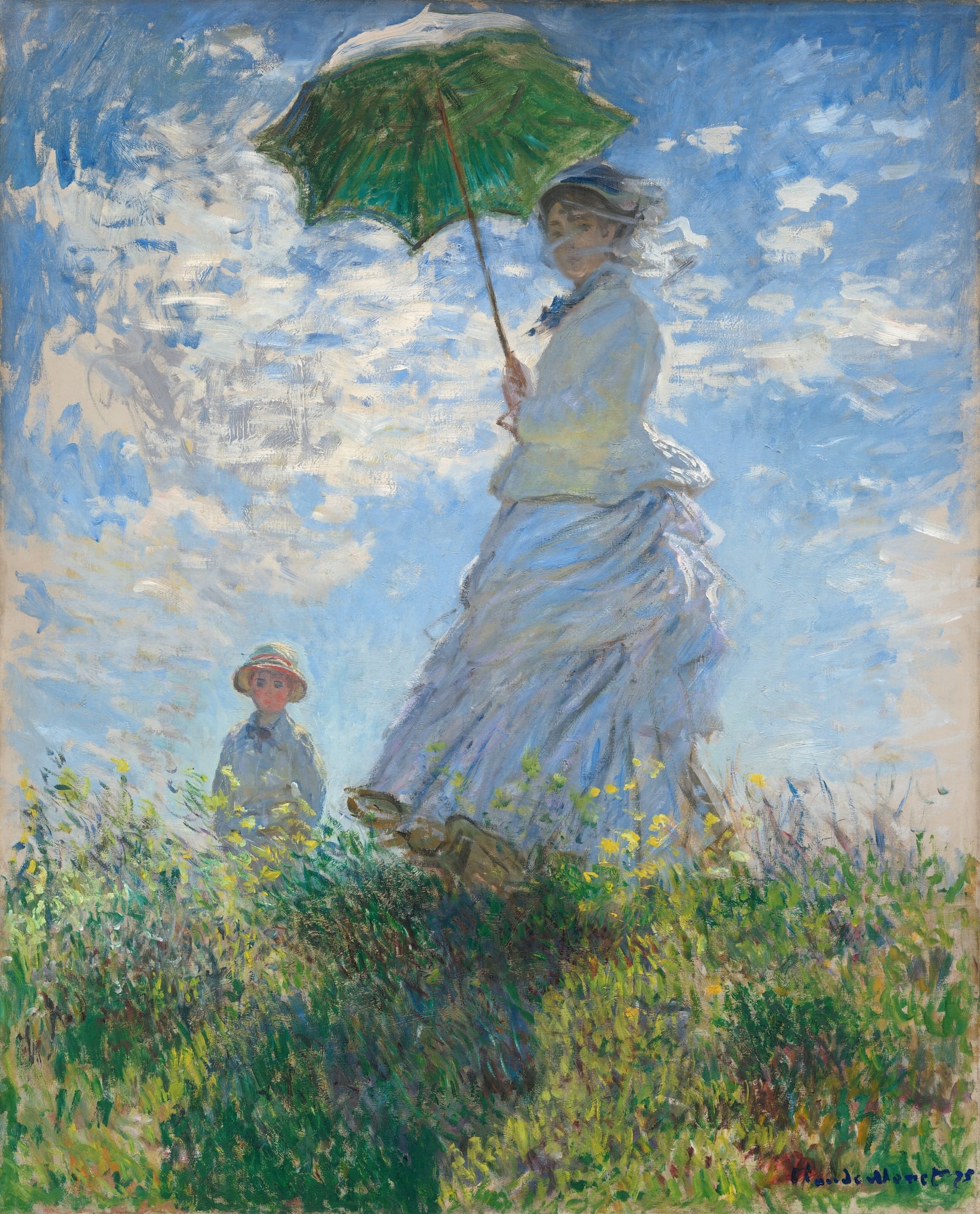

Woman with a Parasol
Claude Monet (1875)
Claude Monet’s Woman with a Parasol fixes a breezy hillside instant in high, shifting light, setting a figure beneath a <strong>green parasol</strong> against a vast, vibrating sky. The low vantage and <strong>broken brushwork</strong> merge dress, clouds, and grasses into one atmosphere, while a child at the rise anchors depth and intimacy <sup>[1]</sup>. It is a manifesto of <strong>plein-air</strong> perception—painting the sensation of air in motion rather than the contours of things <sup>[2]</sup>.
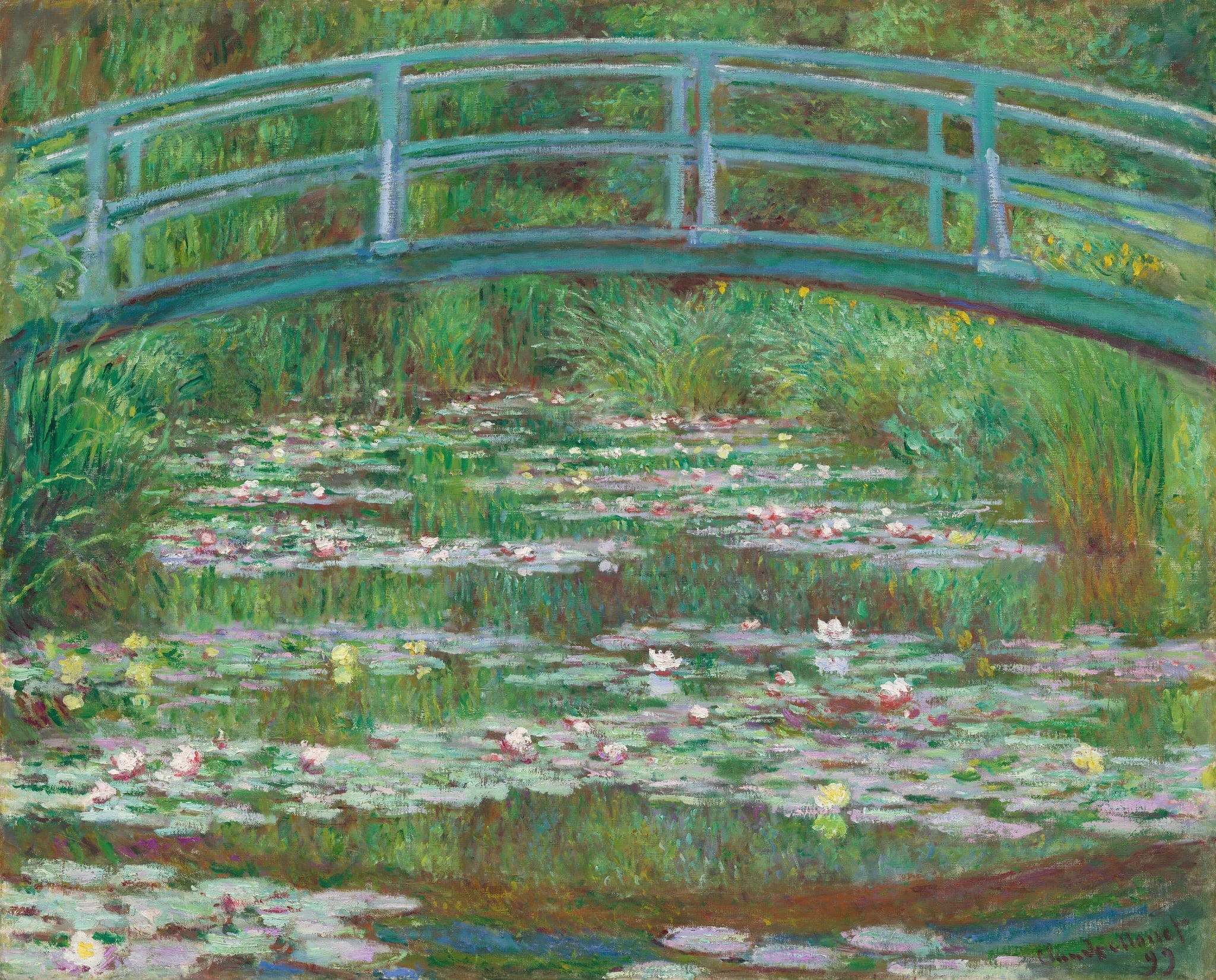

The Japanese Footbridge
Claude Monet (1899)
Claude Monet’s The Japanese Footbridge turns his Giverny garden into an <strong>immersive field of perception</strong>: a pale blue-green arc spans water crowded with lilies, while grasses and willows dissolve into vibrating greens. By eliminating the sky and anchoring the scene with the bridge, Monet makes <strong>reflection, passage, and time</strong> the picture’s true subjects <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
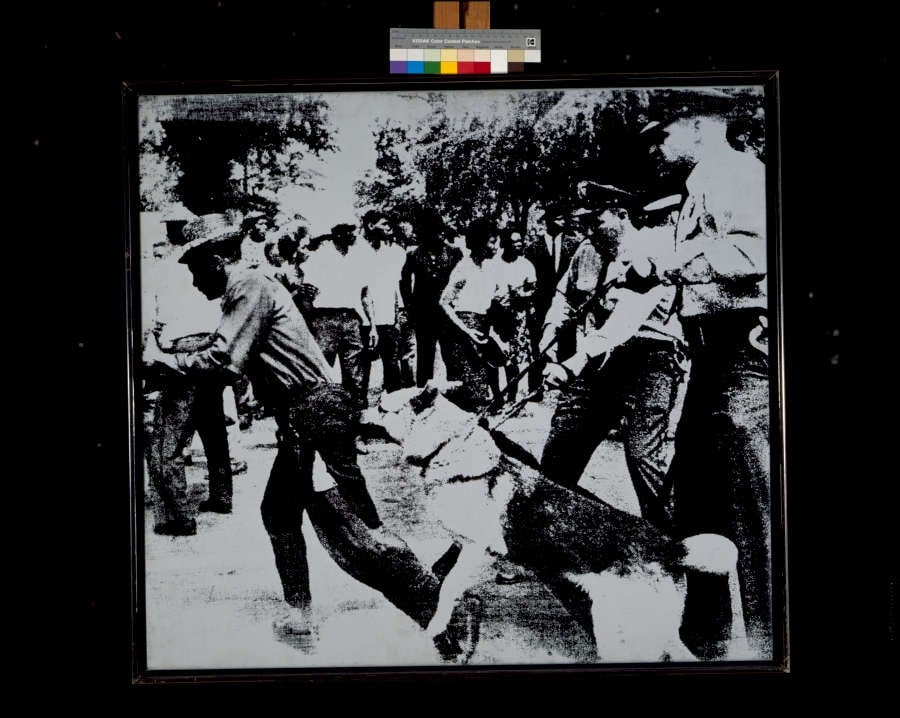

Race Riot
Andy Warhol (1964)
Race Riot crystallizes a split-second of state force: a police dog lunges while officers with batons surge and a ring of onlookers compresses the scene into a <strong>claustrophobic frieze</strong>. Warhol’s stark, high-contrast silkscreen translates a LIFE wire-photo into a <strong>mechanized emblem</strong> of American racial violence and its mass-media circulation <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
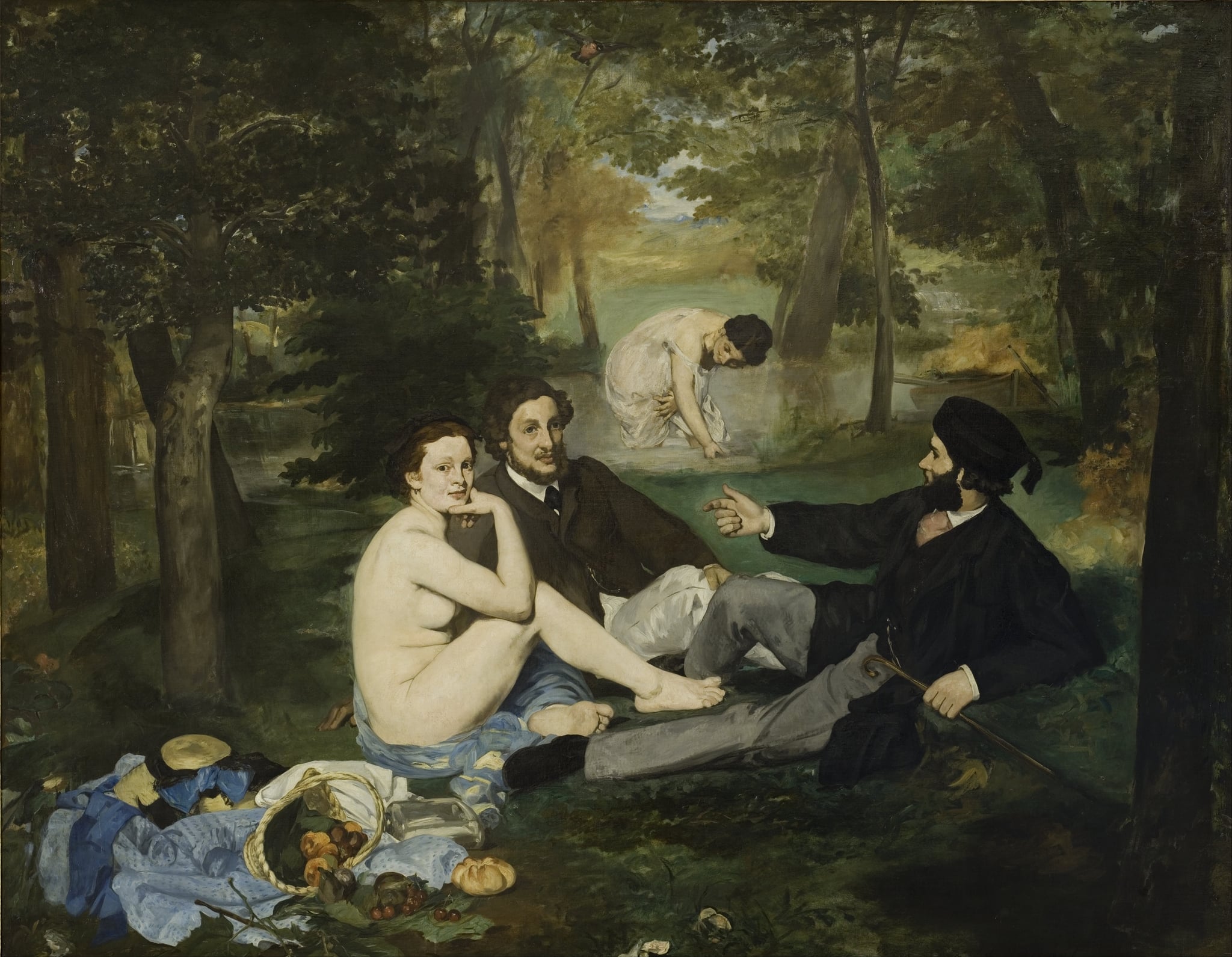

Luncheon on the Grass
Édouard Manet (1863)
Luncheon on the Grass stages a confrontation between <strong>modern Parisian leisure</strong> and <strong>classical precedent</strong>. A nude woman meets our gaze beside two clothed men, while a distant bather and an overturned picnic puncture naturalistic illusion. Manet’s scale and flat, studio-like light convert a park picnic into a manifesto of <strong>modern painting</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
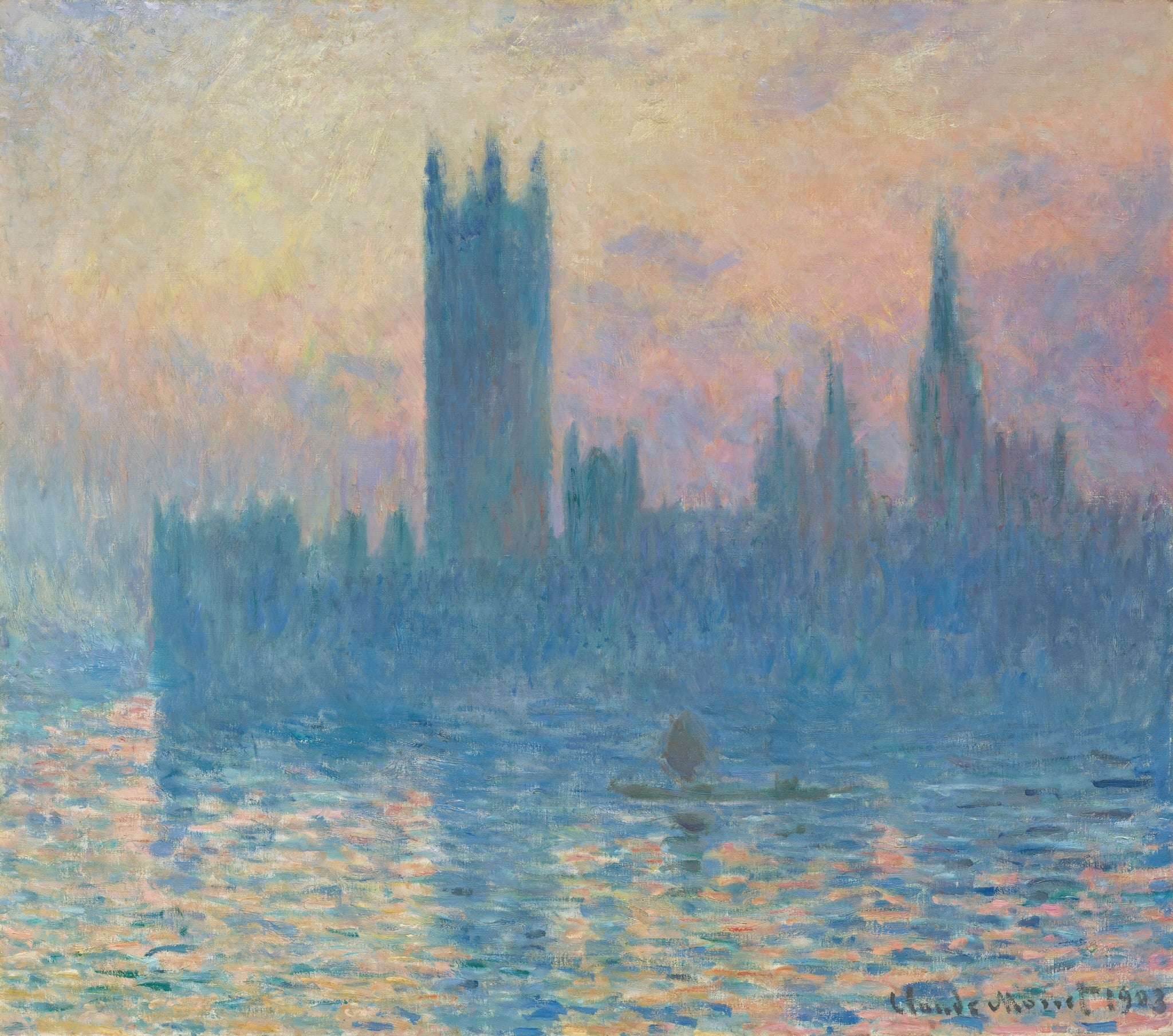

Houses of Parliament
Claude Monet (1903)
Claude Monet’s Houses of Parliament renders Westminster as a <strong>dissolving silhouette</strong> in a wash of peach, mauve, and pale gold, where stone and river are leveled by <strong>luminous fog</strong>. Short, vibrating strokes turn architecture into <strong>atmosphere</strong>, while a tiny boat anchors human scale amid the monumental scene.

Rouen Cathedral Series
Claude Monet (1894)
Claude Monet’s Rouen Cathedral Series (1892–94) turns a Gothic monument into a laboratory of <strong>light, time, and perception</strong>. In this sunstruck façade, portals, gables, and a warm, orange-tinged rose window flicker in pearly violets and buttery yellows against a crystalline blue sky, while tiny figures at the base anchor the scale. The painting insists that <strong>light—not stone—is the true subject</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
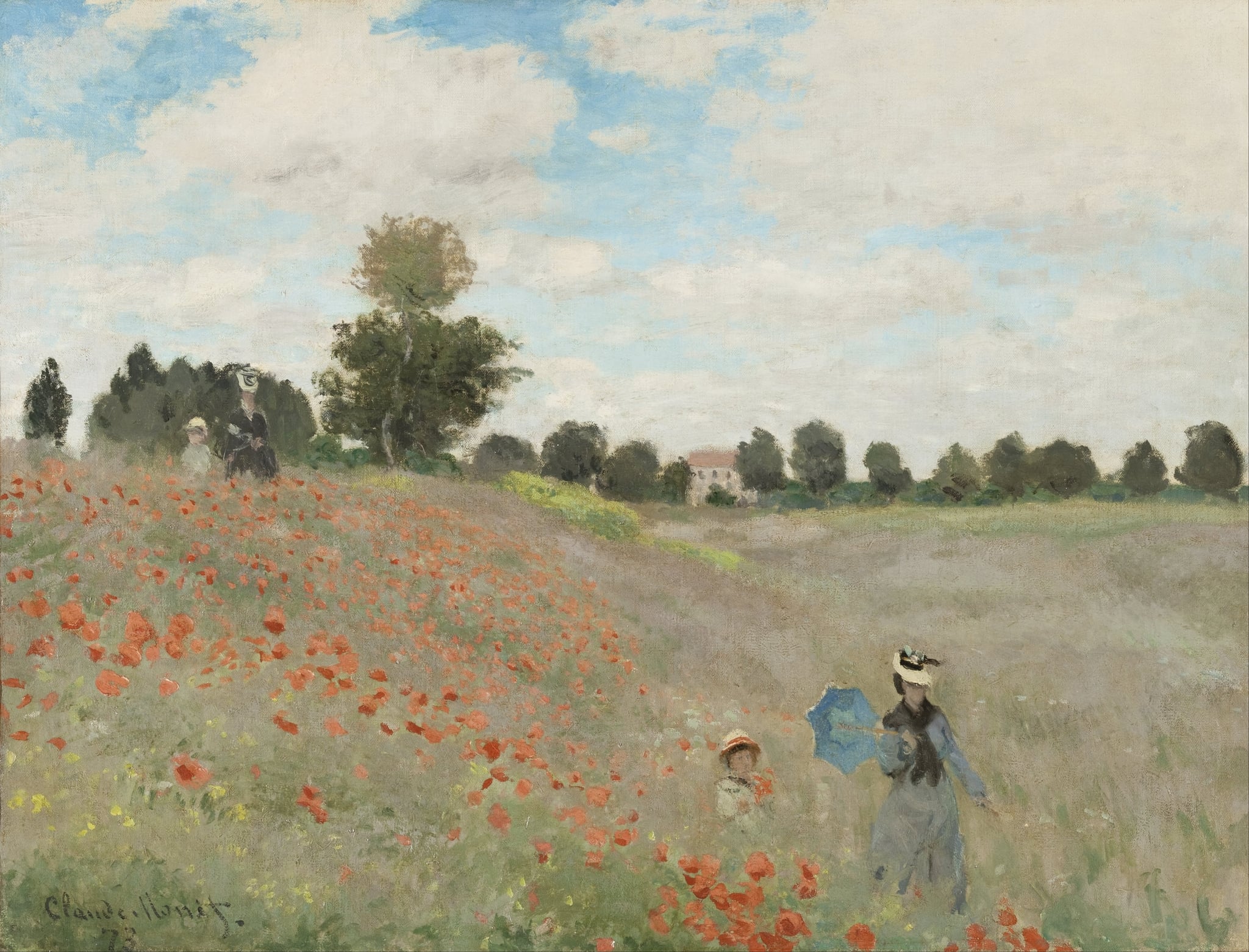

Poppies
Claude Monet (1873)
Claude Monet’s Poppies (1873) turns a suburban hillside into a theater of <strong>light, time, and modern leisure</strong>. A red diagonal of poppies counters cool fields and sky, while a woman with a <strong>blue parasol</strong> and a child appear twice along the slope, staging a gentle <strong>echo of moments</strong> rather than a single event <sup>[1]</sup>. The painting asserts sensation over contour, letting broken touches make the day itself the subject.

