The divine & the sacred
Featured Artworks

Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I
Gustav Klimt (1907)
Gustav Klimt’s Portrait of Adele Bloch-Bauer I stages its sitter as a <strong>secular icon</strong>—a living presence suspended in a field of gold that converts space into <strong>pattern and power</strong>. The naturalistic face and hands emerge from a reliquary-like cascade of eyes, triangles, and tesserae, turning light, ornament, and status into the painting’s true subjects <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