The Railway
Édouard Manet (1873)
Manet’s The Railway is a charged tableau of <strong>modern life</strong>: a composed woman confronts us while a child, bright in <strong>white and blue</strong>, peers through the iron fence toward a cloud of <strong>steam</strong>. The image turns a casual pause at the Gare Saint‑Lazare into a meditation on <strong>spectatorship, separation, and change</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
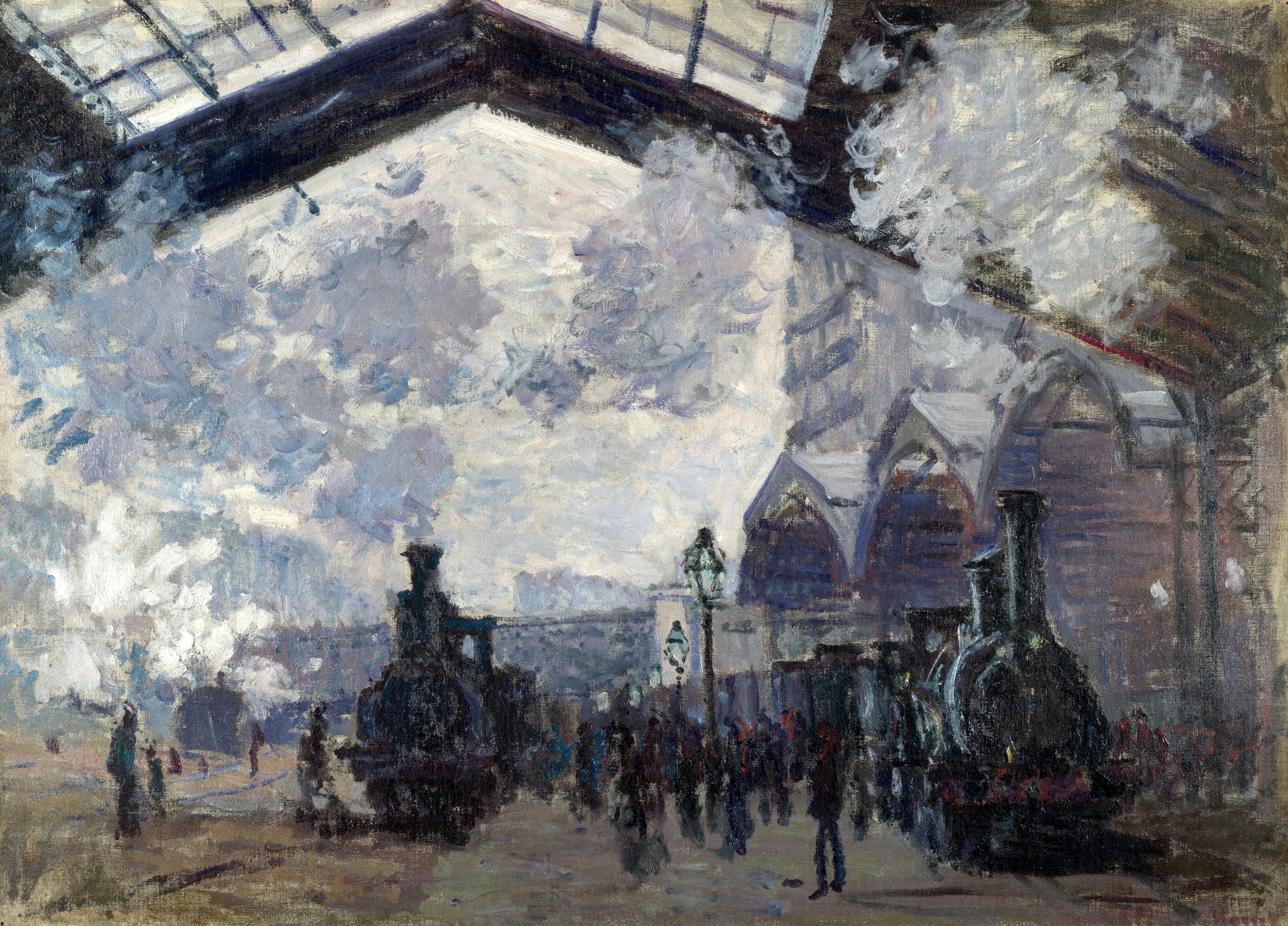

Gare Saint-Lazare
Claude Monet (1877)
Monet’s Gare Saint-Lazare turns an iron-and-glass train shed into a theater of <strong>steam, light, and motion</strong>. Twin locomotives, gas lamps, and a surge of figures dissolve into bluish vapor under the diagonal canopy, recasting industrial smoke as <strong>luminous atmosphere</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
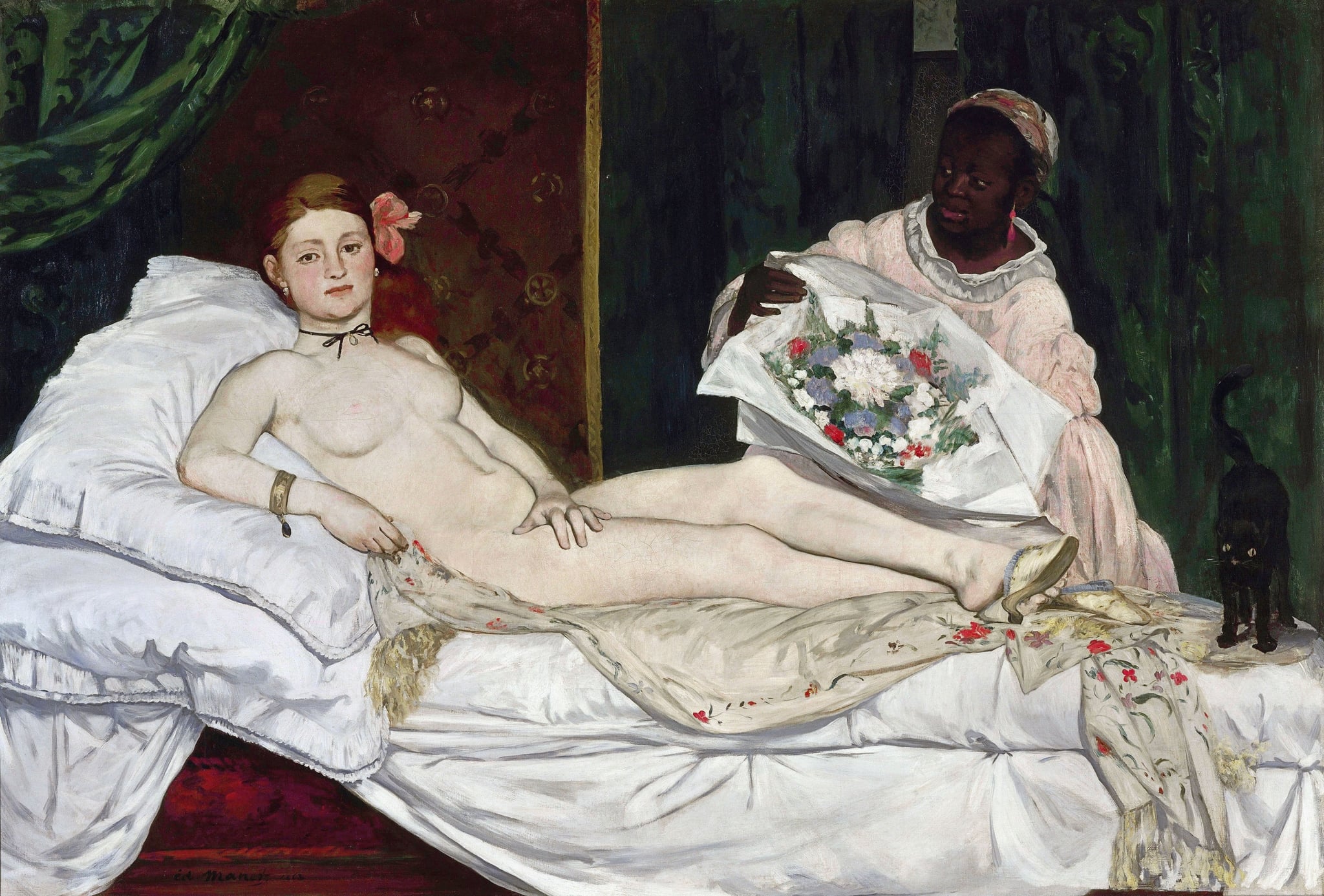

Olympia
Édouard Manet (1863 (Salon 1865))
A defiantly contemporary nude confronts the viewer with a steady gaze and a guarded pose, framed by crisp light and luxury trappings. In Olympia, <strong>Édouard Manet</strong> strips myth from the female nude to expose the <strong>modern economy of desire</strong>, power, and looking <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
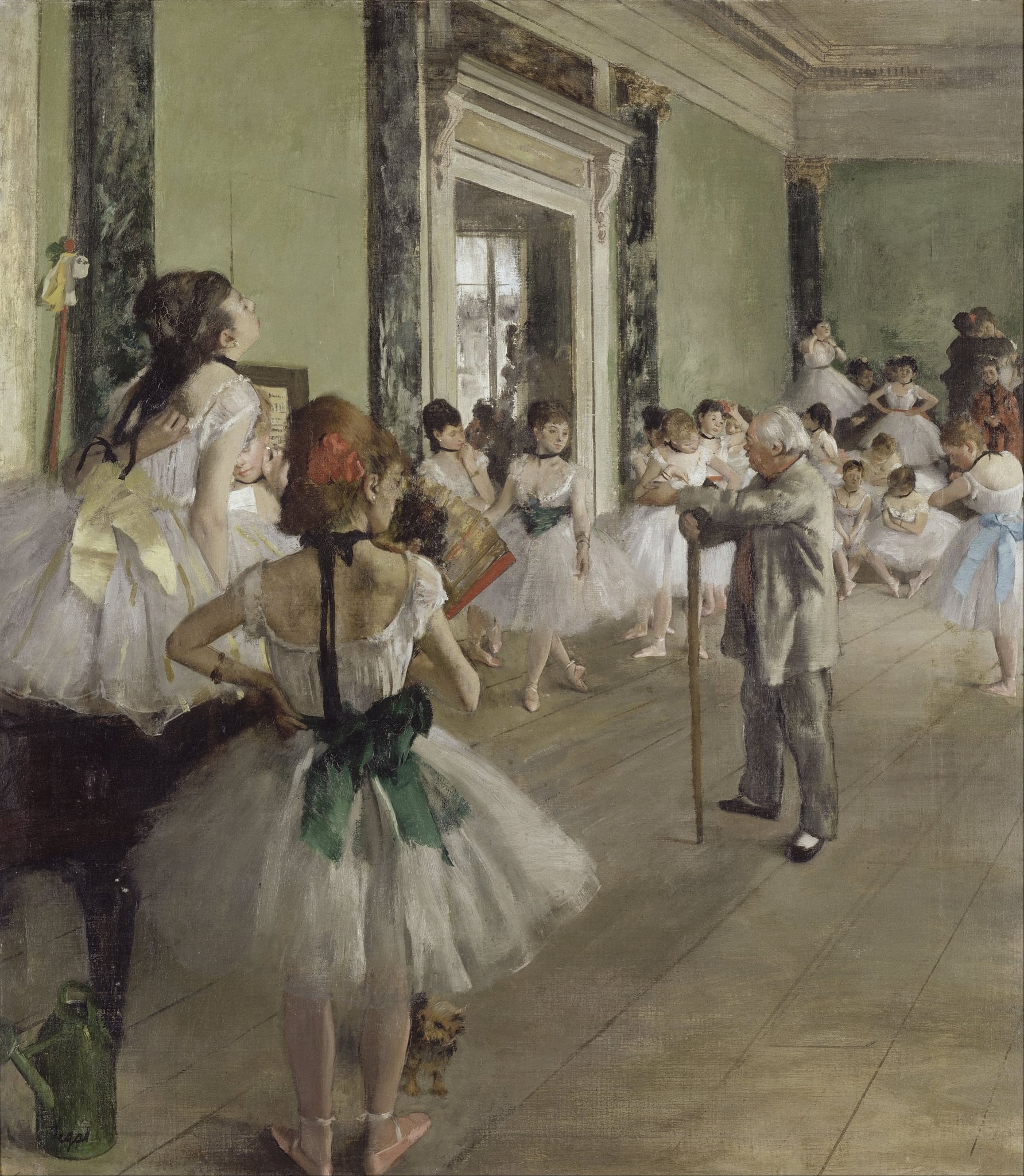

The Ballet Class
Edgar Degas (1873–1876)
<strong>The Ballet Class</strong> shows the work behind grace: a green-walled studio where young dancers in white tutus rest, fidget, and stretch while the gray-suited master stands with his cane. Degas’s diagonal floorboards, cropped viewpoints, and scattered props—a watering can, a music stand, even a tiny dog—stage a candid vision of routine rather than spectacle. The result is a modern image of discipline, hierarchy, and fleeting poise.
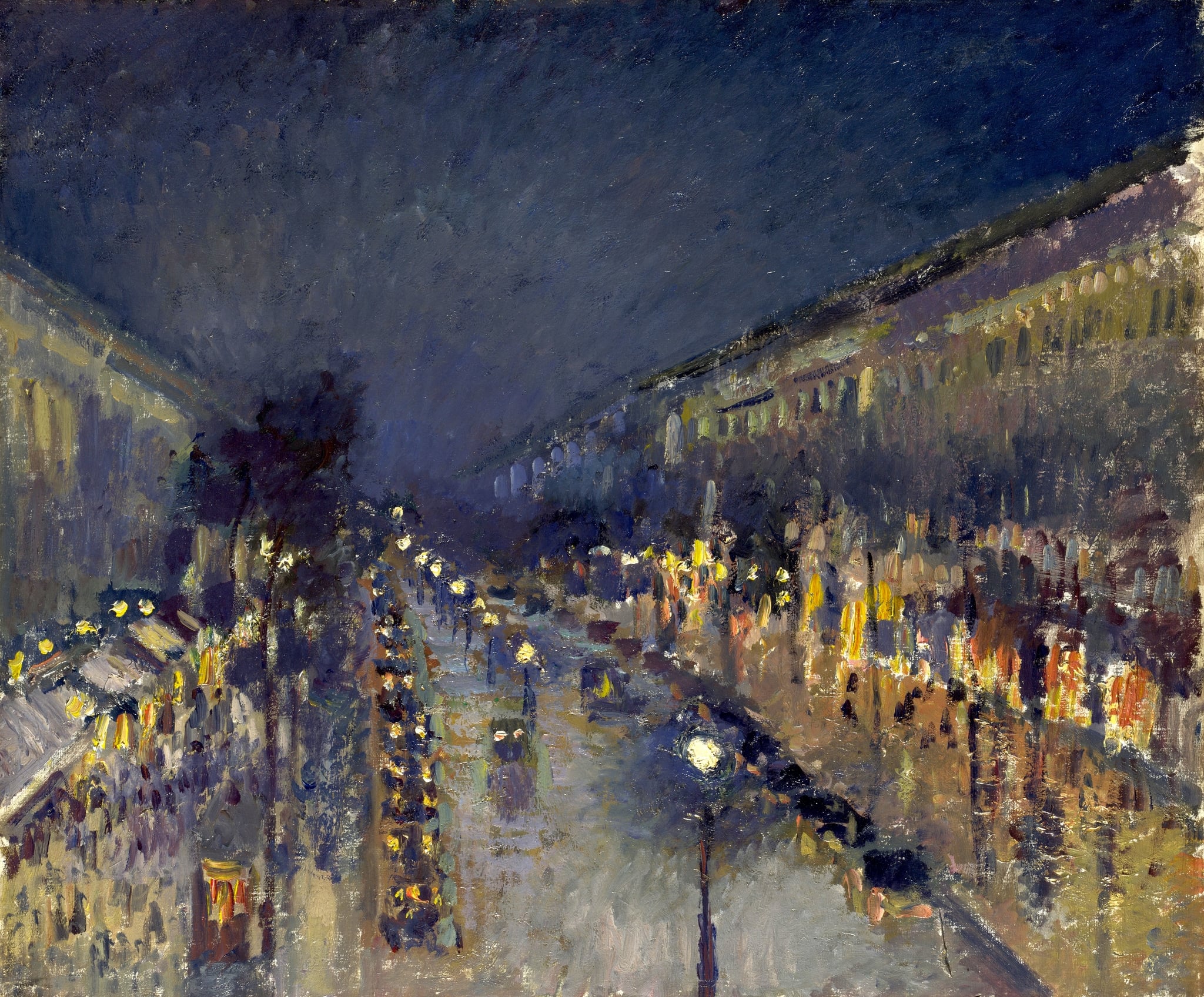

Boulevard Montmartre at Night
Camille Pissarro (1897)
A high window turns Paris into a flowing current: in Boulevard Montmartre at Night, Camille Pissarro fuses <strong>modern light</strong> and <strong>urban movement</strong> into a single, restless rhythm. Cool electric halos and warm gaslit windows shimmer across rain‑slick stone, where carriages and crowds dissolve into <strong>pulse-like blurs</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
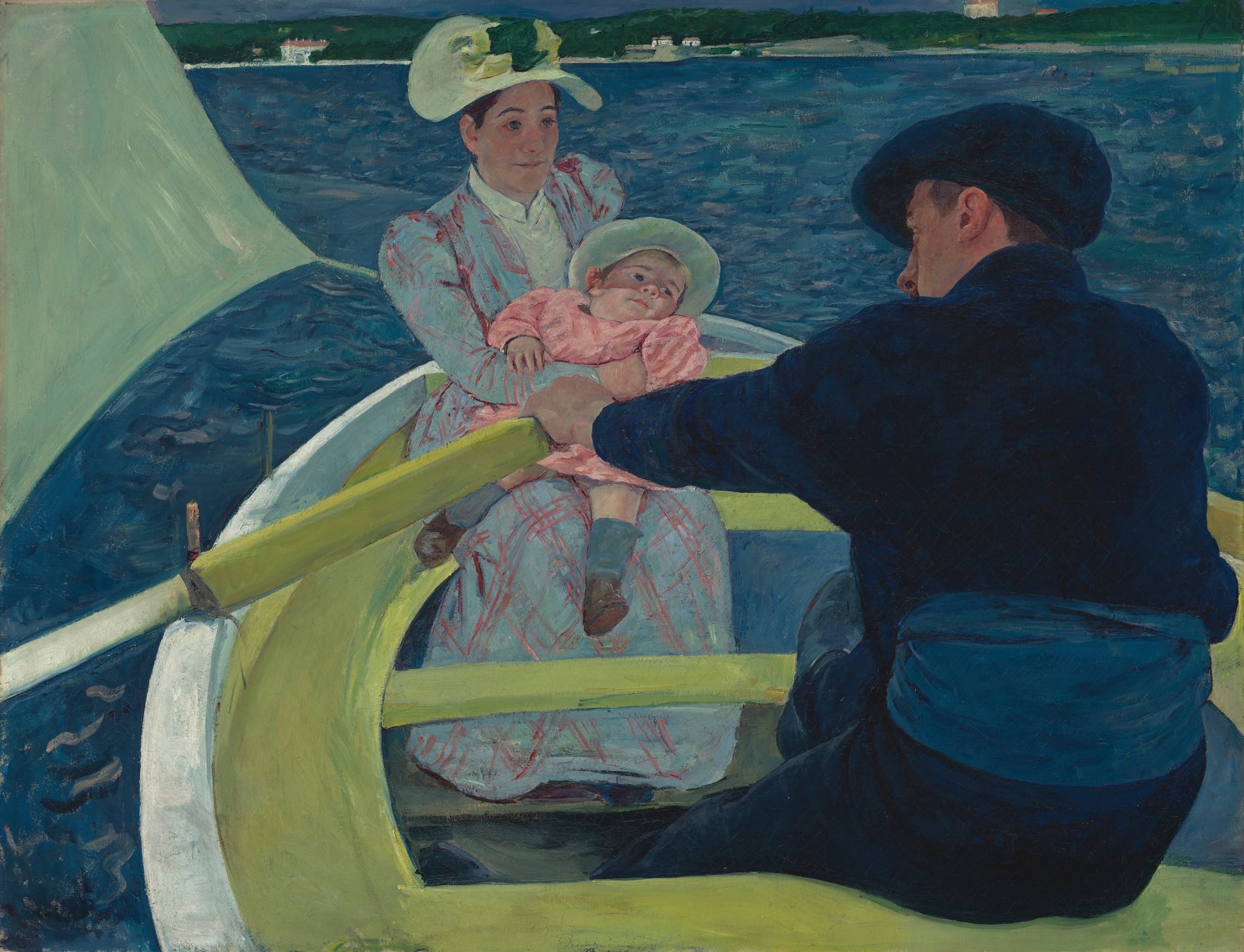

The Boating Party
Mary Cassatt (1893–1894)
In The Boating Party, Mary Cassatt fuses <strong>intimate caregiving</strong> with <strong>modern mobility</strong>, compressing mother, child, and rower inside a skiff that cuts diagonals across ultramarine water. Bold arcs of citron paint and a high, flattened horizon reveal a deliberate <strong>Japonisme</strong> logic that stabilizes the scene even as motion surges around it <sup>[1]</sup>. The painting asserts domestic life as a public, modern subject while testing the limits of Impressionist space and color.

The Boulevard Montmartre on a Winter Morning
Camille Pissarro (1897)
From a high hotel window, Camille Pissarro renders Paris as a living system—its Haussmann boulevard dissolving into winter light, its crowds and vehicles fused into a soft, <strong>rhythmic flow</strong>. Broken strokes in cool grays, lilacs, and ochres turn fog, steam, and motion into <strong>texture of time</strong>, dignifying the city’s ordinary morning pulse <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Woman Reading
Édouard Manet (1880–82)
Manet’s Woman Reading distills a fleeting act into an emblem of <strong>modern self-possession</strong>: a bundled figure raises a journal-on-a-stick, her luminous profile set against a brisk mosaic of greens and reds. With quick, loaded strokes and a deliberately cropped <strong>beer glass</strong> and paper, Manet turns perception itself into subject—asserting the drama of a private mind within a public café world <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Magpie
Claude Monet (1868–1869)
Claude Monet’s The Magpie turns a winter field into a study of <strong>luminous perception</strong>, where blue-violet shadows articulate snow’s light. A lone <strong>magpie</strong> perched on a wooden gate punctuates the silence, anchoring a scene that balances homestead and open countryside <sup>[1]</sup>.

Summer's Day
Berthe Morisot (about 1879)
Two women drift on a boat in the Bois de Boulogne, their dresses, hats, and a bright blue parasol fused with the lake’s flicker by Morisot’s swift, <strong>zig‑zag brushwork</strong>. The scene turns a brief outing into a poised study of <strong>modern leisure</strong> and <strong>female companionship</strong> in public space <sup>[1]</sup>.

Woman Ironing
Edgar Degas (c. 1876–1887)
In Woman Ironing, Degas builds a modern icon of labor through <strong>contre‑jour</strong> light and a forceful diagonal from shoulder to iron. The worker’s silhouette, red-brown dress, and the cool, steamy whites around her turn repetition into <strong>ritualized transformation</strong>—wrinkled cloth to crisp order <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Red Roofs
Camille Pissarro (1877)
In Red Roofs, Camille Pissarro knits village and hillside into a single living fabric through a <strong>screen of winter trees</strong> and vibrating, tactile brushwork. The warm <strong>red-tiled roofs</strong> act as chromatic anchors within a cool, silvery atmosphere, asserting human shelter as part of nature’s rhythm rather than its negation <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The composition’s <strong>parallel planes</strong> and color echoes reveal a deliberate structural order that anticipates Post‑Impressionist concerns <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Jeanne (Spring)
Édouard Manet (1881)
Édouard Manet’s Jeanne (Spring) fuses a time-honored allegory with <strong>modern Parisian fashion</strong>: a crisp profile beneath a cream parasol, set against <strong>luminous, leafy greens</strong>. Manet turns couture—hat, glove, parasol—into the language of <strong>renewal and youth</strong>, making spring feel both perennial and up-to-the-minute <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Madame Monet and Her Son
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s 1874 canvas Madame Monet and Her Son crystallizes <strong>modern domestic leisure</strong> and <strong>plein‑air immediacy</strong> in Argenteuil. A luminous white dress pools into light while a child in a pale‑blue sailor suit reclines diagonally; a strutting rooster punctuates the greens with warm color. The brushwork fuses figure and garden so the moment reads as <strong>lived, not staged</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

Vase of Flowers
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (c. 1889)
Vase of Flowers is a late‑1880s still life in which Pierre-Auguste Renoir turns a humble blue‑green jug and a tumbling bouquet into a <strong>laboratory of color and touch</strong>. Against a warm ocher wall and reddish tabletop, coral and vermilion blossoms flare while cool greens and violets anchor the mass, letting <strong>color function as drawing</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. The work affirms Renoir’s belief that flower painting was a space for bold experimentation that fed his figure art.

The Skiff (La Yole)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1875)
In The Skiff (La Yole), Pierre-Auguste Renoir stages a moment of modern leisure on a broad, vibrating river, where a slender, <strong>orange skiff</strong> cuts across a field of <strong>cool blues</strong>. Two women ride diagonally through the shimmer; an <strong>oar’s sweep</strong> spins a vortex of color as a sailboat, villa, and distant bridge settle the scene on the Seine’s suburban edge <sup>[1]</sup>. Renoir turns motion and light into a single sensation, using a high‑chroma, complementary palette to fuse human pastime with nature’s flux <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Floor Scrapers
Gustave Caillebotte (1875)
Gustave Caillebotte’s The Floor Scrapers stages three shirtless workers planing a parquet floor as shafts of light pour through an ornate balcony door. The painting fuses <strong>rigorous perspective</strong> with <strong>modern urban labor</strong>, turning curls of wood and raking light into a ledger of time and effort <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. Its cool, gilded interior makes visible how bourgeois elegance is built on bodily work.

On the Beach
Édouard Manet (1873)
On the Beach captures a paused interval of modern leisure: two fashionably dressed figures sit on pale sand before a <strong>banded, high-horizon sea</strong>. Manet’s <strong>economical brushwork</strong>, restricted greys and blacks, and radical cropping stage a scene of absorption and wind‑tossed motion that feels both intimate and detached <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Cliff Walk at Pourville
Claude Monet (1882)
Claude Monet’s The Cliff Walk at Pourville renders wind, light, and sea as interlocking forces through <strong>shimmering, broken brushwork</strong>. Two small walkers—one beneath a pink parasol—stand near the <strong>precipitous cliff edge</strong>, their presence measuring the vastness of turquoise water and bright sky dotted with white sails. The scene fuses leisure and the <strong>modern sublime</strong>, making perception itself the subject <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman at Her Toilette
Berthe Morisot (1875–1880)
Woman at Her Toilette stages a private ritual of self-fashioning, not a spectacle of vanity. A woman, seen from behind, lifts her arm to adjust her hair as a <strong>black velvet choker</strong> punctuates Morisot’s silvery-violet haze; the <strong>mirror’s blurred reflection</strong> with powders, jars, and a white flower refuses a clear face. Morisot’s <strong>feathery facture</strong> turns a fleeting toilette into modern subjectivity made visible <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Rehearsal of the Ballet Onstage
Edgar Degas (ca. 1874)
Degas’s The Rehearsal of the Ballet Onstage turns a moment of practice into a modern drama of work and power. Under <strong>harsh footlights</strong>, clustered ballerinas stretch, yawn, and repeat steps as a <strong>ballet master/conductor</strong> drives the tempo, while <strong>abonnés</strong> lounge in the wings and a looming <strong>double bass</strong> anchors the labor of music <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

Irises
Vincent van Gogh (1889)
Painted in May 1889 at the Saint-Rémy asylum garden, Vincent van Gogh’s <strong>Irises</strong> turns close observation into an act of repair. Dark contours, a cropped, print-like vantage, and vibrating complements—violet/blue blossoms against <strong>yellow-green</strong> ground—stage a living frieze whose lone <strong>white iris</strong> punctuates the field with arresting clarity <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Wheatfield with Crows
Vincent van Gogh (1890)
A panoramic wheatfield splits around a rutted track under a storm-charged sky while black crows rush toward us. Van Gogh drives complementary blues and yellows into collision, fusing <strong>nature’s vitality</strong> with <strong>inner turbulence</strong>.

Portrait of Dr. Gachet
Vincent van Gogh (1890)
Portrait of Dr. Gachet distills Van Gogh’s late ambition for a <strong>modern, psychological portrait</strong> into vibrating color and touch. The sitter’s head sinks into a greenish hand above a <strong>blazing orange-red table</strong>, foxglove sprig nearby, while waves of <strong>cobalt and ultramarine</strong> churn through coat and background. The chromatic clash turns a quiet pose into an <strong>empathic image of fragility and care</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

San Giorgio Maggiore at Dusk
Claude Monet (1908–1912)
Claude Monet’s San Giorgio Maggiore at Dusk fuses the Benedictine church’s dark silhouette with a sky flaming from apricot to cobalt, turning architecture into atmosphere. The campanile’s vertical and its wavering reflection anchor a sea of trembling color, staging a meditation on <strong>permanence</strong> and <strong>flux</strong>.

Regatta at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
On a brilliant afternoon at the Normandy coast, a diagonal <strong>pebble beach</strong> funnels spectators with parasols toward a bay scattered with <strong>white-sailed yachts</strong>. Monet’s quick, broken strokes set <strong>wind, water, and light</strong> in synchrony, turning a local regatta into a modern scene of leisure held against the vastness of sea and sky <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Sea of Ice
Caspar David Friedrich (1823–1824)
Caspar David Friedrich’s The Sea of Ice turns nature into a <strong>frozen architecture</strong> that crushes a ship and, with it, human pretension. The painting stages the <strong>Romantic sublime</strong> as both awe and negation, replacing heroic conquest with the stark finality of ice and silence <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Artist's Garden at Vétheuil
Claude Monet (1881)
Claude Monet’s The Artist’s Garden at Vétheuil stages a sunlit ascent through a corridor of towering sunflowers toward a modest house, where everyday life meets cultivated nature. Quick, broken strokes make leaves and shadows tremble, asserting <strong>light</strong> and <strong>painterly surface</strong> over linear contour. Blue‑and‑white <strong>jardinieres</strong> anchor the foreground, while a child and dog briefly pause on the path, turning the garden into a <strong>domestic sanctuary</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Camille (The Woman in the Green Dress)
Claude Monet (1866)
Monet’s Camille (The Woman in the Green Dress) turns a full-length portrait into a study of <strong>modern spectacle</strong>. The spotlit emerald-and-black skirt, set against a near-black curtain, makes <strong>fashion</strong> the engine of meaning and the vehicle of status.

The Art of Painting
Johannes Vermeer (c. 1666–1668)
Johannes Vermeer’s The Art of Painting is a self-aware allegory that equates <strong>painting with history and fame</strong>. Framed by a parted <strong>tapestry</strong> like a stage curtain, an artist in historical dress paints the muse <strong>Clio</strong>, while a vast <strong>map of the Seventeen Provinces</strong> and a <strong>double‑headed eagle</strong> chandelier fold national memory into the studio scene <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
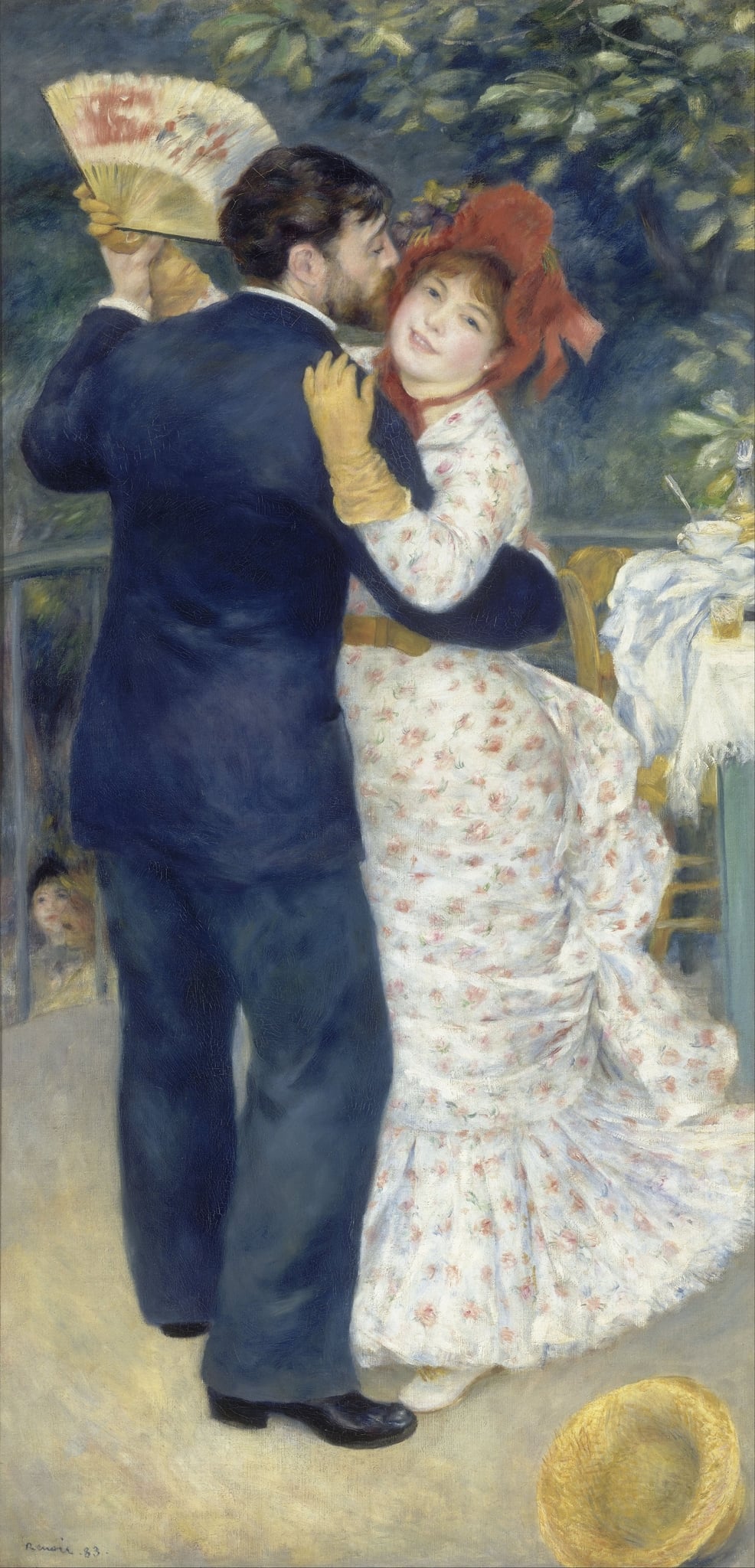

Dance in the Country
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1883)
Dance in the Country shows a couple swept into a close embrace on a café terrace, their bodies turning in a soft spiral as foliage and sunlight dissolve into <strong>dappled color</strong>. Renoir orchestrates <strong>bourgeois leisure</strong>—the tossed straw boater, a small table with glass and napkin, the woman’s floral dress and red bonnet—to stage a moment where decorum and desire meet. The result is a modern emblem of shared pleasure, poised between Impressionist shimmer and a newly <strong>firm, linear touch</strong>.
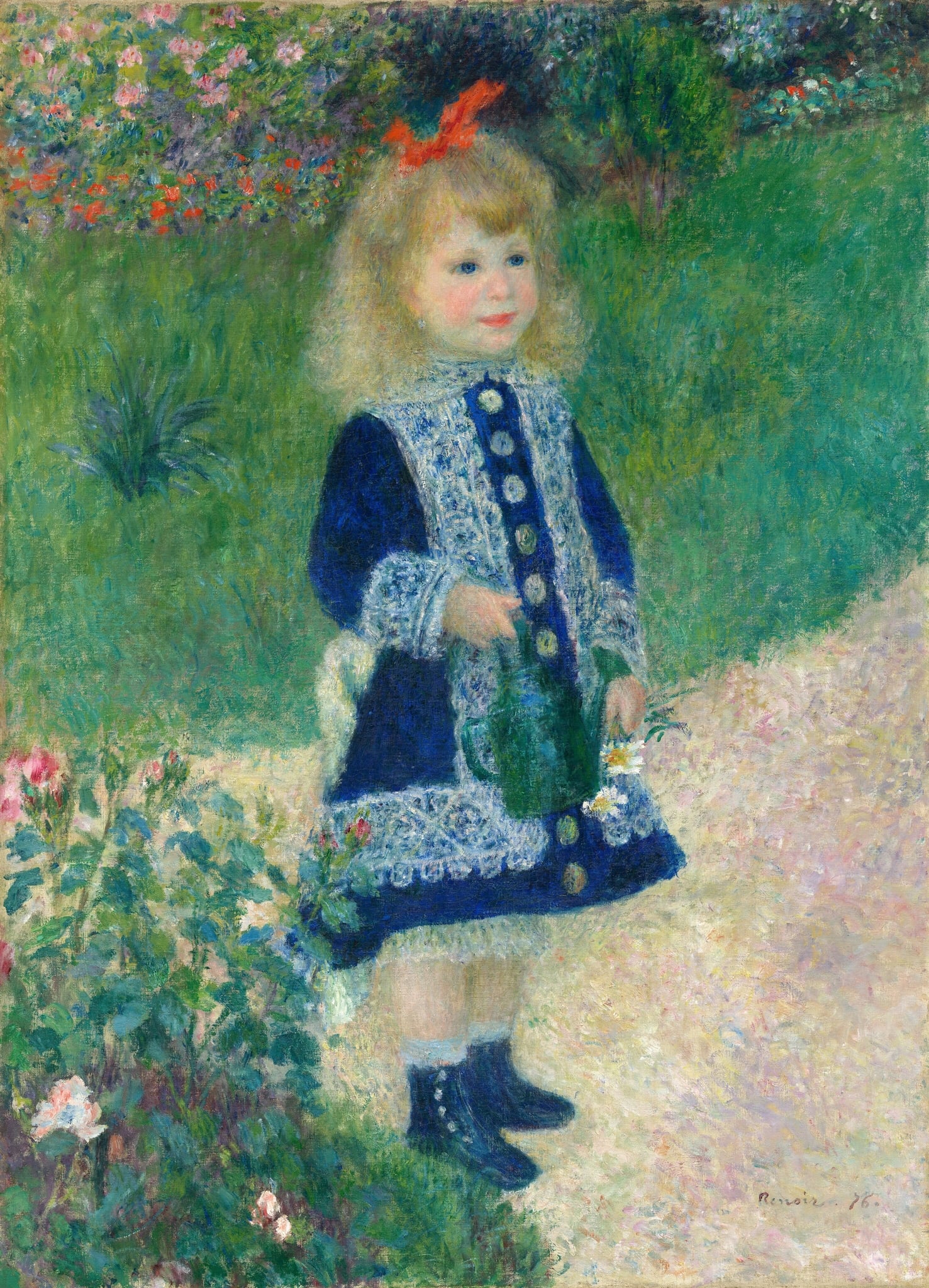
Girl with a Watering Can
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1876)
Renoir’s 1876 Girl with a Watering Can fuses a crisply perceived child with a dissolving garden atmosphere, using <strong>prismatic color</strong> and <strong>controlled facial modeling</strong> to stage innocence within modern leisure <sup>[1]</sup>. The cobalt dress, red bow, and green can punctuate a haze of pinks and greens, making nurture and growth the scene’s quiet thesis.

Portrait of Jeanne Samary
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1877)
Renoir’s Portrait of Jeanne Samary (1877) turns a modern actress into a study of <strong>radiance and immediacy</strong>, fusing figure and air with shimmering strokes. Cool blue‑green dress notes spark against a warm <strong>coral-pink atmosphere</strong>, while the cheek‑in‑hand pose crystallizes a moment of intimate poise <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.
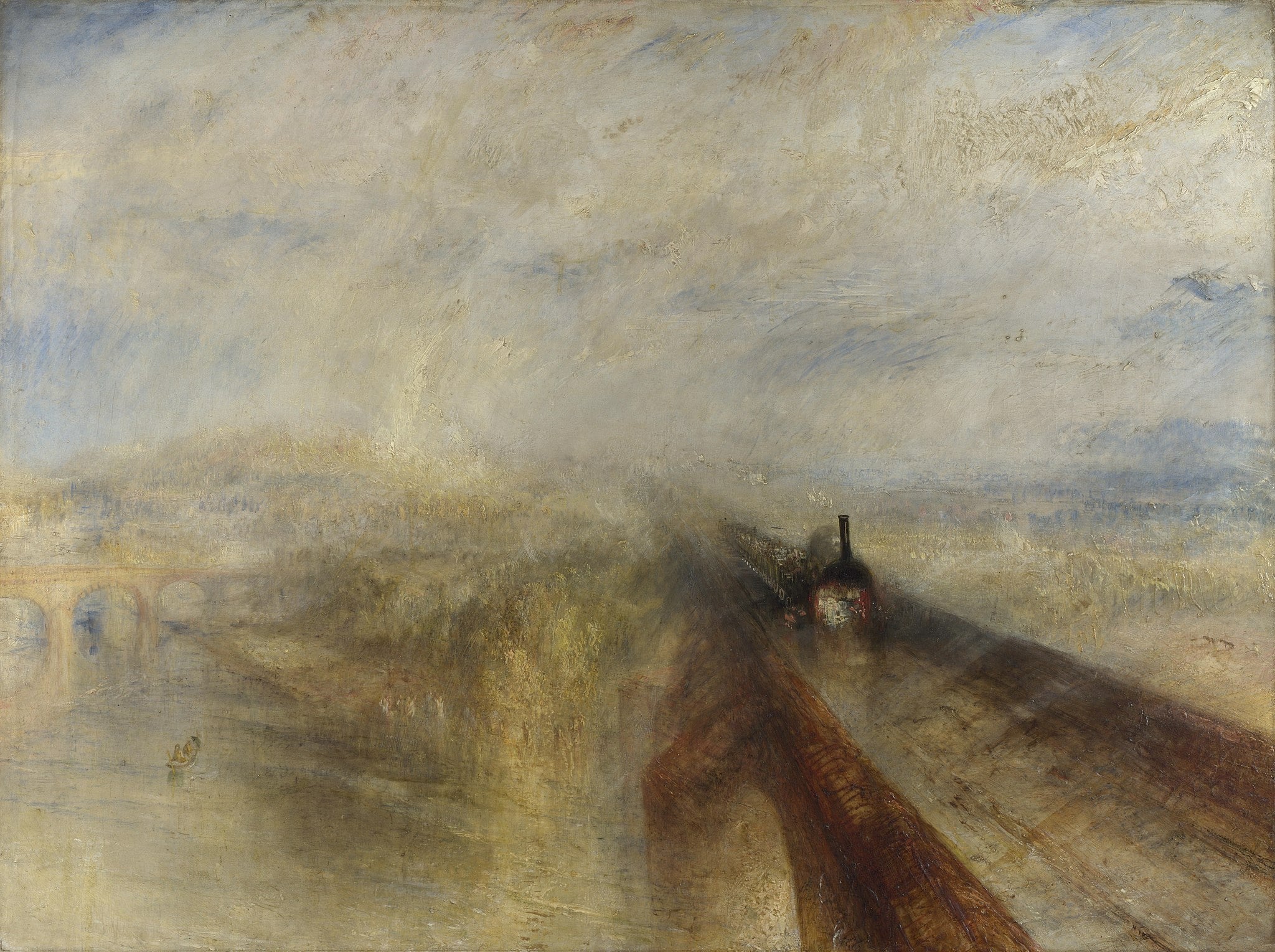

Rain, Steam and Speed
J. M. W. Turner (1844)
In Rain, Steam and Speed, J. M. W. Turner fuses weather and industry into a single onrushing vision, as a dark locomotive thrusts along the diagonal of Brunel’s Maidenhead Railway Bridge through veils of rain and light. The blurred fields, river, and town dissolve into a charged atmosphere where <strong>rain</strong>, <strong>steam</strong>, and <strong>speed</strong> become the true subjects. Counter-motifs—a small boat beneath pale arches and a near-invisible hare ahead of the train—stage a drama between pre‑industrial life and modern velocity <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Place de la Concorde
Edgar Degas (1875)
Degas’s Place de la Concorde turns a famous Paris square into a study of <strong>modern isolation</strong> and <strong>instantaneous vision</strong>. Figures stride past one another without contact, their bodies abruptly <strong>cropped</strong> and adrift in a wide, airless plaza—an urban stage where elegance masks estrangement <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
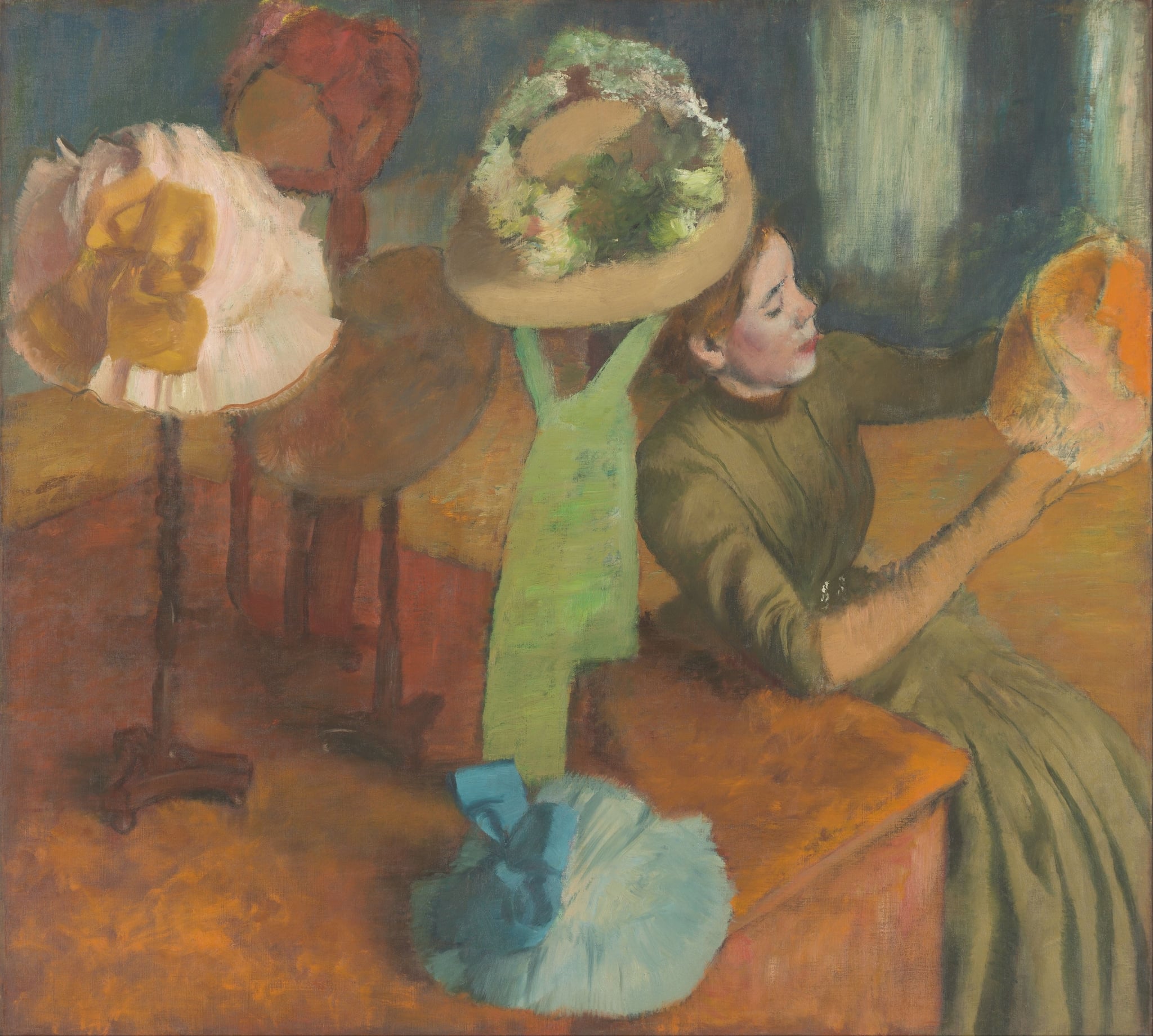

The Millinery Shop
Edgar Degas (1879–1886)
Edgar Degas’s The Millinery Shop stages modern Paris through a quiet act of <strong>work</strong> rather than display. A young woman, cropped in profile, studies a glowing <strong>orange hat</strong> while faceless stands crowned with ribbons and plumes press toward the picture plane. Degas turns a boutique into a meditation on <strong>labor, commodities, and identity</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
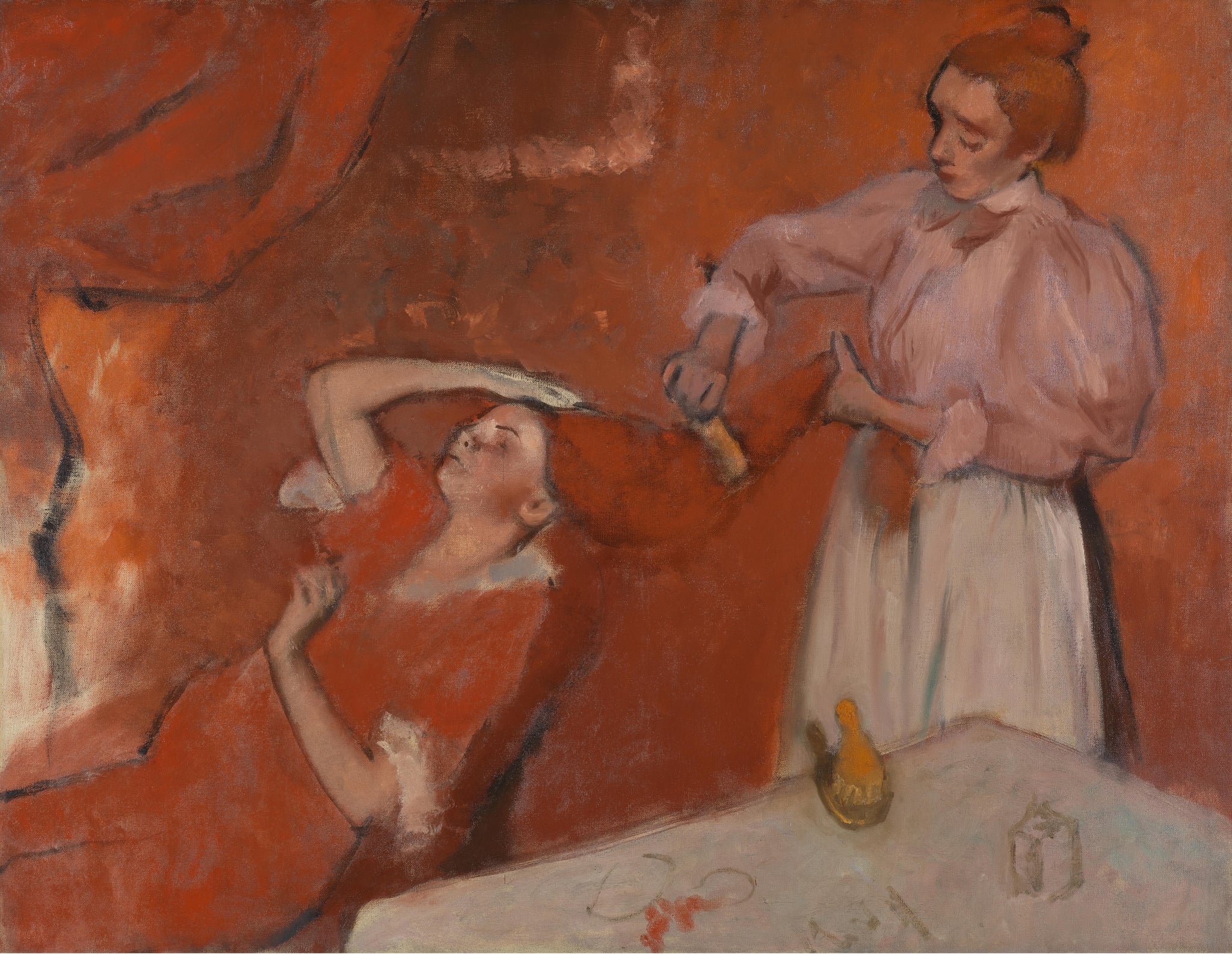

Combing the Hair
Edgar Degas (c.1896)
Edgar Degas’s Combing the Hair crystallizes a private ritual into a scene of <strong>compressed intimacy</strong> and <strong>classed labor</strong>. The incandescent field of red fuses figure and room, turning the hair into a <strong>binding ribbon</strong> between attendant and sitter <sup>[1]</sup>.
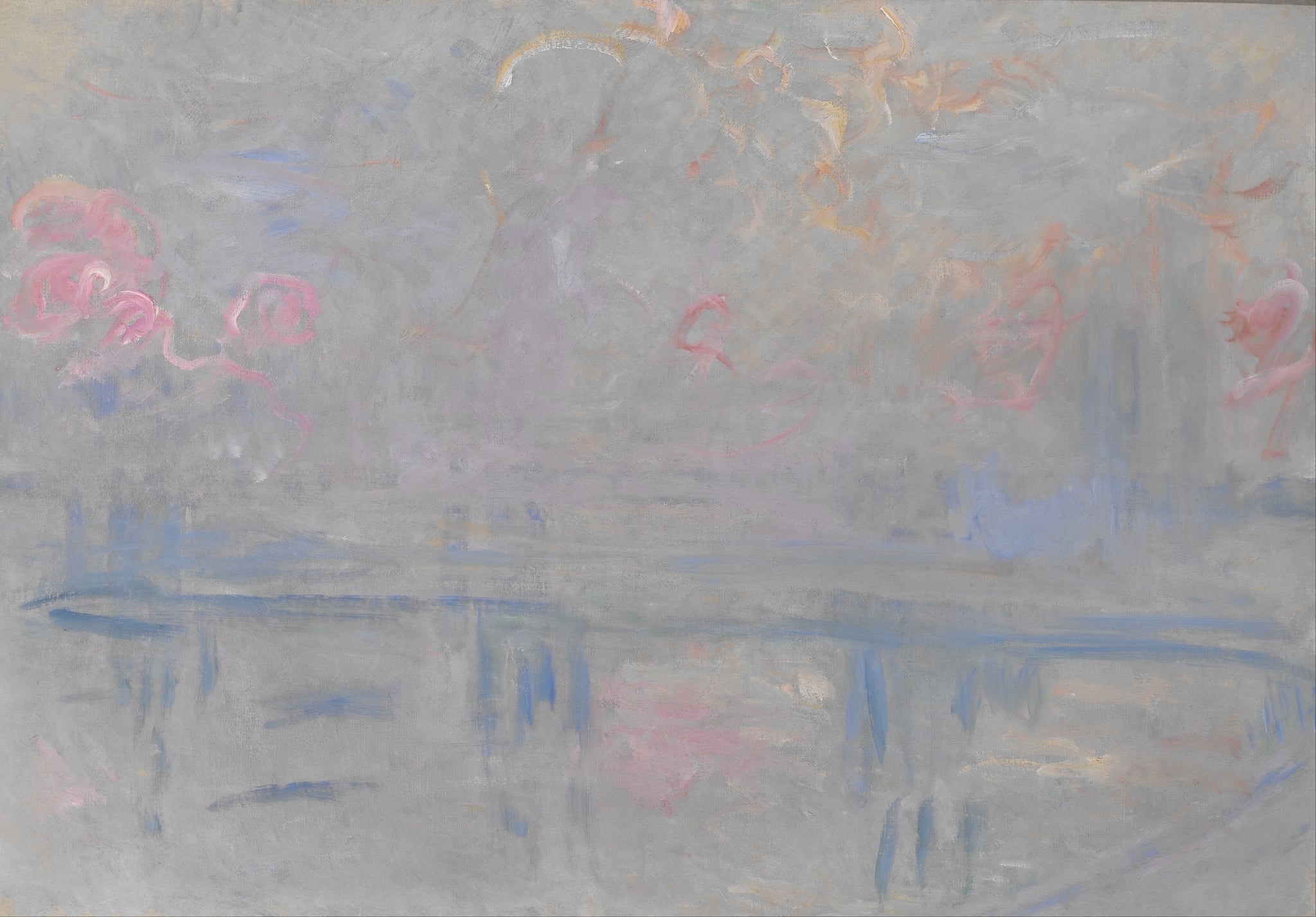

Charing Cross Bridge
Claude Monet (1901)
In Charing Cross Bridge, Claude Monet turns London into <strong>atmosphere</strong> itself: the bridge flattens into a cool, horizontal band while mauves, lavenders, and pearly grays veil the city. Spirals of <strong>pink steam</strong> and pockets of pale <strong>blue</strong> read as trains, lamps, or smoke transfigured by weather, so place becomes <strong>sensation</strong> rather than structure.
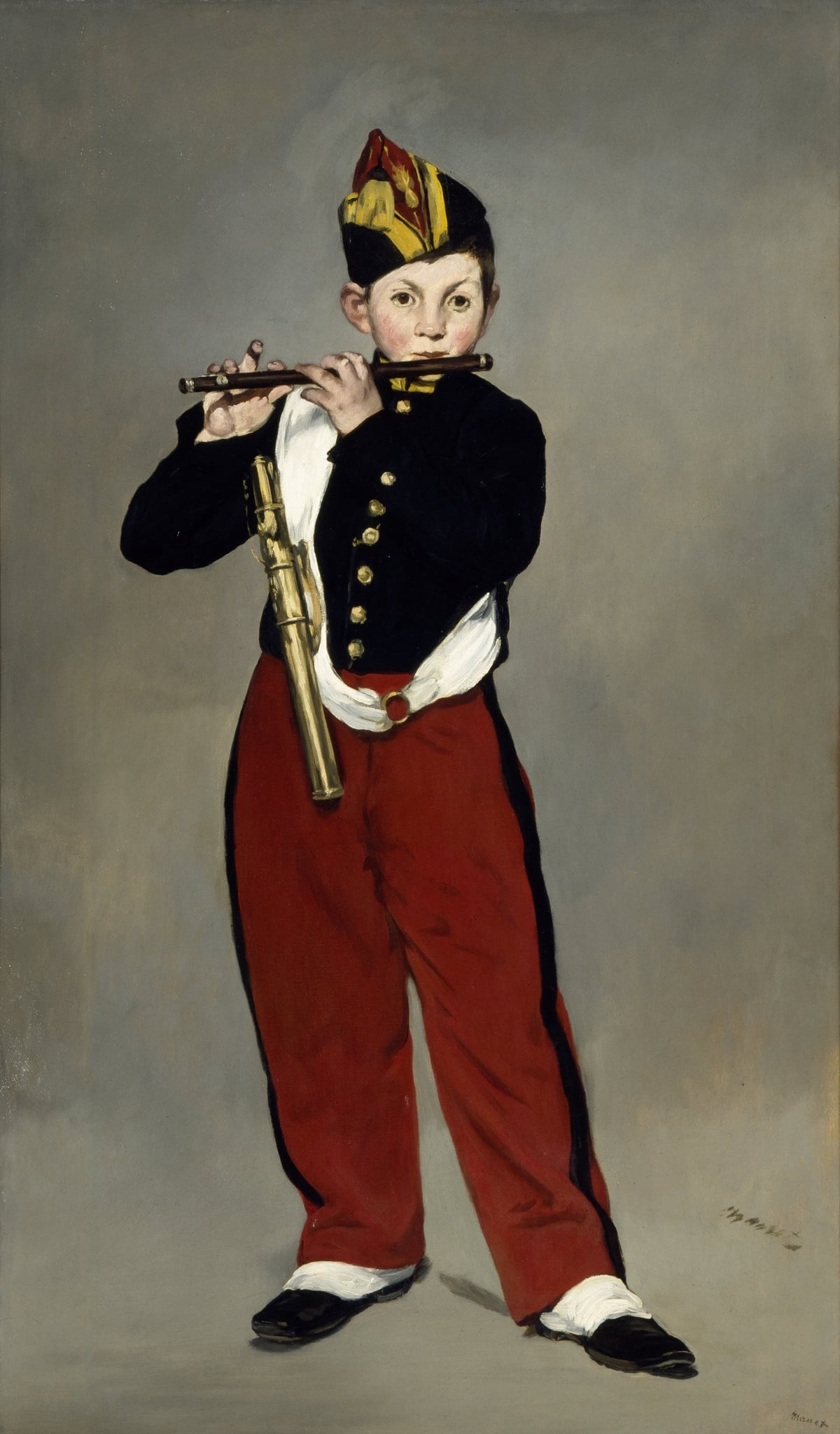

The Fifer
Édouard Manet (1866)
In The Fifer, <strong>Édouard Manet</strong> monumentalizes an anonymous military child by isolating him against a flat, gray field, converting everyday modern life into a subject of high pictorial dignity. The crisp <strong>silhouette</strong>, blocks of <strong>unmodulated color</strong> (black tunic, red trousers, white gaiters), and glints on the brass case make sound and discipline palpable without narrative scaffolding <sup>[1]</sup>. Drawing on <strong>Velázquez’s single-figure-in-air</strong> formula yet inflected by japonisme’s flatness, Manet forges a new modern image that the Salon rejected in 1866 <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
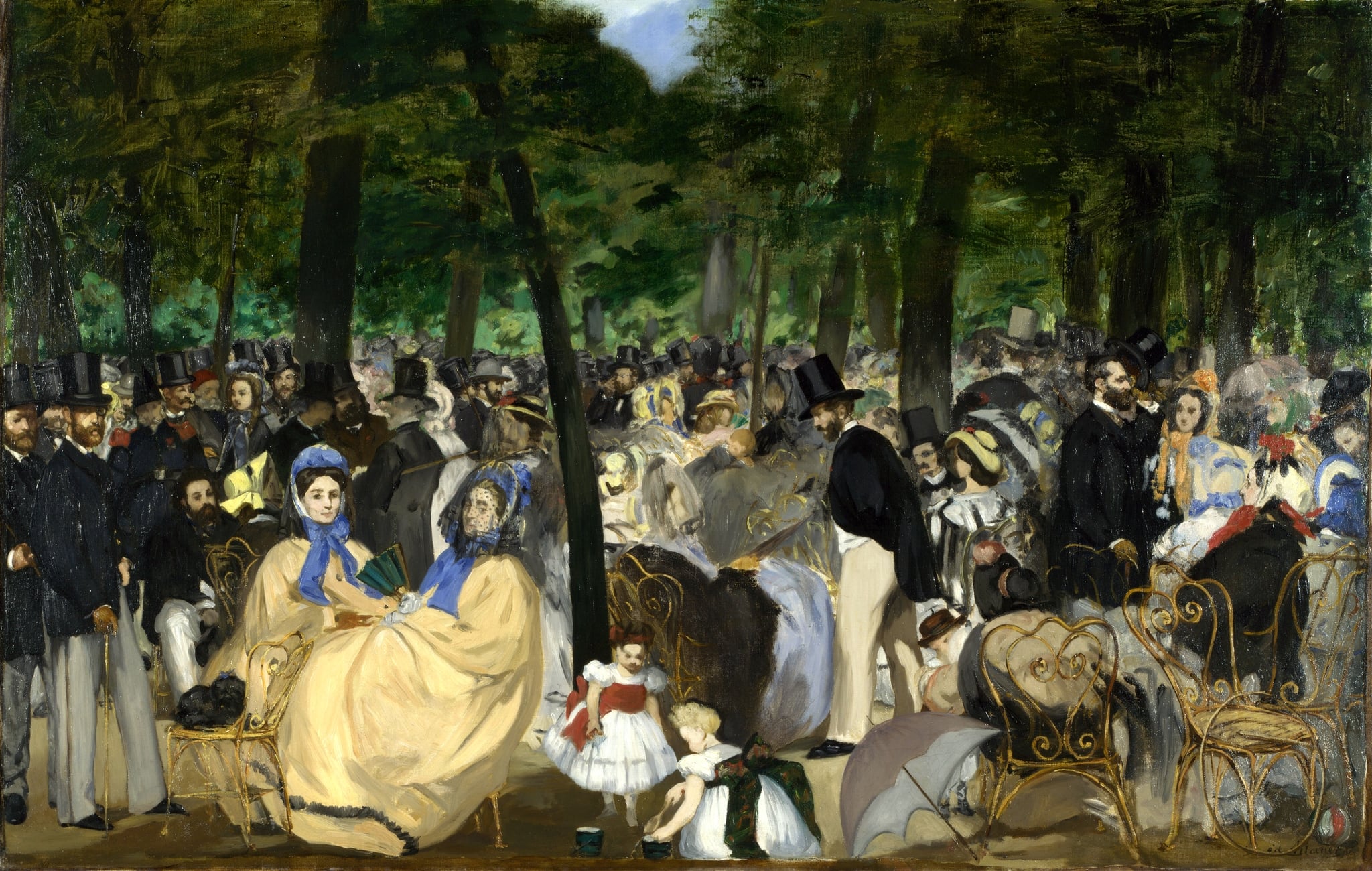

Music in the Tuileries
Édouard Manet (1862)
Édouard Manet’s Music in the Tuileries turns a Sunday concert into a manifesto of <strong>modern life</strong>: a frieze of top hats, crinolines, and iron chairs flickering beneath <strong>toxic green</strong> foliage. Instead of a hero or center, the painting disperses attention across a restless crowd, making <strong>looking itself</strong> the drama of the scene <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Berthe Morisot with a Bouquet of Violets
Édouard Manet (1872)
Édouard Manet’s Berthe Morisot with a Bouquet of Violets is a close, modern portrait built as a <strong>symphony in black</strong> punctuated by a tiny violet knot. Side‑light chisels the face from a cool, silvery ground while hat, scarf, and coat merge into one dark silhouette, and the eyes are painted strikingly <strong>black</strong> for effect <sup>[1]</sup>. The single touch of violets introduces a discreet, coded <strong>tenderness</strong> within the portrait’s refined restraint <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.
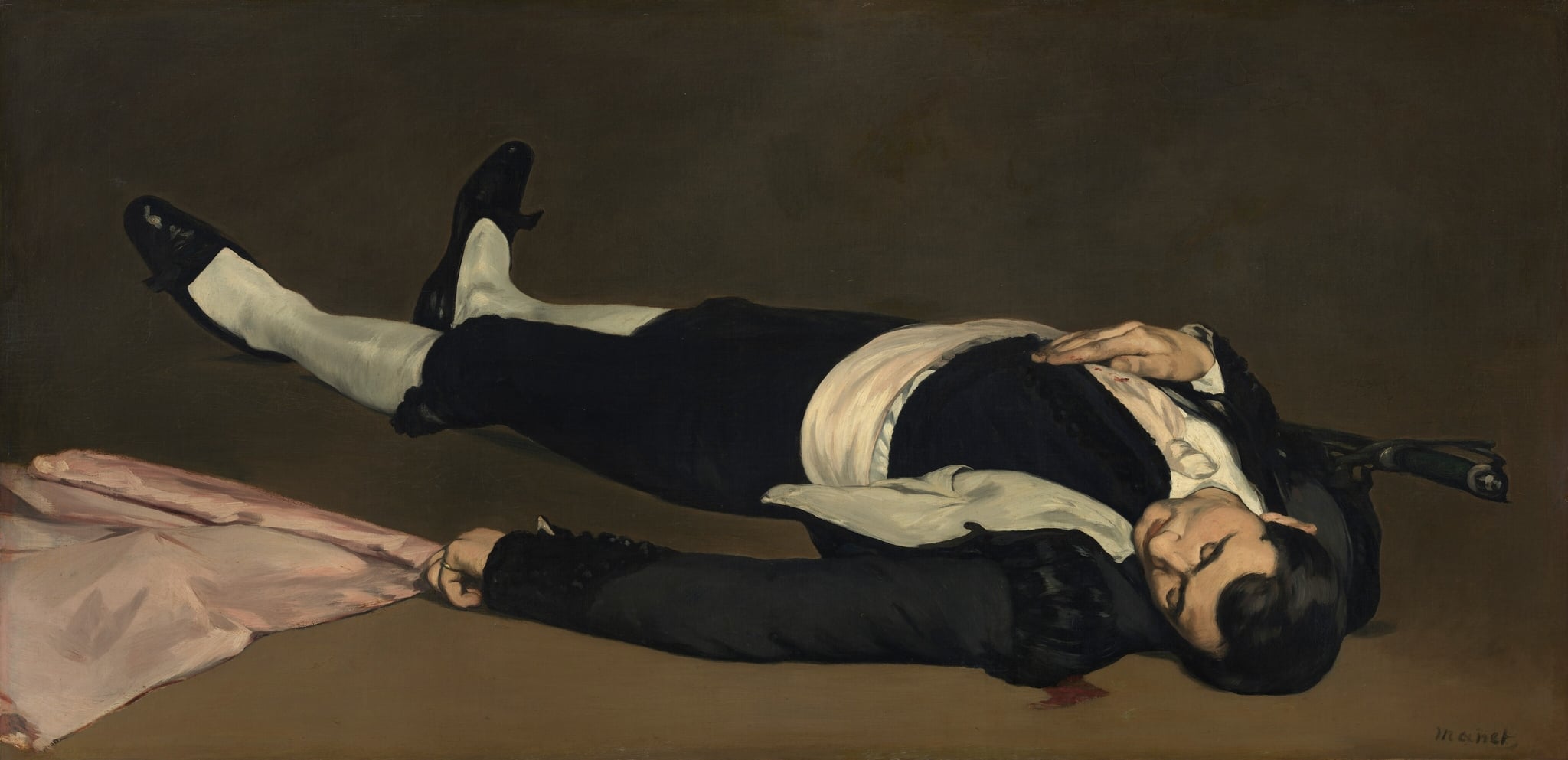

The Dead Toreador
Édouard Manet (probably 1864)
Manet’s The Dead Toreador isolates a matador’s corpse in a stark, horizontal close‑up, replacing the spectacle of the bullring with <strong>silence</strong> and <strong>abrupt finality</strong>. Black costume, white stockings, a pale pink cape, the sword’s hilt, and a small <strong>pool of blood</strong> become the painting’s cool, modern vocabulary of death <sup>[1]</sup>.
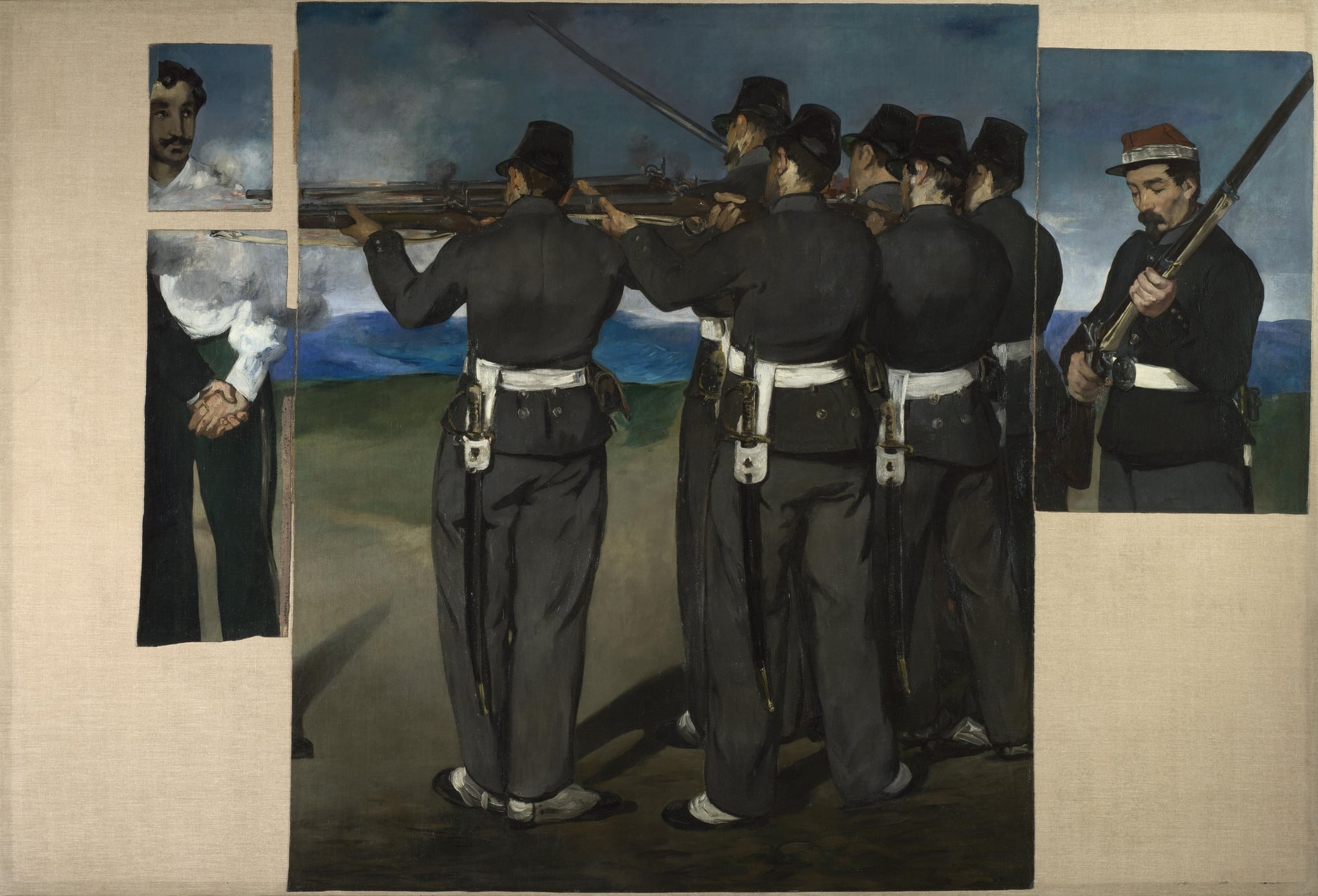

The Execution of Emperor Maximilian
Édouard Manet (1867–1868)
Manet’s The Execution of Emperor Maximilian confronts state violence with a <strong>cool, reportorial</strong> style. The wall of gray-uniformed riflemen, the <strong>fragmented canvas</strong>, and the dispassionate loader at right turn the killing into <strong>impersonal machinery</strong> that implicates the viewer <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
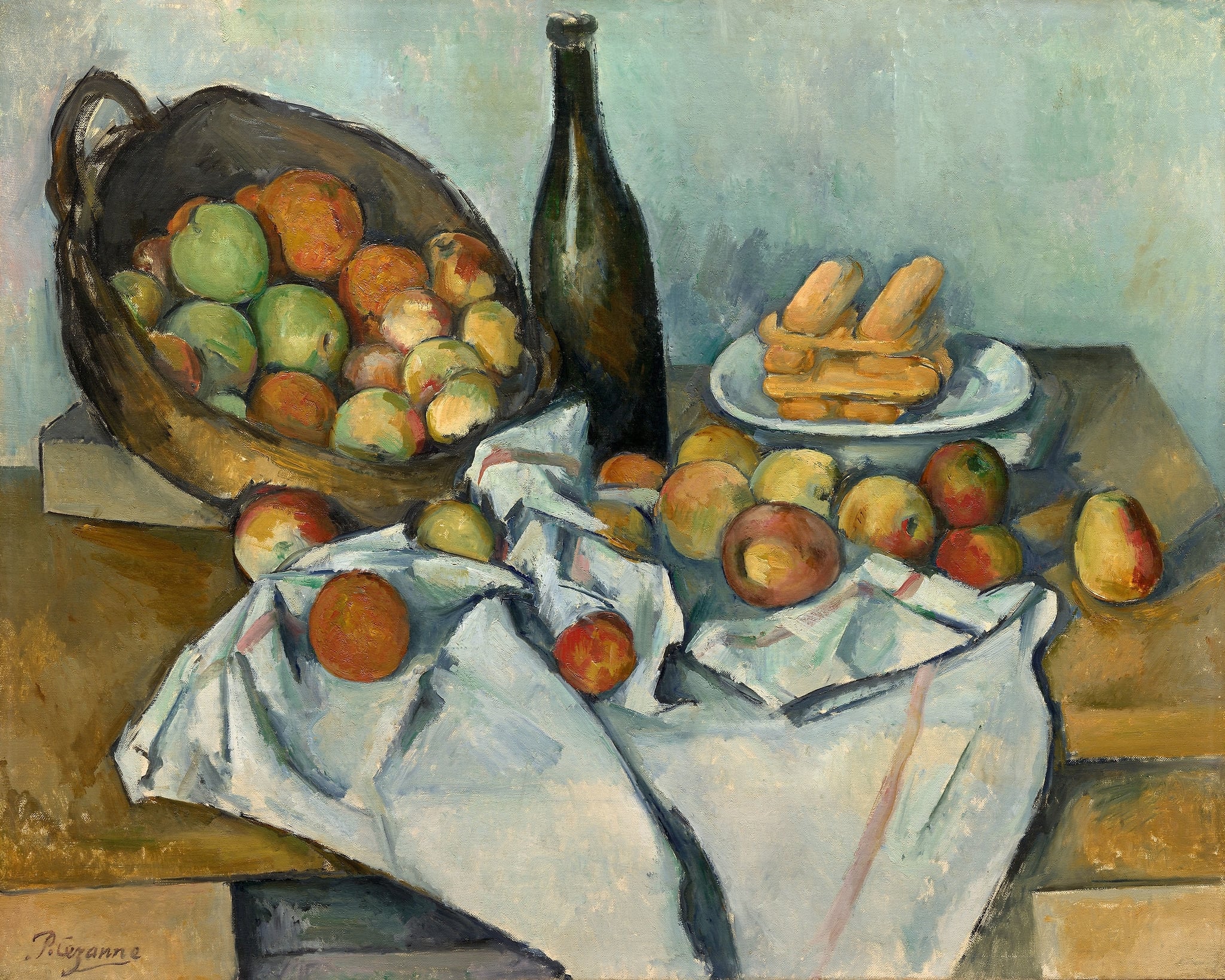
The Basket of Apples
Paul Cézanne (c. 1893)
Paul Cézanne’s The Basket of Apples stages a quiet drama of <strong>balance and perception</strong>. A tilted basket spills apples across a <strong>rumpled white cloth</strong> toward a <strong>dark vertical bottle</strong> and a plate of <strong>biscuits</strong>, while the tabletop’s edges refuse to align—an intentional play of <strong>multiple viewpoints</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
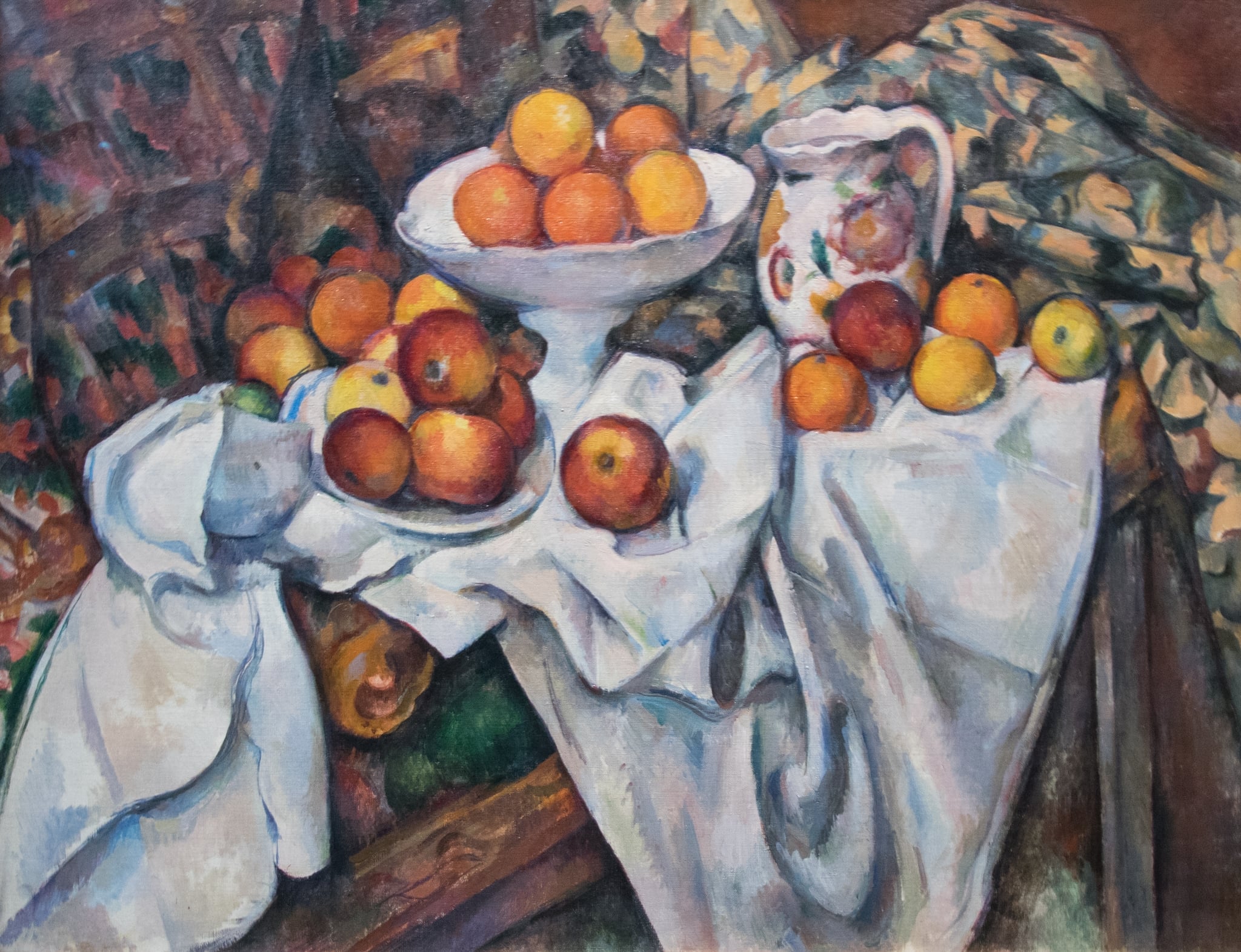

Still Life with Apples and Oranges
Paul Cézanne (c. 1899)
Paul Cézanne’s Still Life with Apples and Oranges builds a quietly monumental world from domestic things. A tilting table, a heaped white compote, a flowered jug, and cascading cloths turn fruit into <strong>durable forms</strong> stabilized by <strong>color relationships</strong> rather than single‑point perspective <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. The result is a still life that feels both solid and subtly <strong>unstable</strong>, a meditation on how we construct vision.
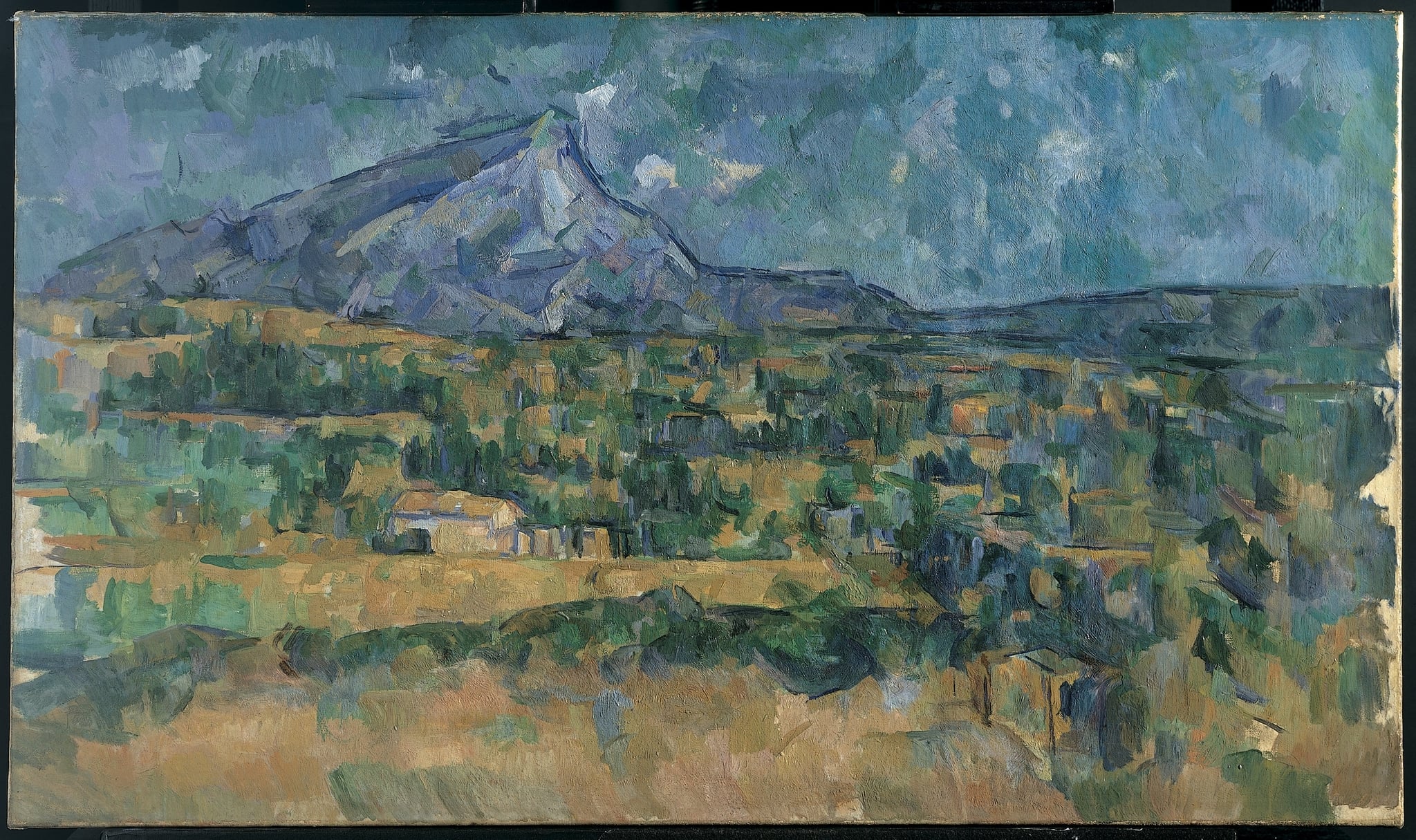

Mont Sainte-Victoire
Paul Cézanne (1902–1906)
Cézanne’s Mont Sainte-Victoire renders the Provençal massif as a constructed order of <strong>planes and color</strong>, not a fleeting impression. Cool blues and violets articulate the mountain’s facets, while <strong>ochres and greens</strong> laminate the fields and blocky houses, binding atmosphere and form into a single structure <sup>[2]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

The Doge's Palace
Claude Monet (1908)
Monet’s The Doge’s Palace translates Venice’s emblem of authority into an <strong>atmospheric drama</strong> of lilac, cream, and ultramarine. Architecture becomes a <strong>screen for light</strong>, as the ogival windows and double arcades blur into vibrating strokes mirrored by the lagoon’s <strong>second architecture</strong>—its reflection <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

Madame Cézanne in a Red Armchair
Paul Cézanne (about 1877)
Paul Cézanne’s Madame Cézanne in a Red Armchair (about 1877) turns a domestic sit into a study of <strong>color-built structure</strong> and <strong>compressed space</strong>. Cool blue-greens of dress and skin lock against the saturated <strong>crimson armchair</strong>, converting likeness into an inquiry about how painting makes stability visible <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
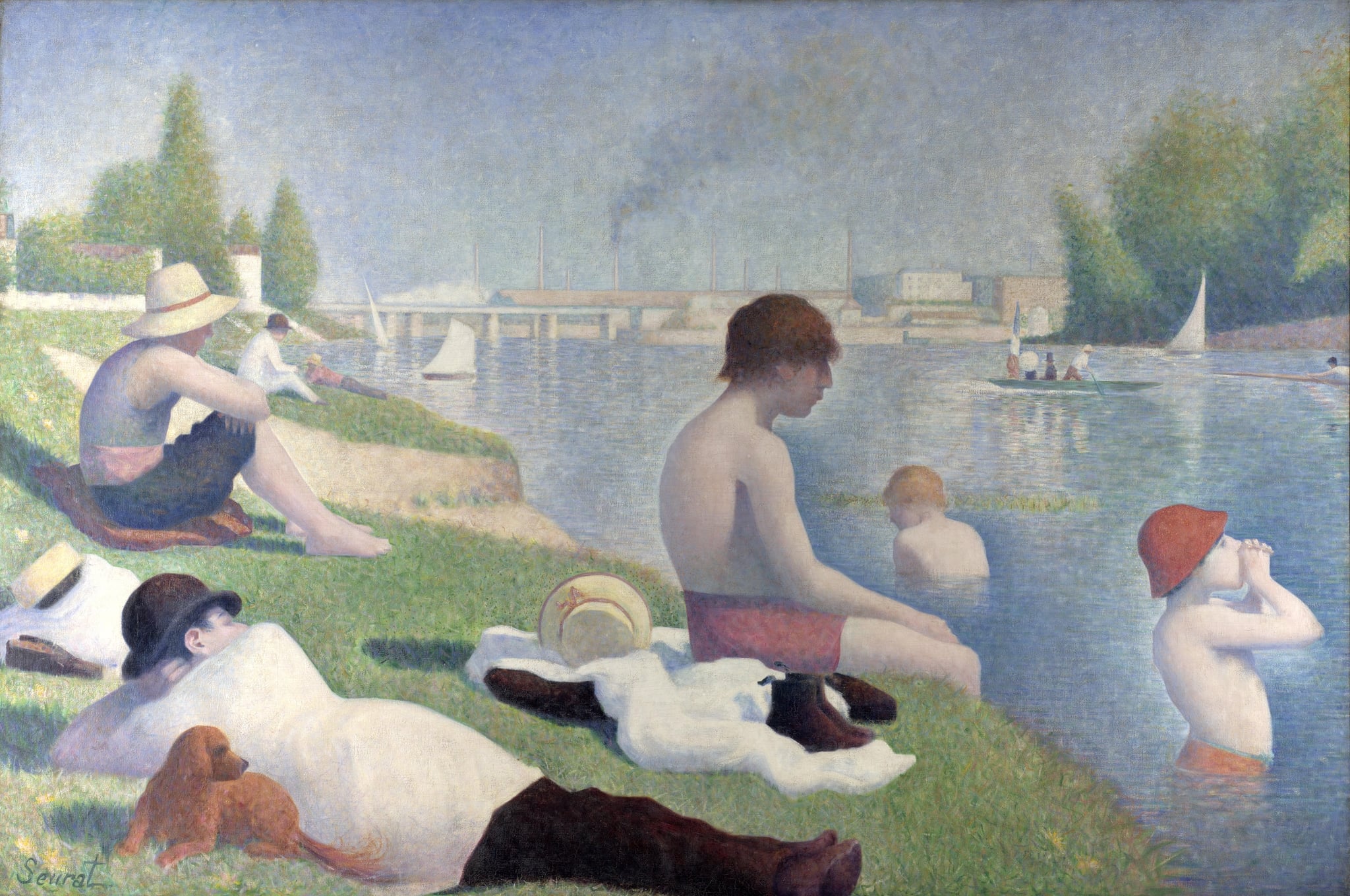

Bathers at Asnières
Georges Seurat (1884)
Bathers at Asnières stages a scene of <strong>modern leisure</strong> on the Seine, where workers recline and wade beneath a hazy, unified light. Seurat fuses <strong>classicizing stillness</strong> with an <strong>industrial backdrop</strong> of chimneys, bridges, and boats, turning ordinary rest into a monumental, ordered image of urban life <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The canvas balances soft greens and blues with geometric structures, producing a calm yet charged harmony.
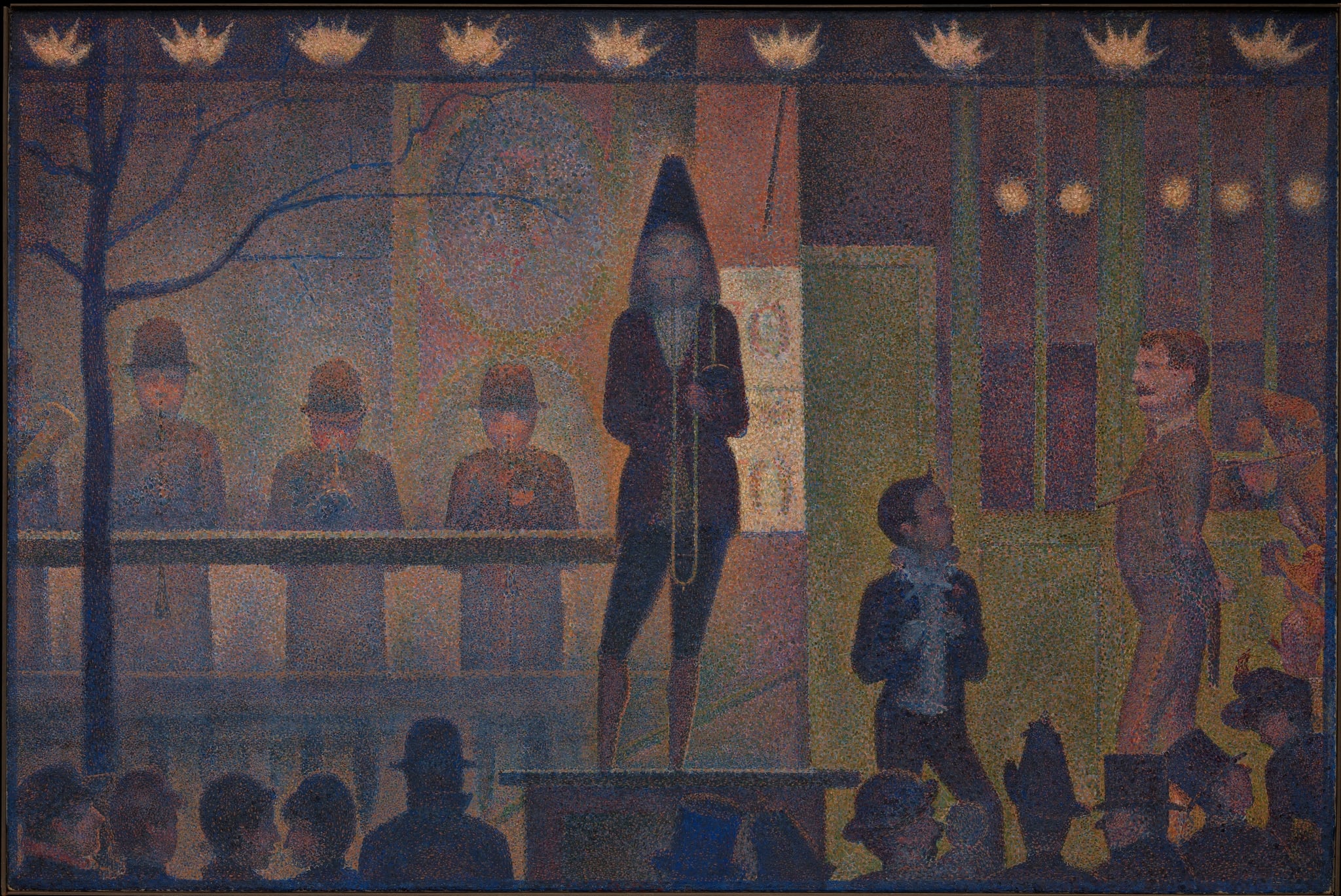

Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque)
Georges Seurat (1887–88)
Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque) distills a bustling Paris fairground into a cool, ritualized <strong>threshold</strong> between street and spectacle. Under nine crownlike <strong>gaslights</strong>, a barker, musicians, and attendants align with geometric restraint while the crowd remains a band of silhouettes, held at the edge. Seurat’s <strong>Neo‑Impressionist</strong> dots make the night hum yet stay eerily still, turning publicity into a modern icon of order and mood <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
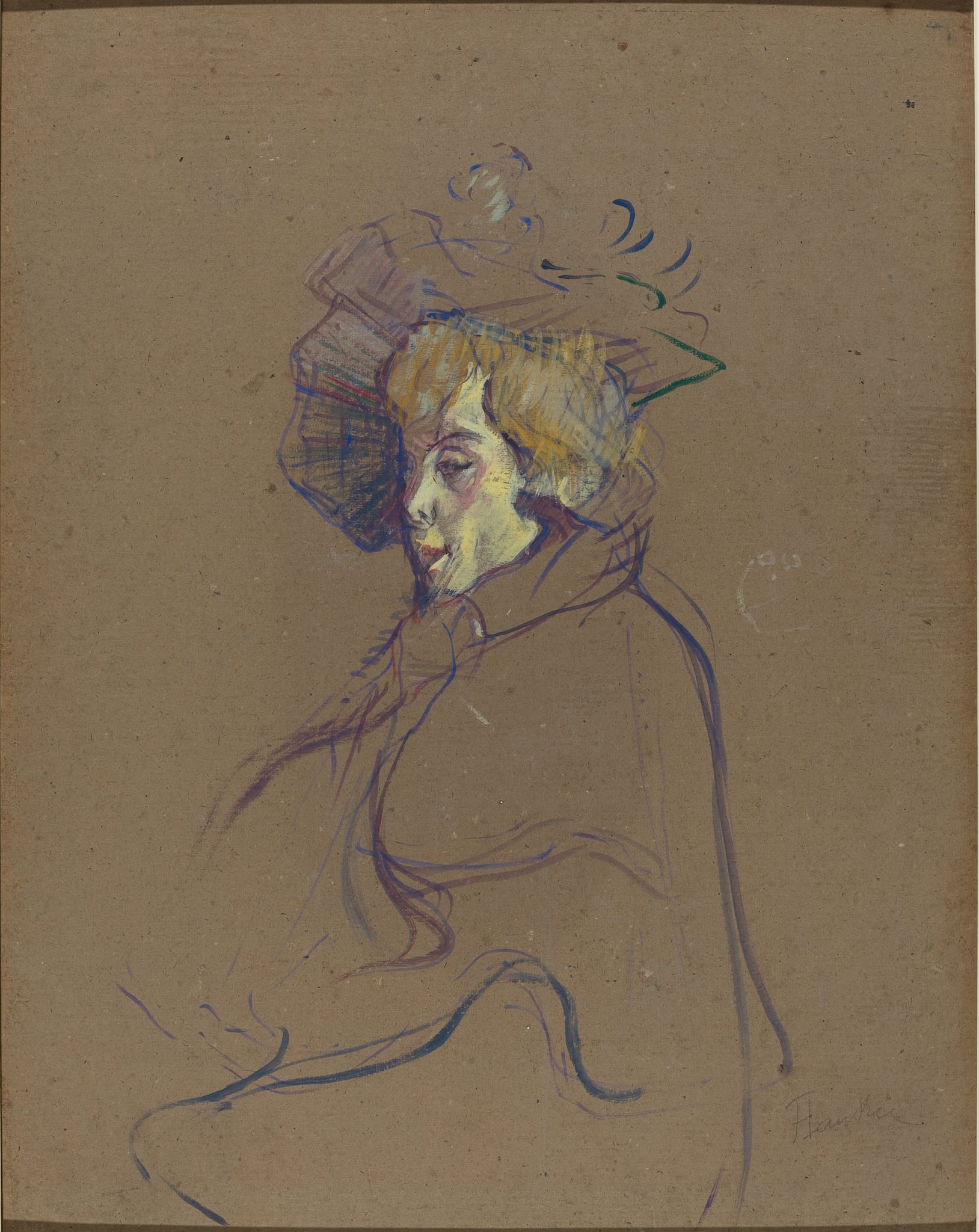

Jane Avril
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (c. 1891–1892)
In Jane Avril, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec crystallizes a public persona from a few <strong>urgent, chromatic strokes</strong>: violet and blue lines whirl into a cloak, while green and indigo dashes crown a buoyant hat. Her face—sharply keyed in <strong>lemon yellow, lilac, and carmine</strong>—hovers between mask and likeness, projecting poise edged with fatigue. The raw brown ground lets her <strong>whiplash silhouette</strong> materialize like smoke from Montmartre’s nightlife.

The Cup of Tea
Mary Cassatt (ca. 1880–81)
Mary Cassatt’s The Cup of Tea distills a moment of bourgeois leisure into a study of <strong>poise</strong>, <strong>etiquette</strong>, and <strong>private reflection</strong>. A woman in a rose‑pink dress and bonnet, white‑gloved, balances a gold‑rimmed cup against the shimmer of <strong>Impressionist</strong> brushwork, while a green planter of pale blossoms echoes her pastel palette <sup>[1]</sup>. The work turns an ordinary ritual into a modern emblem of women’s experience.
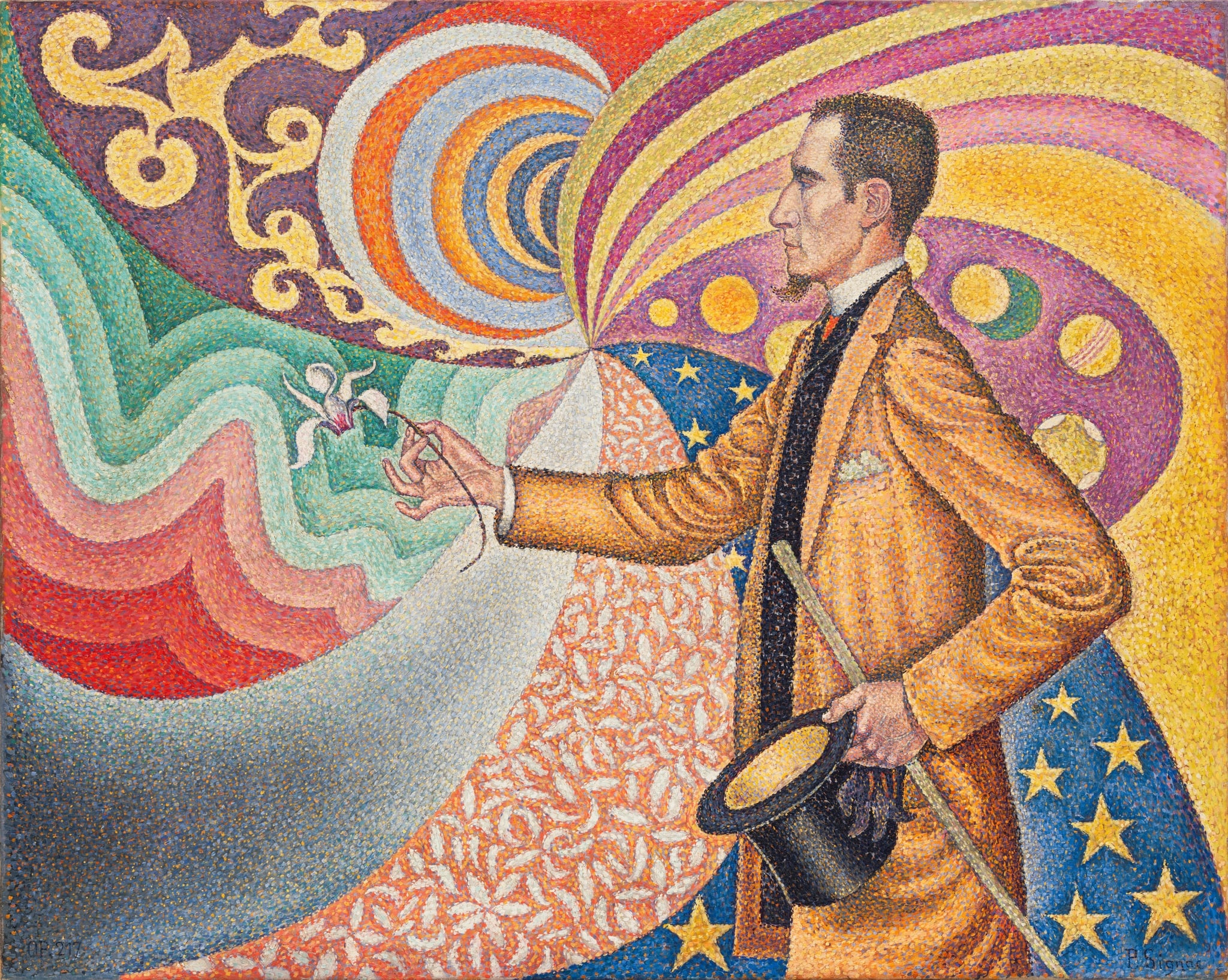

Portrait of Félix Fénéon
Paul Signac (1890)
Portrait of Félix Fénéon turns a critic into a <strong>conductor of color</strong>: a dandy in a yellow coat proffers a delicate cyclamen as concentric disks, whiplash arabesques, stars, and palette-like circles whirl around him. Rendered in precise <strong>Pointillist</strong> dots, the scene stages the fusion of <strong>art, science, and modern style</strong>.<sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>

The Boulevard Montmartre on a Spring Morning
Camille Pissarro (1897)
From a high hotel window, Camille Pissarro turns Paris’s grands boulevards into a river of light and motion. In The Boulevard Montmartre on a Spring Morning, pale roadway, <strong>tender greens</strong>, and <strong>flickering brushwork</strong> fuse crowds, carriages, and iron streetlamps into a single urban current <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. The scene demonstrates Impressionism’s commitment to time, weather, and modern life, distilled through a fixed vantage across a serial project <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
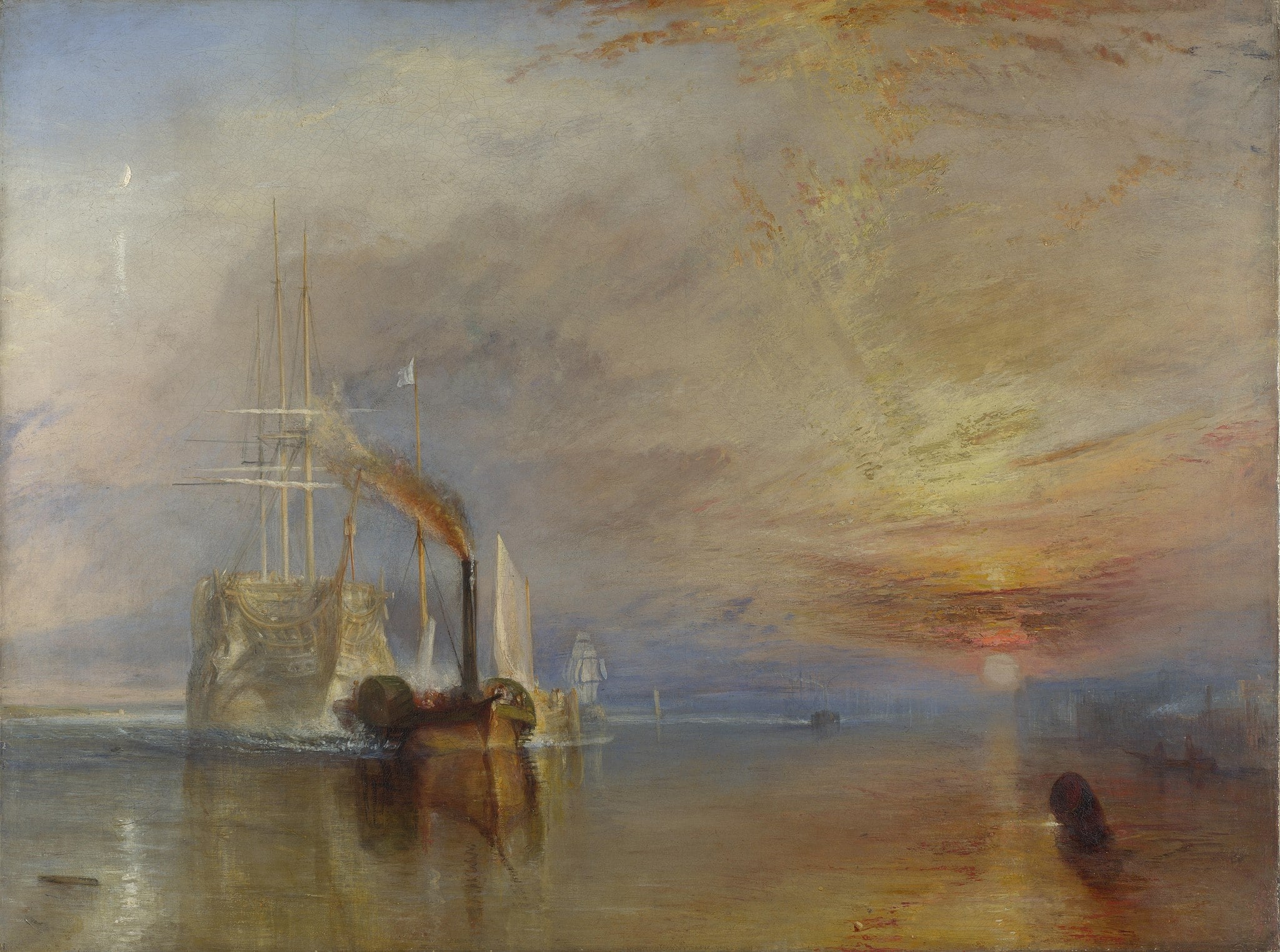

The Fighting Temeraire
J. M. W. Turner (1839)
In The Fighting Temeraire, J. M. W. Turner sets a <strong>ghostly man‑of‑war</strong> against a <strong>sooty steam tug</strong> under a blazing, emblematic sunset. The pale ship’s towering masts and slack rigging read like memory, while the tug’s black smoke cuts through the rigging where a flag once flew, signaling <strong>power passing from sail to steam</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. A crescent moon and a humble buoy punctuate a river turned to molten gold, marking both ending and beginning <sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

The Church at Moret
Alfred Sisley (1894)
Alfred Sisley’s The Church at Moret turns a Flamboyant Gothic façade into a living barometer of light, weather, and time. With <strong>cool blues, lilacs, and warm ochres</strong> laid in broken strokes, the stone seems to breathe as tiny townspeople drift along the street. The work asserts <strong>permanence meeting transience</strong>: a communal monument held steady while the day’s atmosphere endlessly remakes it <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Reading
Berthe Morisot (1873)
In Berthe Morisot’s <strong>Reading</strong> (1873), a woman in a pale, patterned dress sits on the grass, absorbed in a book while a <strong>green parasol</strong> and <strong>folded fan</strong> lie nearby. Morisot’s quick, luminous brushwork dissolves the landscape into <strong>atmospheric greens</strong> as a distant carriage passes, turning an outdoor scene into a study of interior life. The work makes <strong>female intellectual absorption</strong> its true subject, aligning modern leisure with private thought.
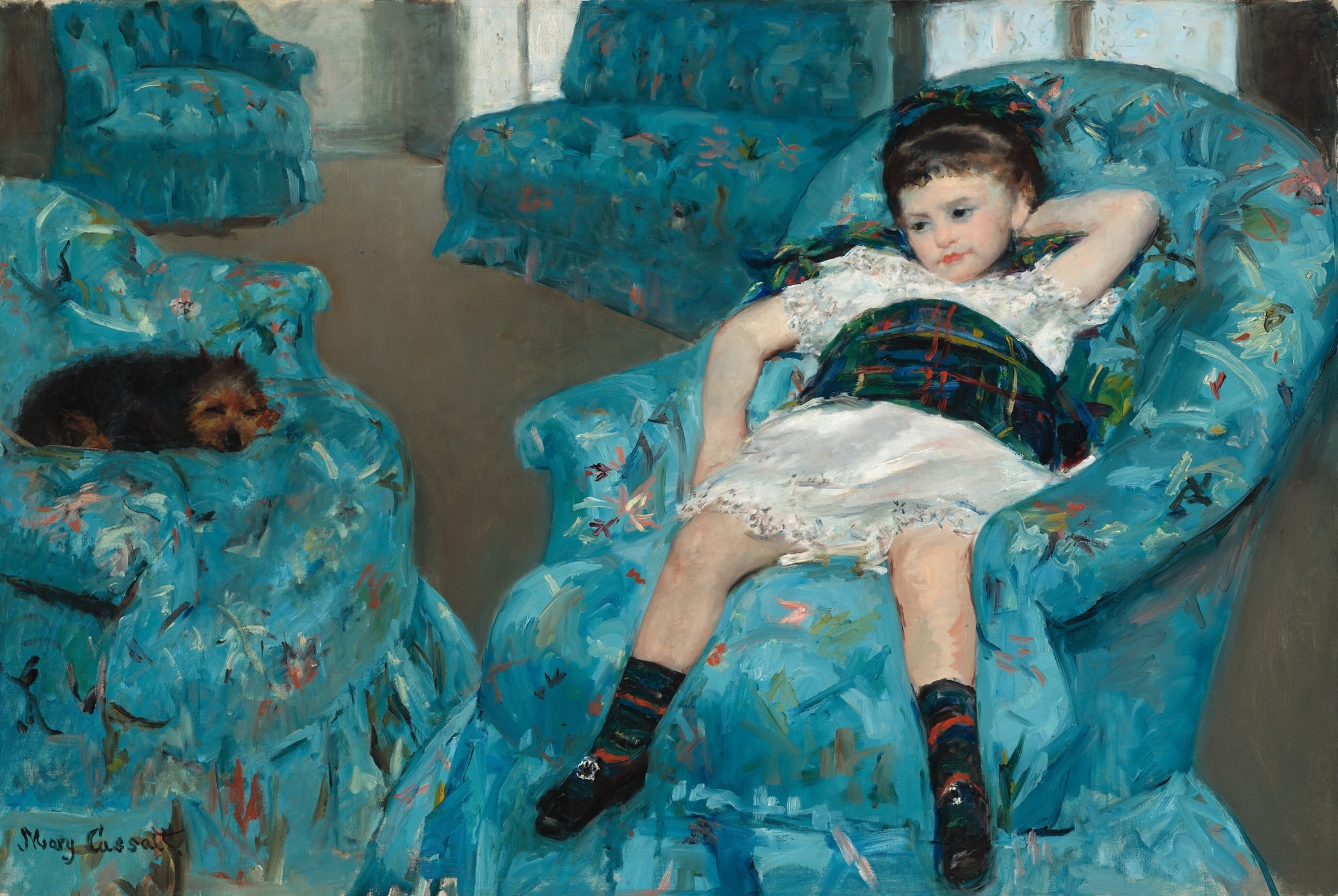

Little Girl in a Blue Armchair
Mary Cassatt (1878)
Mary Cassatt’s Little Girl in a Blue Armchair renders a child slumped diagonally across an oversized seat, surrounded by a flotilla of blue chairs and cool window light. With brisk, broken strokes and a skewed recession, Cassatt asserts a modern, unsentimental view of childhood—bored, autonomous, and <strong>out of step with adult decorum</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. Subtle collaboration with <strong>Degas</strong> in the background design sharpens the picture’s daring spatial thrust <sup>[2]</sup>.
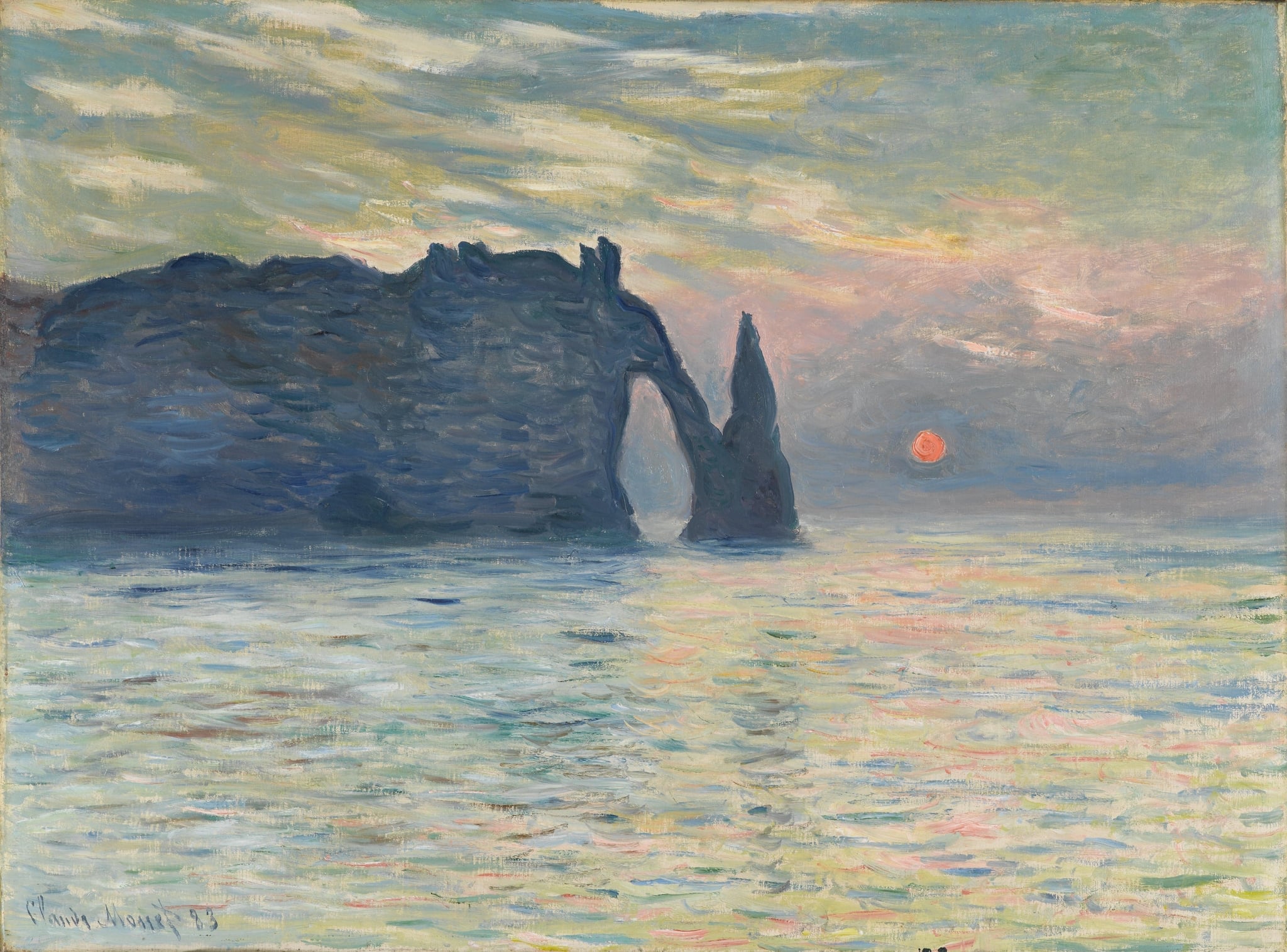

The Cliff, Etretat
Claude Monet (1882–1883)
<strong>The Cliff, Etretat</strong> stages a confrontation between <strong>permanence and flux</strong>: the dark mass of the arch and needle holds like a monument while ripples of coral, green, and blue light skate across the water. The low <strong>solar disk</strong> fixes the instant, and Monet’s fractured strokes make the sea and sky feel like time itself turning toward dusk. The arch reads as a <strong>threshold</strong>—an opening to the unknown that organizes vision and meaning <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
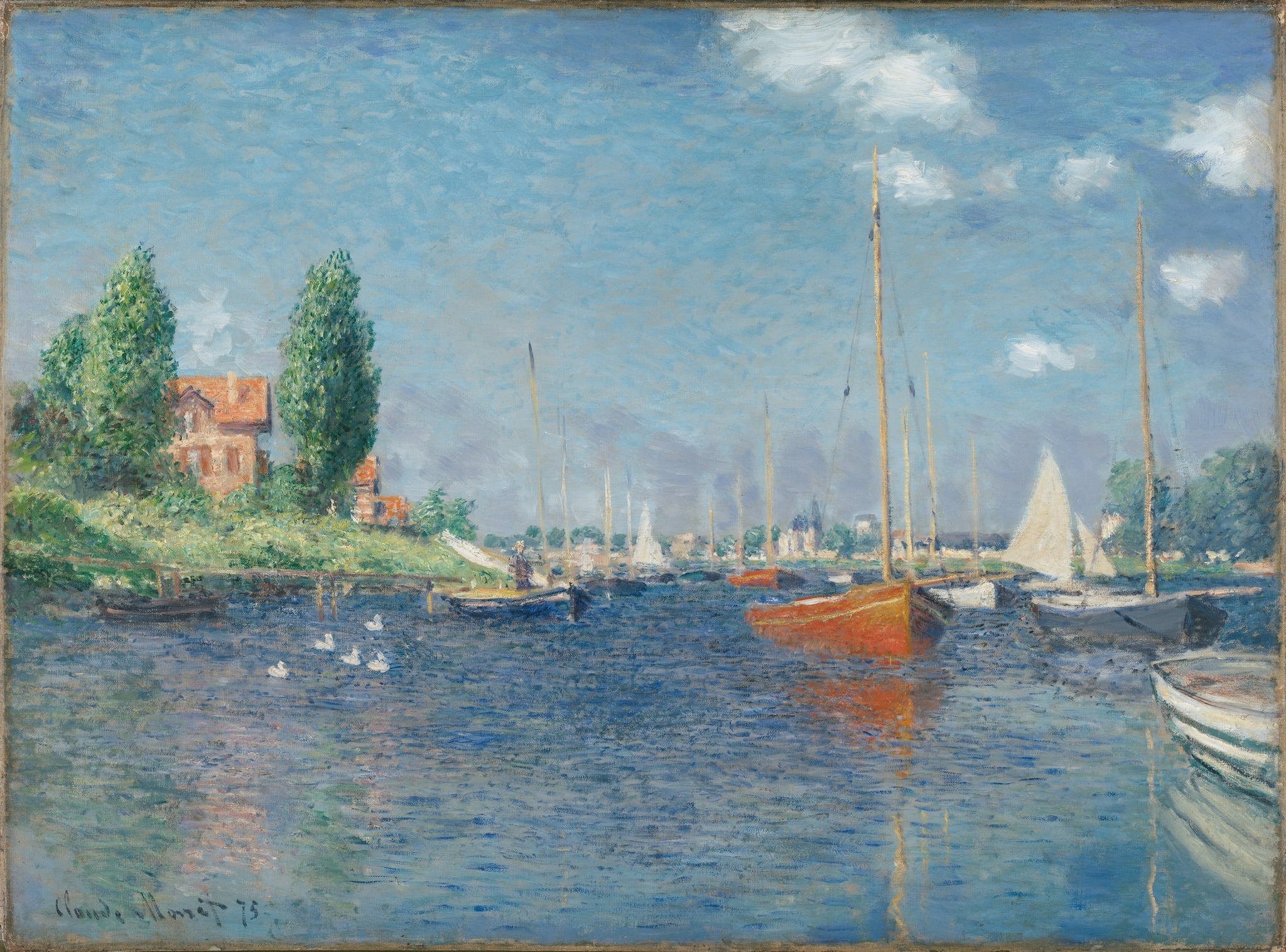

The Red Boats, Argenteuil
Claude Monet (1875)
Claude Monet’s The Red Boats, Argenteuil crystallizes a luminous afternoon on the Seine, where two <strong>vermilion hulls</strong> anchor a scene of leisure and light. The tremoring <strong>reflections</strong> and vertical <strong>masts/poplars</strong> weave nature and modern recreation into a single atmospheric field <sup>[1]</sup>.

Camille Monet on a Garden Bench
Claude Monet (1873)
Claude Monet’s Camille Monet on a Garden Bench (1873) stages an intimate pause where <strong>light, grief, and modern leisure</strong> intersect. Camille, shaded and withdrawn, holds a letter while a <strong>top‑hatted neighbor</strong> hovers; a bright bank of <strong>red geraniums</strong> and a strolling woman with a parasol ignite the distance <sup>[1]</sup>. Monet converts a domestic garden into a scene about <strong>psychological distance</strong> amid fleeting sunlight.
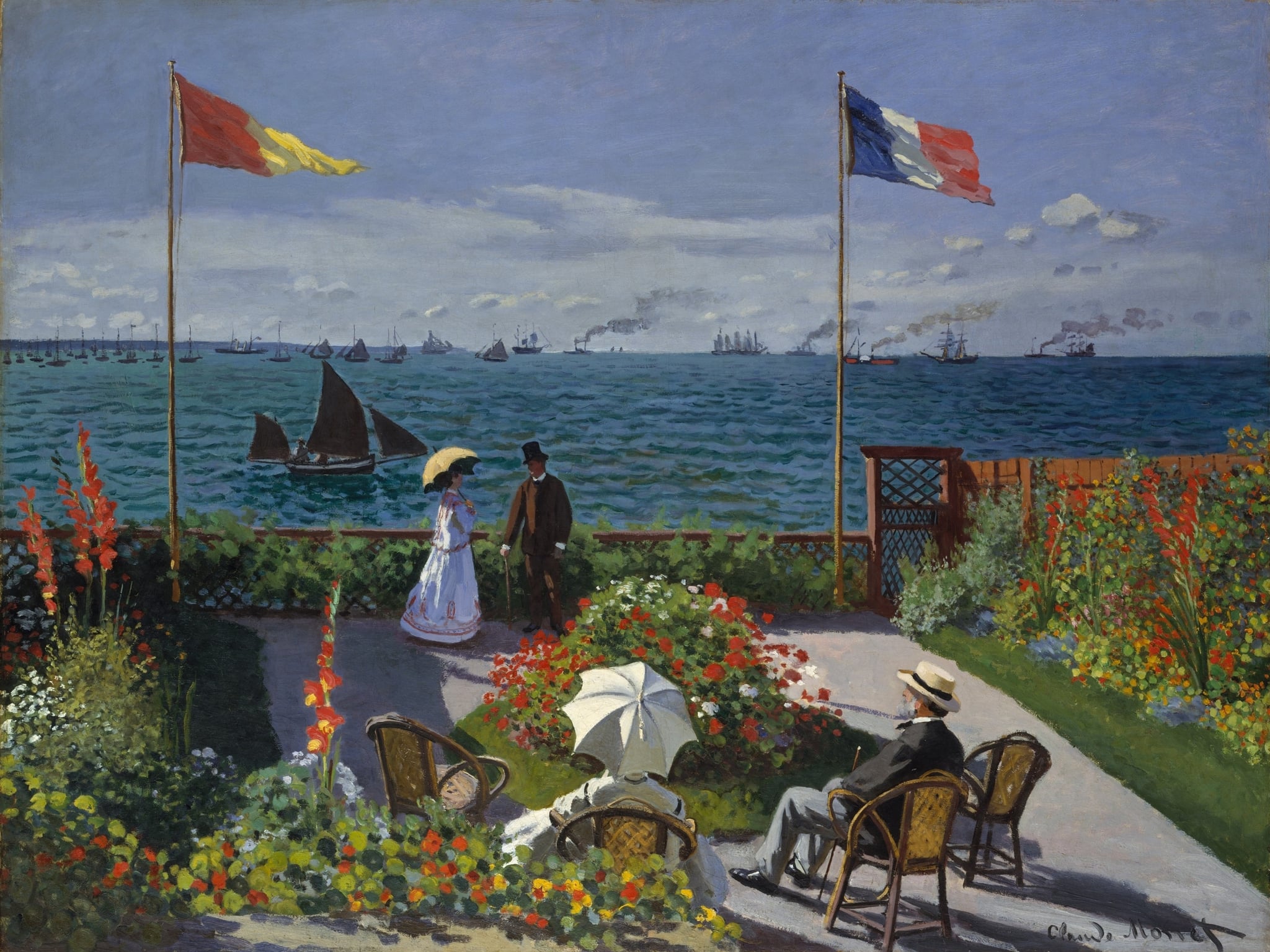

The Terrace at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
Claude Monet’s The Terrace at Sainte-Adresse stages a sunlit garden against the Channel, where <strong>bourgeois leisure</strong> unfolds between two wind-whipped flags and a horizon shared by <strong>sail and steam</strong>. Bright flowers, wicker chairs, and a white parasol form an ordered foreground, while the busy harbor and snapping tricolor project a confident, modern nation. The banded design—garden, sea, sky—reveals Monet’s early <strong>Japonisme</strong> and his drive to fuse fleeting light with a consciously structured composition <sup>[1]</sup>.
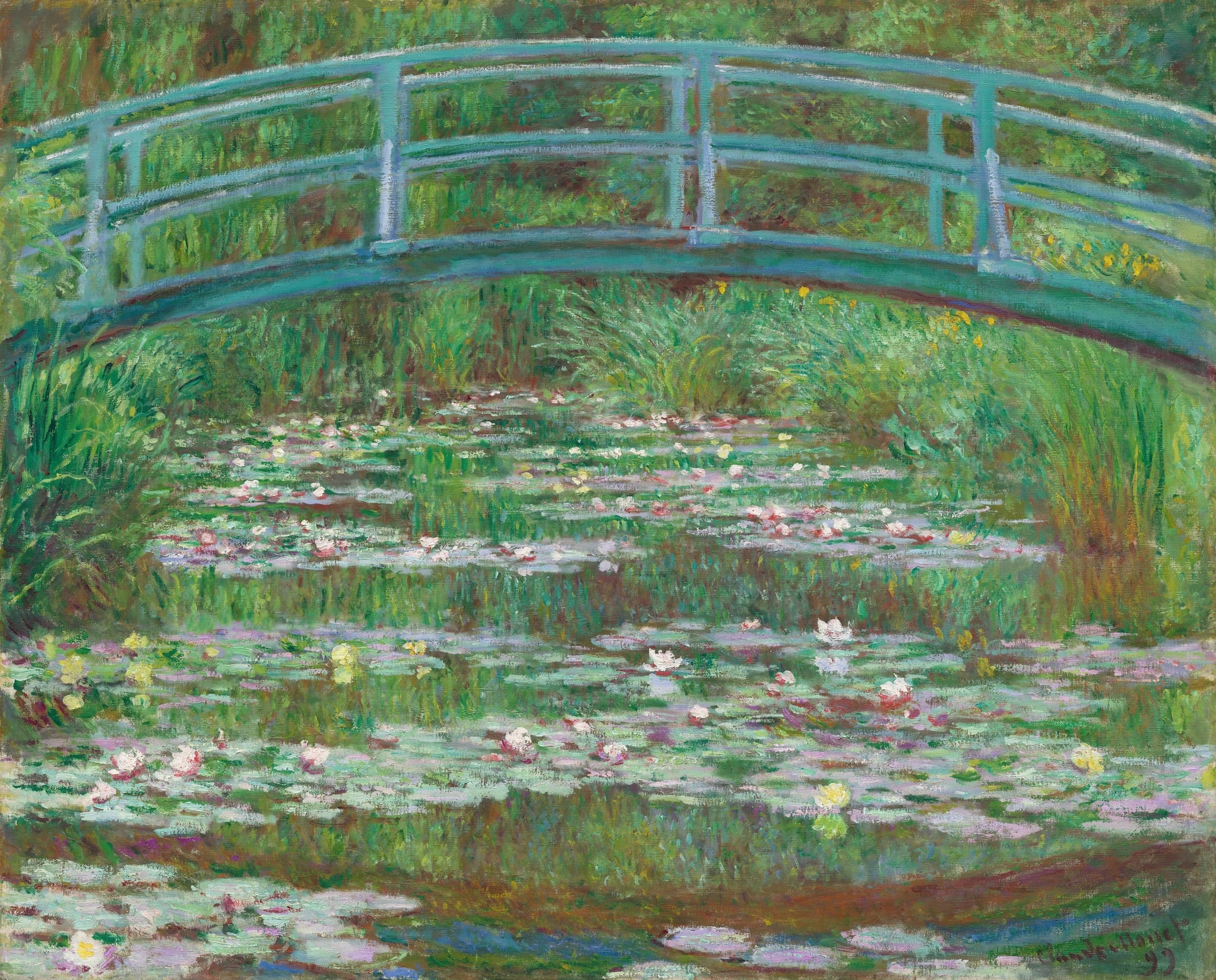

The Japanese Bridge
Claude Monet (1899)
Claude Monet’s The Japanese Bridge centers a pale <strong>blue‑green arch</strong> above a horizonless pond, where water‑lily pads and blossoms punctuate a field of shifting reflections. The bridge reads as both structure and <strong>contemplative threshold</strong>, suspending the eye between surface shimmer and mirrored depths <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
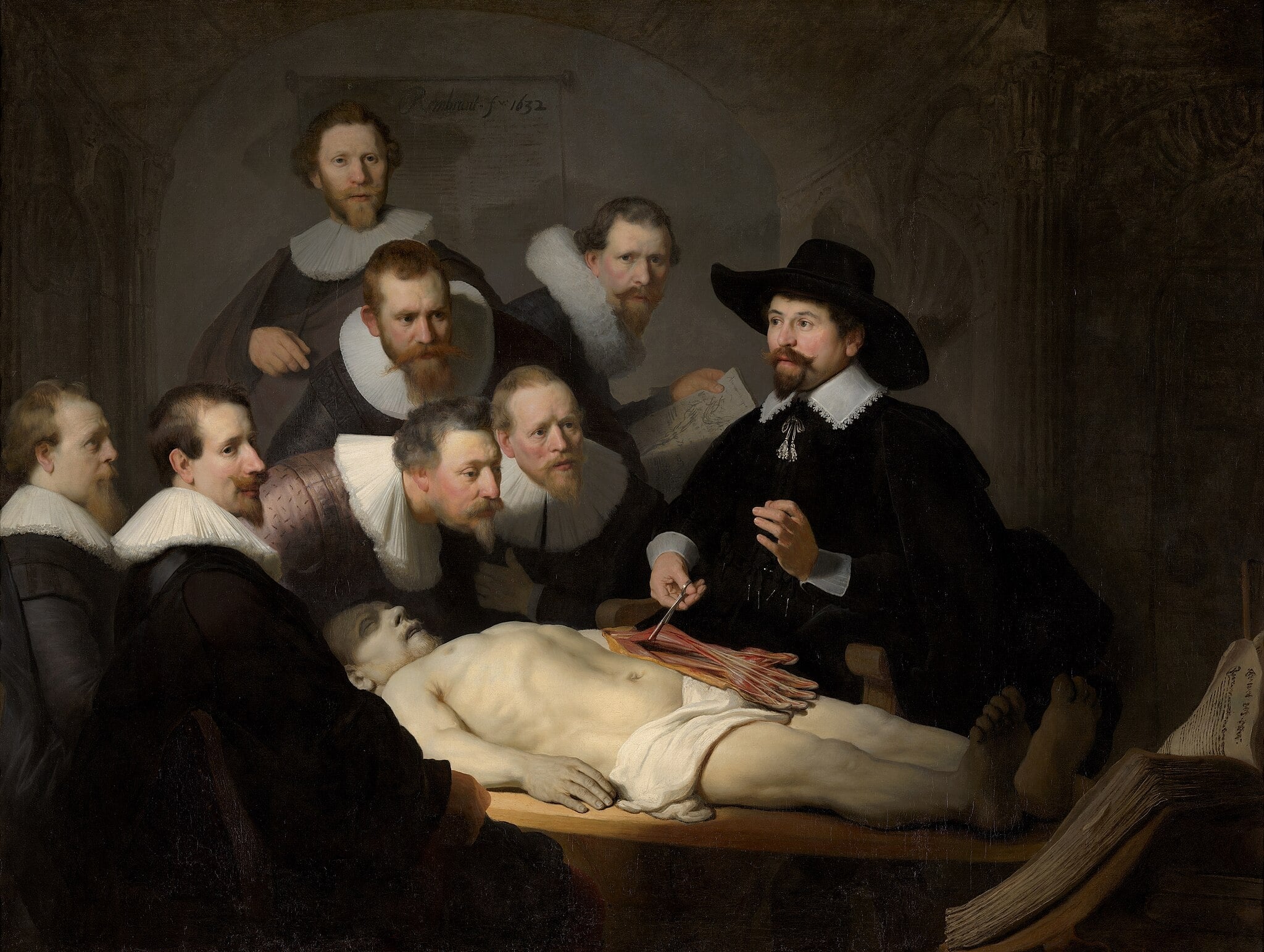

The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp
Rembrandt van Rijn (1632)
Rembrandt van Rijn turns a civic commission into a drama of <strong>knowledge made visible</strong>. A cone of light binds the ruff‑collared surgeons, the pale cadaver, and Dr. Tulp’s forceps as he raises the <strong>forearm tendons</strong> to explain the hand. Book and body face each other across the table, staging the tension—and alliance—between <strong>textual authority</strong> and <strong>empirical observation</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
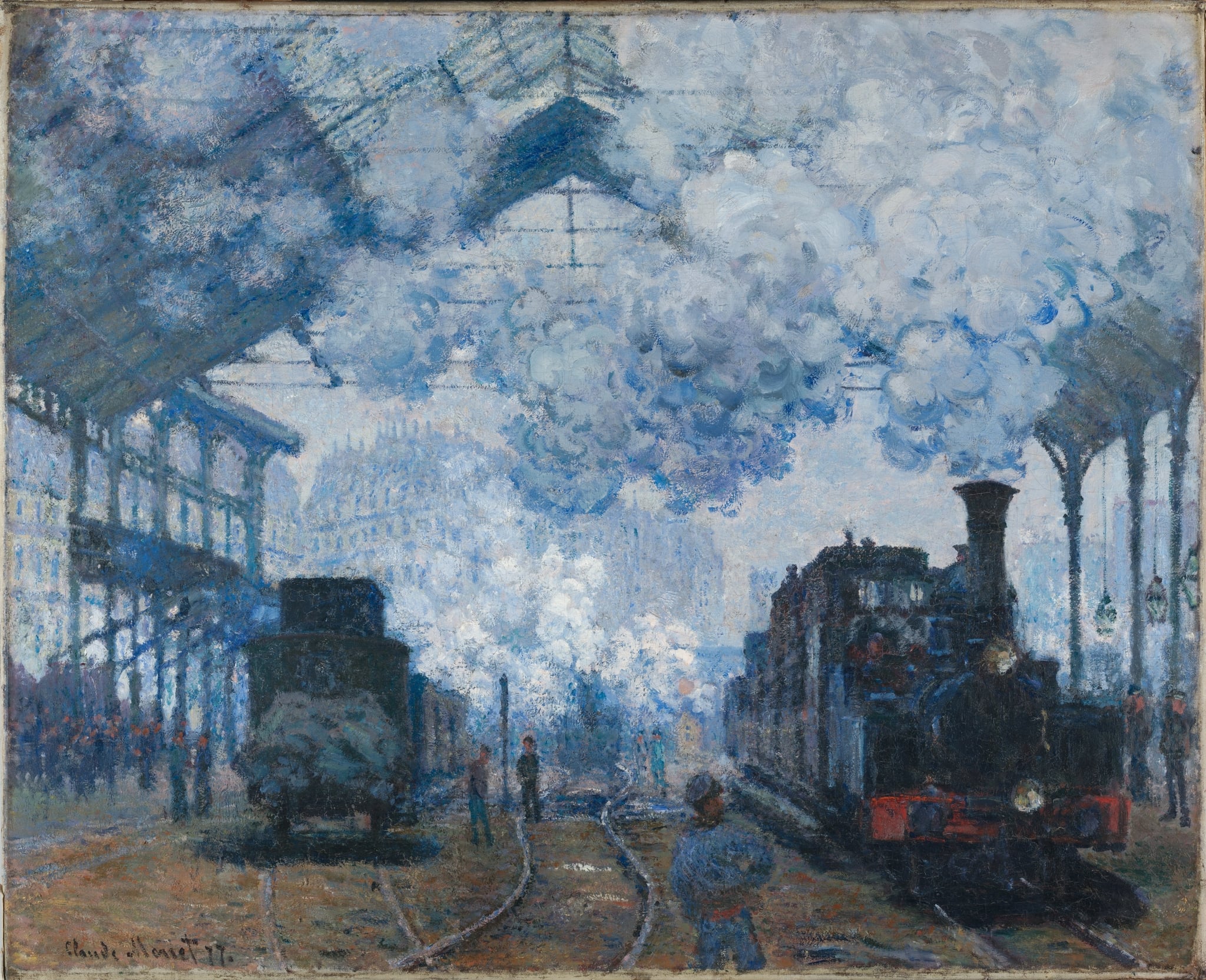

The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train
Claude Monet (1877)
Claude Monet’s The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train plunges viewers into a <strong>vapor-filled nave of iron and glass</strong>, where billowing steam, hot lamps, and converging rails forge a drama of industrial modernity. The right-hand locomotive, its red buffer beam glowing, materializes out of a <strong>blue-gray atmospheric envelope</strong>, turning motion and time into visible substance <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Haystack, Sunset
Claude Monet (1891)
Two conical stacks blaze against a cooling horizon, turning stored grain into a drama of <strong>light, time, and rural wealth</strong>. Monet’s broken strokes fuse warm oranges and cool violets so the stacks seem to glow from within, embodying the <strong>transience</strong> of a single sunset and the <strong>endurance</strong> of agrarian cycles <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
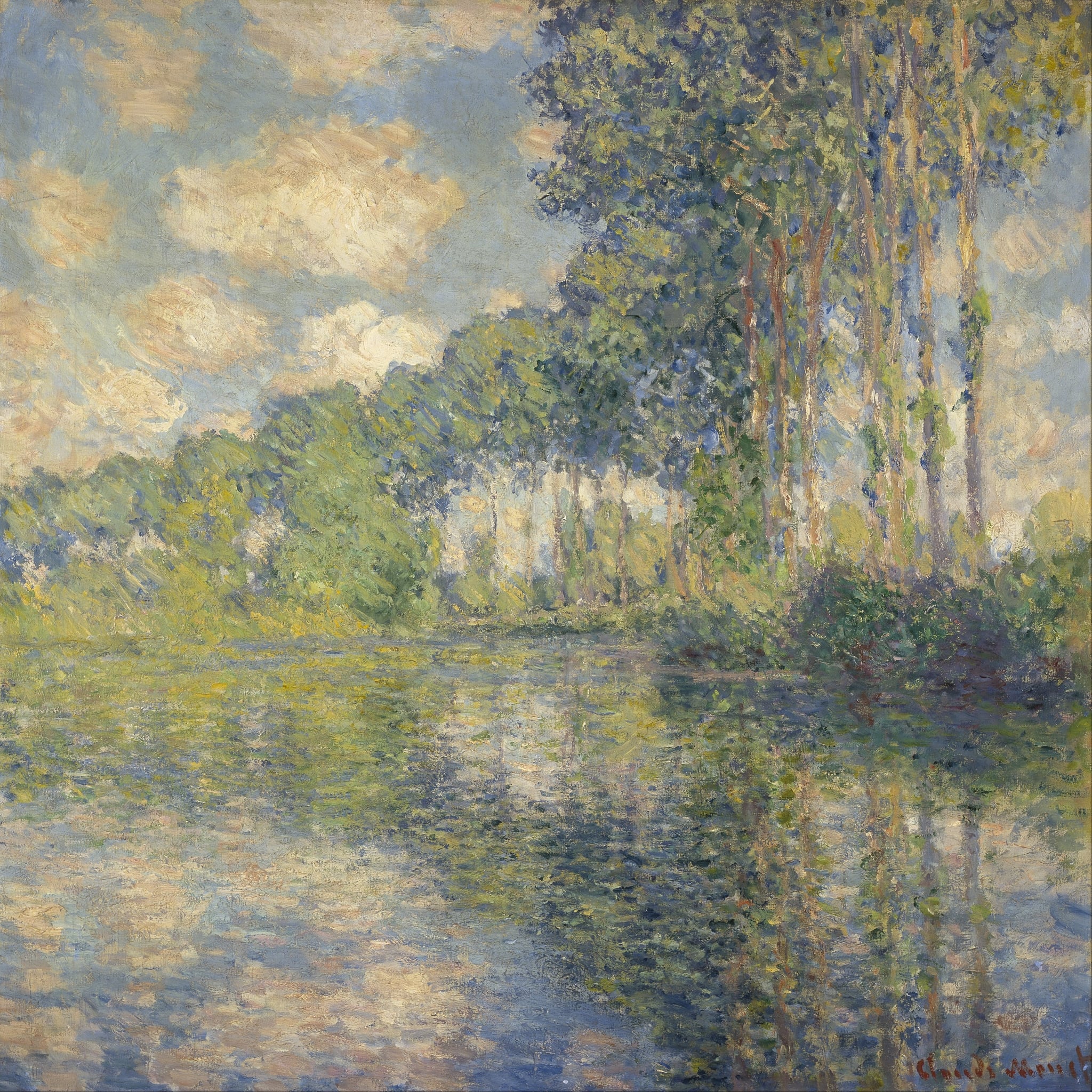

Poplars on the Epte
Claude Monet (1891)
Claude Monet’s Poplars on the Epte turns a modest river bend into a meditation on <strong>time, light, and perception</strong>. Upright trunks register as steady <strong>vertical chords</strong>, while their broken, shimmering reflections loosen form into <strong>pure sensation</strong>. The image stages a tension between <strong>order and flux</strong> that anchors the series within Impressionism’s core aims <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
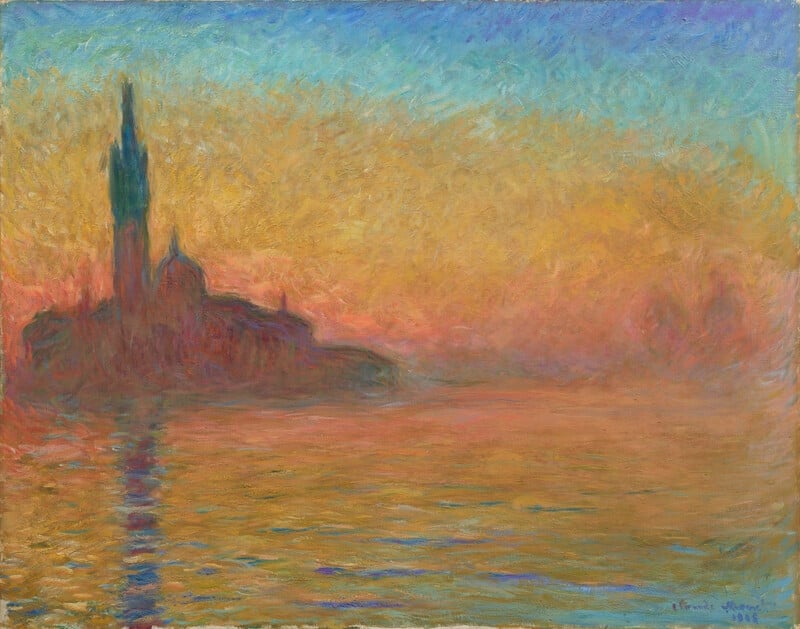
San Giorgio Maggiore by Twilight
Claude Monet (1908)
Claude Monet’s San Giorgio Maggiore by Twilight turns Venice into a <strong>luminous threshold</strong> where stone, air, and water merge. The dark, melting silhouette of the church and its vertical reflection anchor a field of <strong>apricot–rose–violet</strong> light that drifts into cool turquoise, making permanence feel provisional <sup>[1]</sup>. Monet’s subject is not the monument, but the <strong>enveloppe</strong> of atmosphere that momentarily creates it <sup>[4]</sup>.

Boulevard des Capucines
Claude Monet (1873–1874)
From a high perch above Paris, Claude Monet turns the Haussmann boulevard into a living current of <strong>light, weather, and motion</strong>. Leafless trees web the view, crowds dissolve into <strong>flickering strokes</strong>, and a sudden <strong>pink cluster of balloons</strong> pierces the cool winter scale <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Theater Box
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s The Theater Box turns a plush loge into a stage where seeing becomes the performance. A luminous woman—pearls, pale gloves, black‑and‑white stripes—faces us, while her companion scans the auditorium through opera glasses. The painting crystallizes Parisian <strong>modernity</strong> and the choreography of the <strong>gaze</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The Piazza San Marco, Venice
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1881)
Renoir’s The Piazza San Marco, Venice redefines St. Mark’s Basilica as <strong>atmosphere</strong> rather than architecture, fusing domes, mosaics, and crowd into vibrating color. Blue‑violet shadows sweep the square while pigeons and passersby resolve into <strong>daubs of light</strong>, declaring modern vision as the true subject <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Seated Bather
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Renoir’s Seated Bather stages a quiet pause between bathing and reverie, fusing the model’s pearly flesh with the flicker of stream and stone. The white drapery pooled around her hips and the soft, frontal gaze convert a simple toilette into a <strong>modern Arcadia</strong> where body and landscape dissolve into light. In this late-Impressionist idiom, Renoir refines the nude as a <strong>timeless ideal</strong> felt through color and touch <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
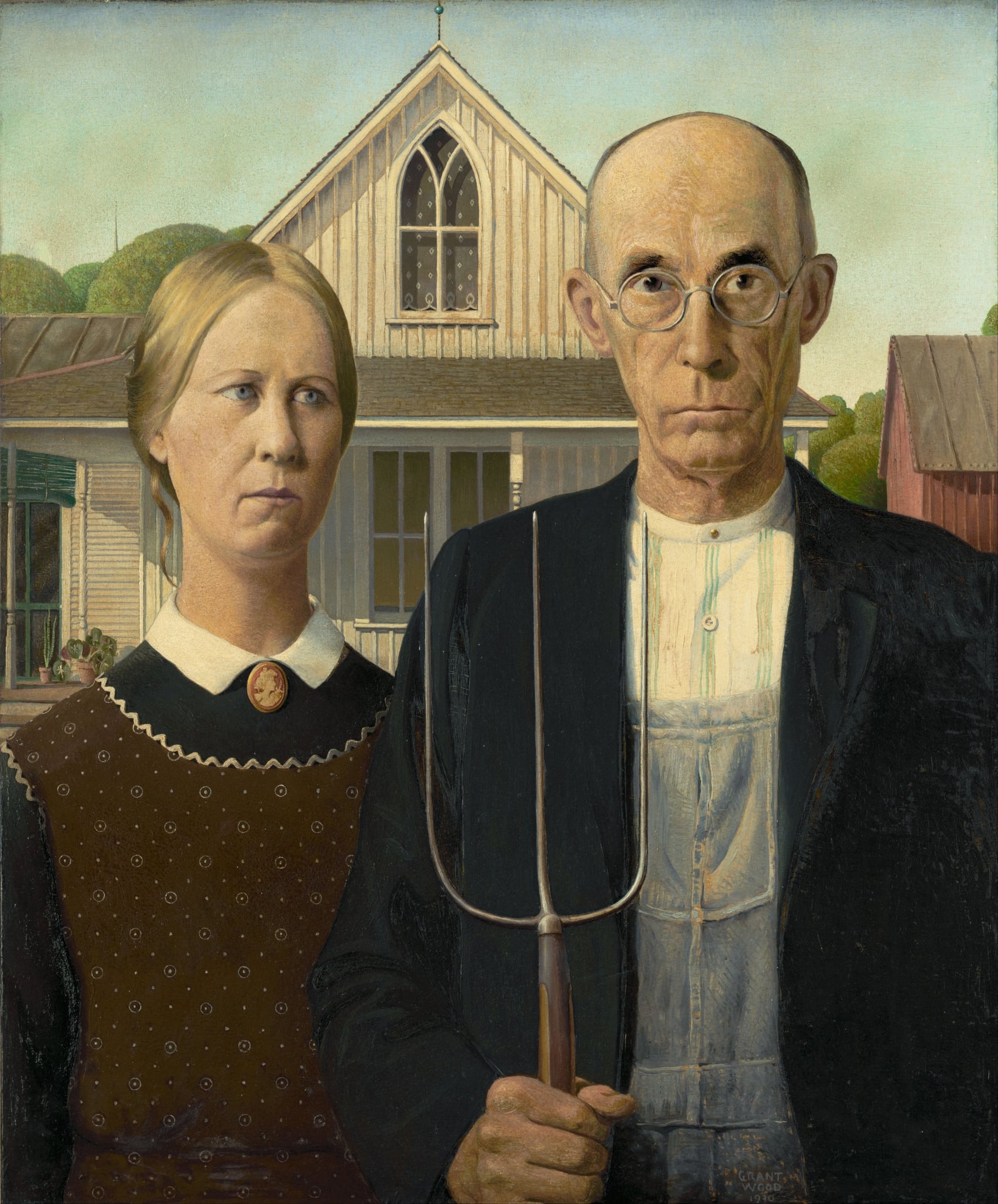

American Gothic
Grant Wood (1930)
Grant Wood’s American Gothic (1930) turns a plain Midwestern homestead into a <strong>moral emblem</strong> by binding two flinty figures to the strict geometry of a Carpenter Gothic gable and a three‑tined pitchfork. The painting’s cool precision and echoing verticals create a <strong>compressed ethic of work, order, and restraint</strong> that can read as both tribute and critique <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Creation of Adam
Michelangelo (c.1511–1512)
Michelangelo’s The Creation of Adam crystallizes the instant before life is conferred, staging a charged interval between two nearly touching hands. The fresco turns Genesis into a study of <strong>imago Dei</strong>, bodily perfection, and the threshold between inert earth and <strong>active spirit</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Still Life with Flowers
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1885)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir’s Still Life with Flowers (1885) sets a jubilant bouquet in a pale, crackled vase against softly dissolving wallpaper and a wicker screen. With quick, clear strokes and a centered, oval mass, the painting unites <strong>Impressionist color</strong> with a <strong>classical, post-Italy structure</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. The slight droop of blossoms turns the domestic scene into a gentle <strong>vanitas</strong>—a savoring of beauty before it fades <sup>[5]</sup>.
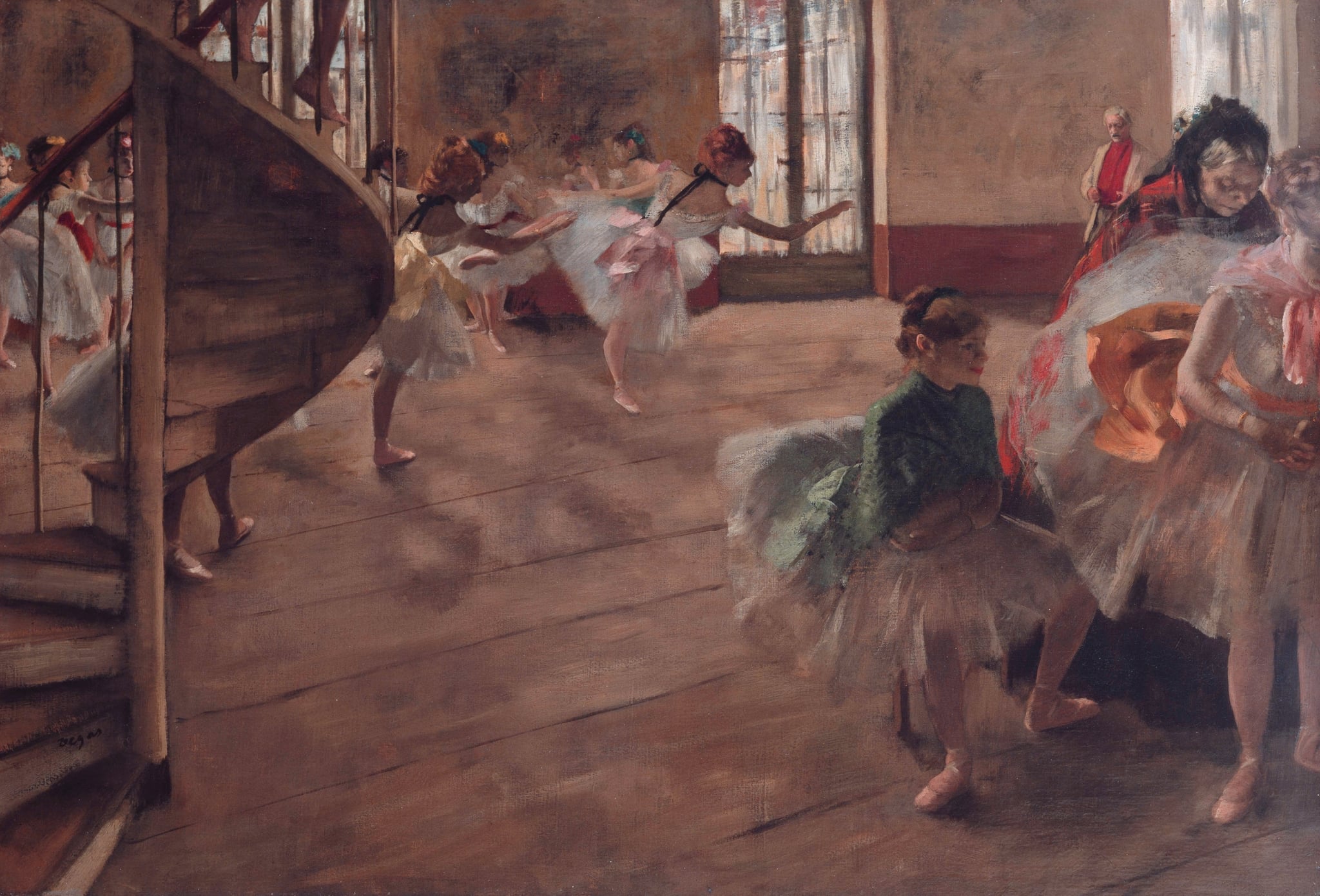

The Ballet Rehearsal
Edgar Degas (c. 1874)
In The Ballet Rehearsal, Edgar Degas turns a practice room into a modern drama where <strong>discipline and desire</strong> collide. A dark <strong>spiral staircase</strong> slices the space, scuffed floorboards yawn open, and clusters of dancers oscillate between poised effort and weary waiting <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.
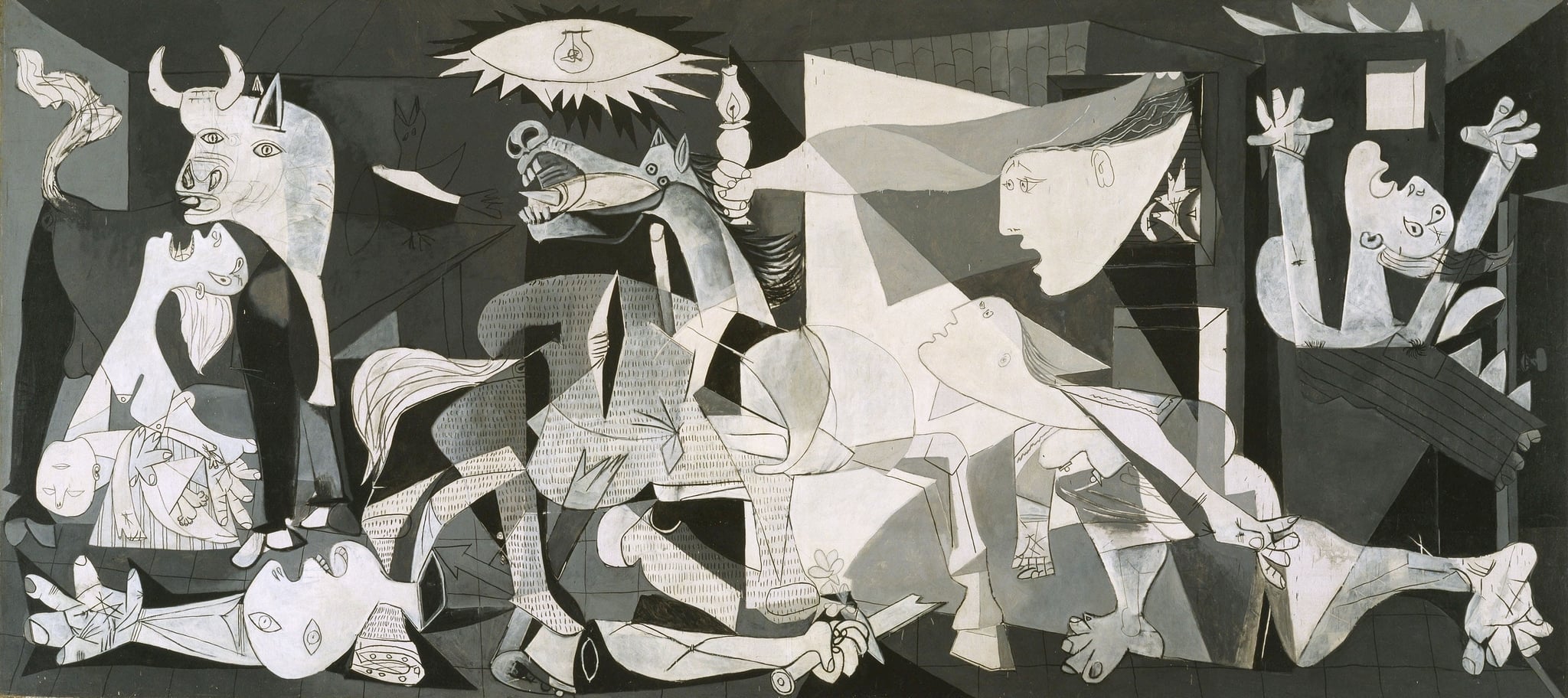

Guernica
Pablo Picasso (1937)
Guernica is a monumental, monochrome indictment of modern war, compressing a town’s annihilation into a frantic tangle of bodies, beasts, and light. Across the canvas, a <strong>shrieking horse</strong>, a <strong>stoic bull</strong>, a <strong>weeping mother with her dead child</strong>, and a <strong>fallen soldier</strong> stage a civic tragedy rather than a heroic battle. The harsh <strong>electric bulb</strong> clashes with a fragile <strong>oil lamp</strong>, turning the scene into a stark drama of terror and witness.
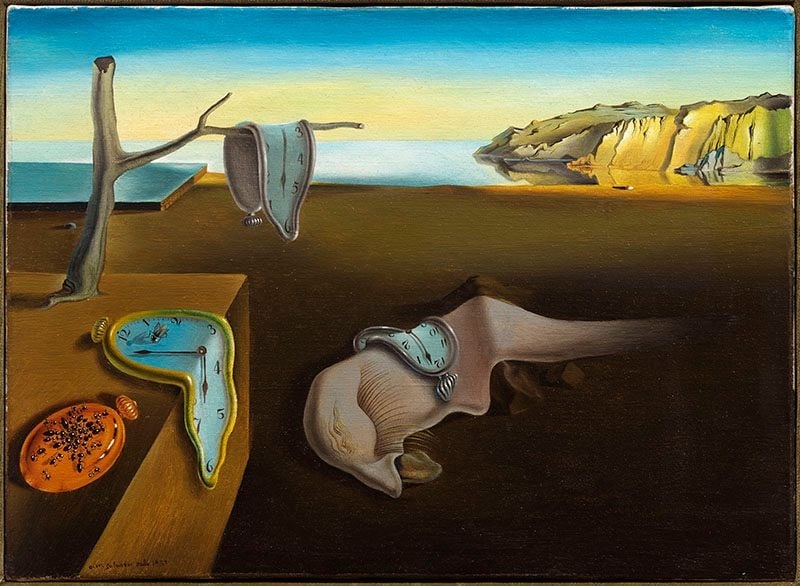

The Persistence of Memory
Salvador Dali (1931)
Salvador Dali’s The Persistence of Memory turns clock time into <strong>soft, malleable matter</strong>, staging a dream in which chronology buckles and the self dissolves. Four pocket watches droop across a barren platform, a dead branch, and a lash‑eyed biomorph, while ants overrun a hard, closed watch—a sign of <strong>decay</strong> and the futility of mechanical order <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Birth of Venus
Sandro Botticelli (c. 1484–1486)
In The Birth of Venus, <strong>Sandro Botticelli</strong> stages the sea-born goddess arriving on a <strong>scallop shell</strong>, blown ashore by intertwined <strong>winds</strong> and greeted by a flower-garlanded attendant who lifts a <strong>rose-patterned mantle</strong>. The painting’s crisp contours, elongated figures, and gilded highlights transform myth into an <strong>ideal of beauty</strong> that signals love, spring, and renewal <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Las Meninas
Diego Velazquez (1656)
In Las Meninas, a luminous Infanta anchors a shadowed studio where the painter pauses at a vast easel and a small wall mirror reflects the monarchs. The scene folds artist, sitters, and viewer into one reflexive tableau, turning court protocol into a meditation on <strong>seeing and being seen</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. A bright doorway at the rear deepens space and time, as if someone has just entered—or is leaving—the picture we occupy <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The School of Athens
Raphael (1509–1511)
Raphael’s The School of Athens orchestrates a grand debate on knowledge inside a perfectly ordered, classical hall whose one-point perspective converges on the central pair, <strong>Plato</strong> and <strong>Aristotle</strong>. Their opposed gestures—one toward the heavens, one level to the earth—establish the fresco’s governing dialectic between <strong>ideal forms</strong> and <strong>empirical reason</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. Around them, mathematicians, scientists, and poets cluster under statues of <strong>Apollo</strong> and <strong>Athena/Minerva</strong>, turning the room into a temple of <strong>Renaissance humanism</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Nighthawks
Edward Hopper (1942)
Edward Hopper’s Nighthawks turns a corner diner into a sealed stage where <strong>fluorescent light</strong> and <strong>curved glass</strong> hold four figures in suspended time. The empty streets and the “PHILLIES” cigar sign sharpen the sense of <strong>urban solitude</strong> while hinting at wartime vigilance. The result is a cool, lucid image of modern life: illuminated, open to view, and emotionally out of reach.

The Garden of Earthly Delights
Hieronymus Bosch (c.1490–1500)
The Garden of Earthly Delights unfolds a three‑act moral narrative—<strong>innocence</strong>, <strong>seduction</strong>, and <strong>retribution</strong>—from Eden to a punitive <strong>Musical Hell</strong>. Bosch binds the scenes through recurring emblems (notably the <strong>owl</strong>) and by echoing Eden’s crystalline fountain in the center’s fragile, candy‑colored architectures, then in Hell’s broken bodies and instruments. The work dazzles with invention while insisting that <strong>sweet, ephemeral pleasures</strong> end in ruin <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Arnolfini Portrait
Jan van Eyck (1434)
In The Arnolfini Portrait, Jan van Eyck stages a poised encounter between a richly dressed couple whose joined hands, a single burning candle, and a convex mirror transform a domestic interior into a scene of <strong>status and sanctity</strong>. The painting asserts the artist’s own <strong>presence</strong>—"Johannes de eyck fuit hic 1434"—as if to validate the moment while showcasing oil painting’s power to make belief tangible through light, texture, and reflection <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Whistler's Mother
James Abbott McNeill Whistler (1871)
Whistler's Mother is an <strong>austere orchestration of tone and geometry</strong> that turns a private sitting into a public monument. The strict profile, black dress, and white lace are set against flat greys, a patterned curtain, and a framed Thames print to create <strong>measured balance and silence</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Hay Wain
John Constable (1821)
Set beside Willy Lott’s cottage on the River Stour, The Hay Wain stages a moment of <strong>unhurried rural labor</strong>: an empty timber cart, drawn by three horses with red-collared tack, pauses mid‑ford as weather shifts above. Constable fuses <strong>empirical observation</strong>—rippling reflections, chimney smoke, flickers of white on leaves—with a composed vista of fields opening to sun. The result is a serene yet alert meditation on <strong>work, weather, and continuity</strong> in the English countryside <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Wanderer above the Sea of Fog
Caspar David Friedrich (ca. 1817)
Caspar David Friedrich’s The Wanderer above the Sea of Fog distills the Romantic encounter with nature into a single <strong>Rückenfigur</strong> poised on jagged rock above a rolling <strong>sea of mist</strong>. The cool, receding vista and the figure’s still stance convert landscape into an <strong>inner drama of contemplation</strong> and the <strong>sublime</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

This is Not a Pipe
Rene Magritte (1929)
A crisply modeled tobacco pipe hovers over a blank beige field, while the cursive line "Ceci n’est pas une pipe" coolly denies what the eye assumes. The clash between image and sentence turns a familiar object into a <strong>thought experiment</strong> about signs and things. Magritte’s deadpan exactitude and ad‑like layout stage a <strong>philosophical trap</strong>: you can see a pipe, but you cannot smoke this picture. <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>

Swans Reflecting Elephants
Salvador Dali (1937)
Swans Reflecting Elephants stages a calm Catalan lagoon where three swans and a thicket of bare trees flip into monumental <strong>elephants</strong> in the mirror of water. Salvador Dali crystallizes his <strong>paranoiac-critical</strong> method: a meticulously painted illusion that makes perception generate its own doubles <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. The work locks grace to gravity, surface to depth, turning the lake into a theater of <strong>metamorphosis</strong>.

The Sleeping Gypsy
Henri Rousseau (1897)
Under a cold moon, a traveler sleeps in a striped robe as a lion pauses to sniff, not strike—an image of <strong>danger held in suspension</strong> and <strong>imagination as protection</strong>. Rousseau’s polished surfaces, flattened distance, and toy-like clarity turn the desert into a <strong>dream stage</strong> where art (the mandolin) and life (the water jar) keep silent vigil <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Raft of the Medusa
Theodore Gericault (1818–1819)
The Raft of the Medusa stages a modern catastrophe as epic tragedy, pivoting from corpses to a surge of <strong>collective hope</strong>. The diagonal mast, torn sail, and a Black figure waving a cloth toward a tiny ship compress the moment when despair turns to <strong>precarious rescue</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

No. 5, 1948
Jackson Pollock (1948)
<strong>No. 5, 1948</strong> is a large, floor‑painted field of poured enamel where tangled skeins of black, gray, umber, and bursts of yellow span the entire support. Its <strong>all‑over</strong> structure rejects a central motif, turning the painting into a record of motion and material behavior. The result is a charged surface that reads as both <strong>image and event</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Jewish Bride
Rembrandt van Rijn (c. 1665–1669)
The Jewish Bride by Rembrandt van Rijn stages an intimate covenant: two figures, read today as <strong>Isaac and Rebecca</strong>, seal their union through touch rather than spectacle. Light concentrates on faces and hands, while the man’s glittering <strong>gold sleeve</strong> and the woman’s <strong>coral-red gown</strong> turn paint itself into a metaphor for fidelity and tenderness <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. This late masterpiece embodies Rembrandt’s <strong>material eloquence</strong>—impasto as feeling—within a hushed, dark setting <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Weeping Woman
Pablo Picasso (1937)
Picasso’s The Weeping Woman turns private mourning into a public, <strong>iconic emblem of civilian grief</strong>. Shattered planes, <strong>acidic greens and purples</strong>, and jewel-like tears force the viewer to feel the fracture of perception that follows trauma <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Lovers
Rene Magritte (1928)
René Magritte’s The Lovers turns a kiss into an emblem of <strong>desire obstructed</strong>: two figures—she in red, he in a dark suit—press together while their heads are swathed in <strong>white cloth</strong>. Within a cool blue‑grey interior bounded by crown molding and a rust-red wall, intimacy becomes an image of <strong>opacity</strong> rather than revelation <sup>[1]</sup>.
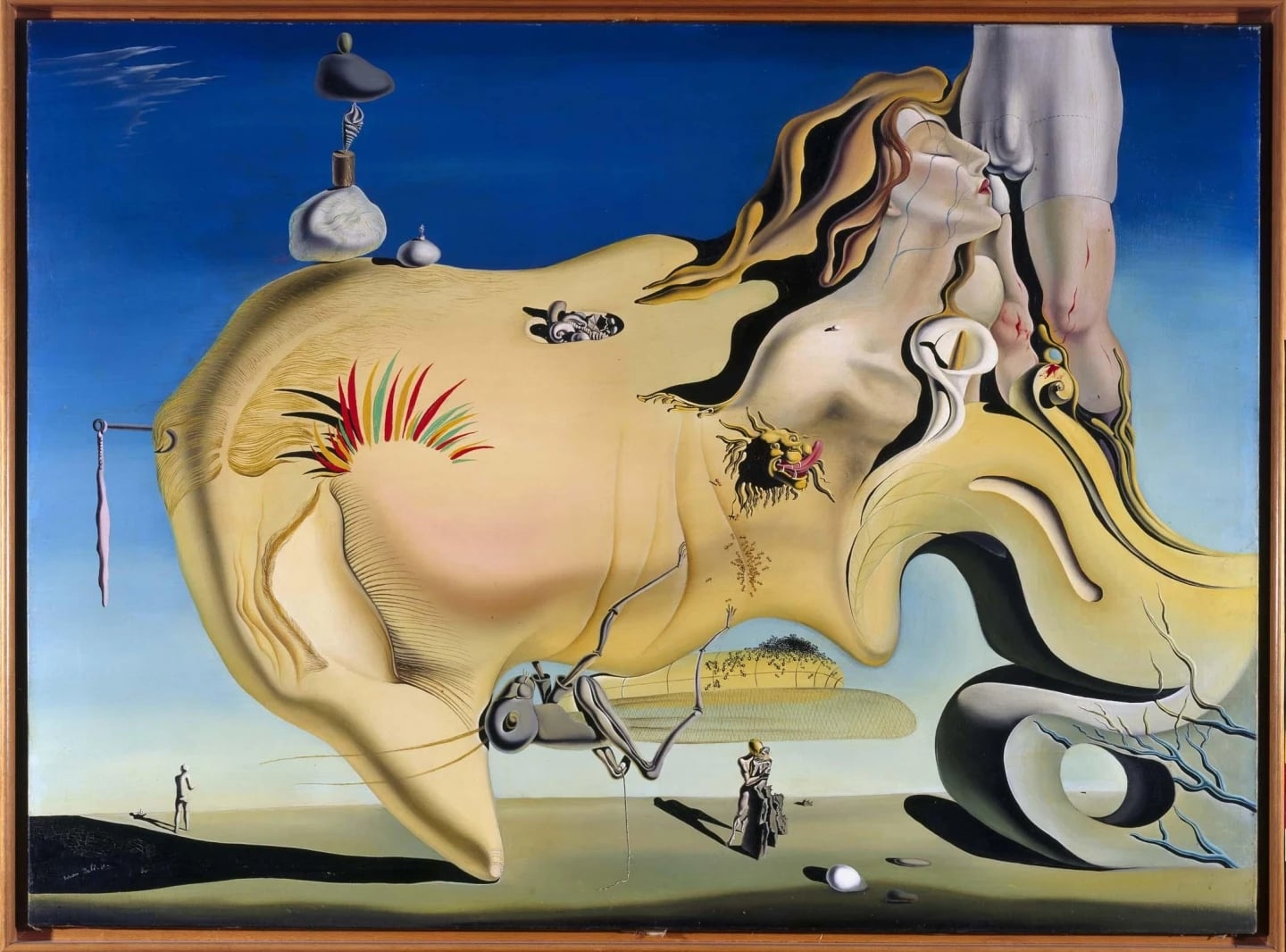

The Great Masturbator
Salvador Dali (1929)
The Great Masturbator condenses Dalí’s newly ignited desire and crippling dread into a single, biomorphic head set against a crystalline Catalan sky. Ants, a gaping grasshopper, a lion’s tongue, a bleeding knee, crutches, stones, and an egg collide to script a confession where <strong>eros</strong> and <strong>decay</strong> are inseparable <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. Its precision staging turns autobiography into a <strong>surreal map of compulsion</strong> at the moment Gala enters his life <sup>[1]</sup>.
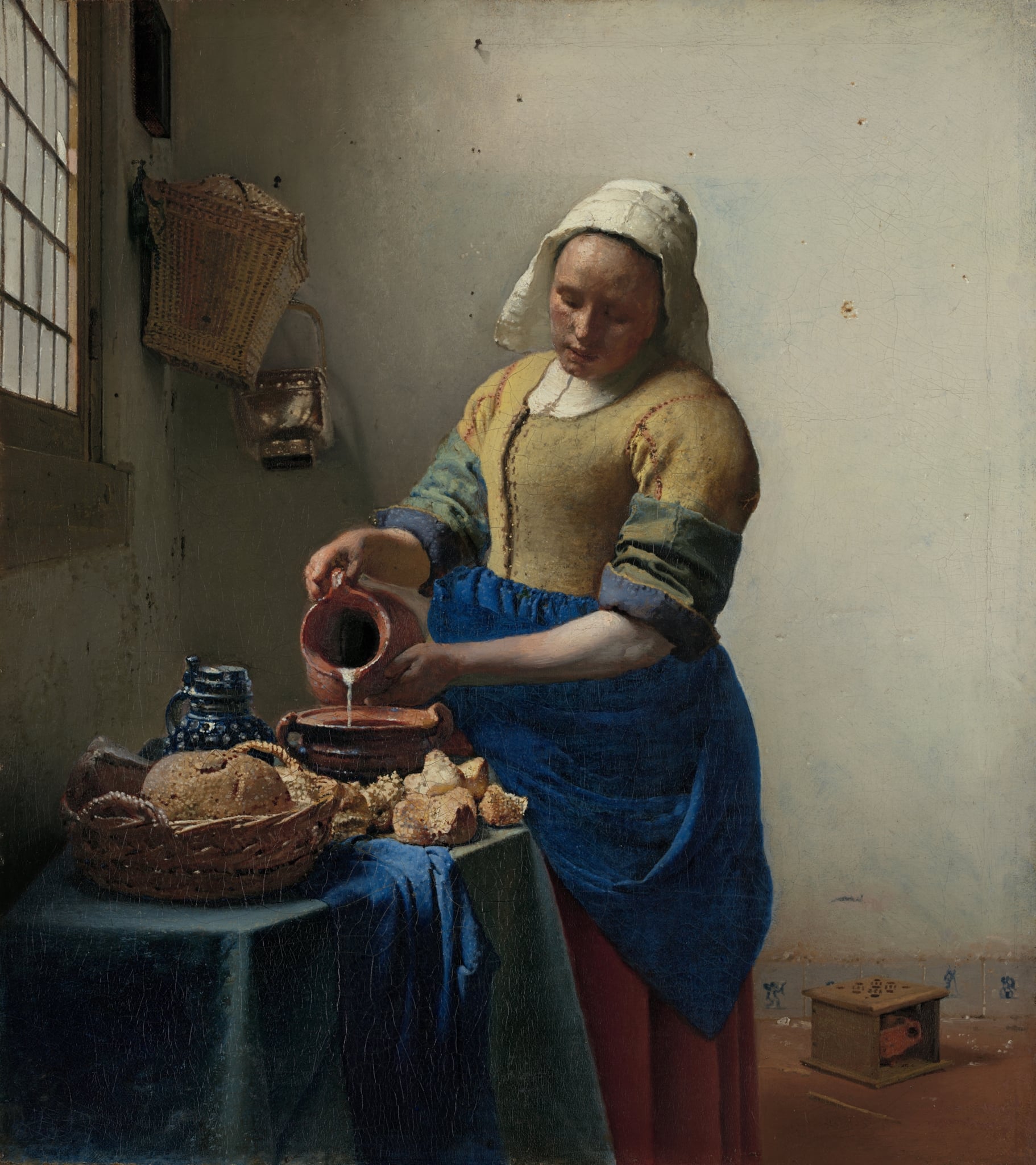

The Milkmaid
Johannes Vermeer (c. 1660)
In The Milkmaid, Vermeer turns an ordinary act—pouring milk—into a scene of <strong>quiet monumentality</strong>. Light from the left fixes the maid’s absorbed attention and ignites the <strong>saturated yellow and blue</strong> of her dress, while the slow thread of milk becomes the image’s pulse <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. Bread, a Delft jug, nail holes, and a small <strong>foot warmer</strong> anchor a world where humble work is endowed with dignity and latent meaning <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Manneporte near Étretat
Claude Monet (1886)
Monet’s The Manneporte near Étretat turns the colossal sea arch into a <strong>threshold of light</strong>: rock, sea, and air interlock as shifting color rather than fixed form. Dense lilac–ochre strokes make the cliff feel massive yet <strong>dematerialized</strong> by illumination, while the arch’s opening stages a quiet, glimmering horizon <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Les Demoiselles d'Avignon
Pablo Picasso (1907)
Les Demoiselles d'Avignon hurls five nudes toward the viewer in a shallow, splintered chamber, turning classical beauty into <strong>sharp planes</strong>, <strong>masklike faces</strong>, and <strong>fractured space</strong>. The fruit at the bottom reads as a sensual lure edged with threat, while the women’s direct gazes indict the beholder as participant. This is the shock point of <strong>proto‑Cubism</strong>, where Picasso reengineers how modern painting means and how looking works <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
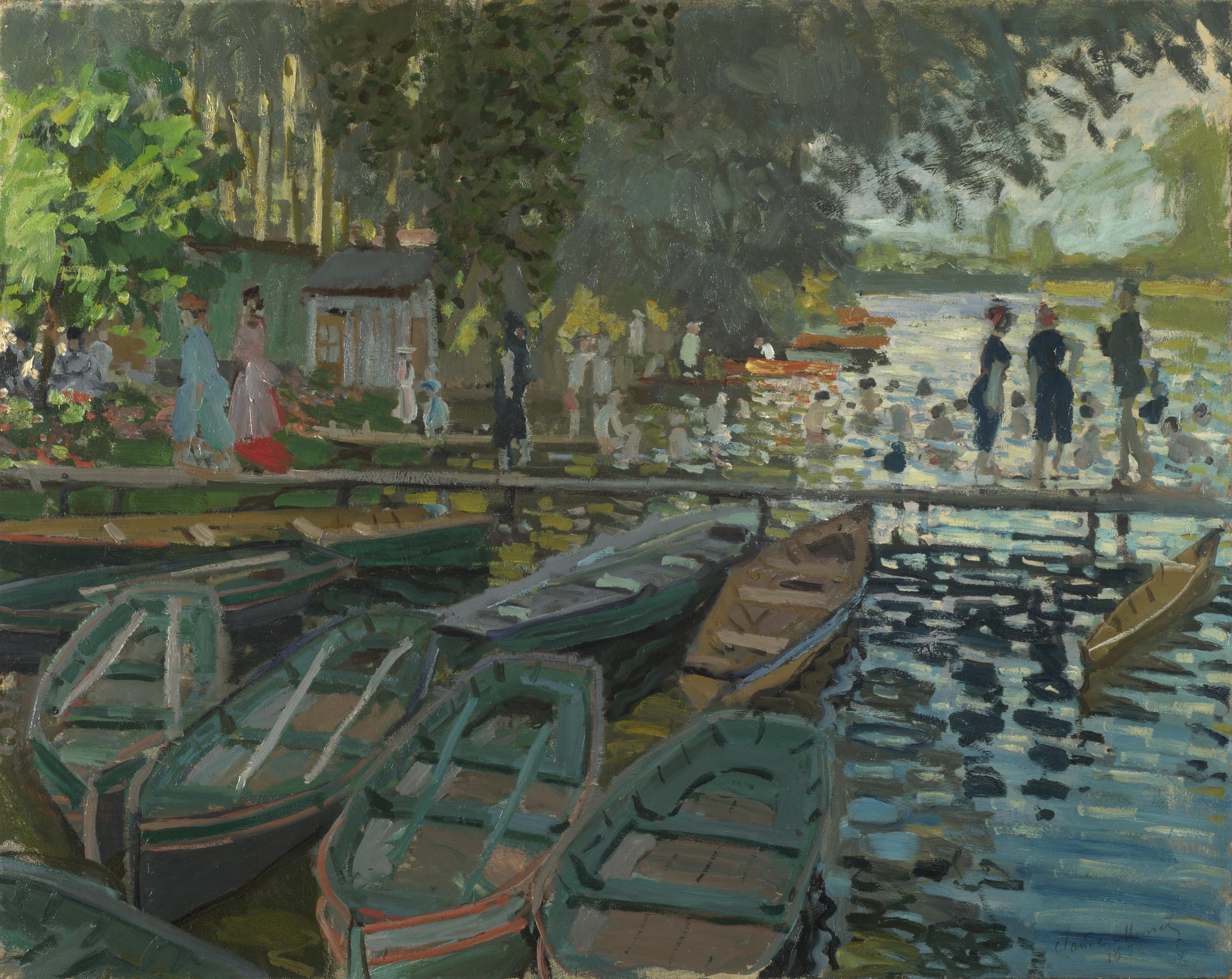

La Grenouillère
Claude Monet (1869)
Monet’s La Grenouillère crystallizes the new culture of <strong>modern leisure</strong> on the Seine: crowded bathers, promenading couples, and rental boats orbit a floating resort. With <strong>flickering brushwork</strong> and a high-key palette, Monet turns water, light, and movement into the true subjects, suspending the scene at the brink of dissolving.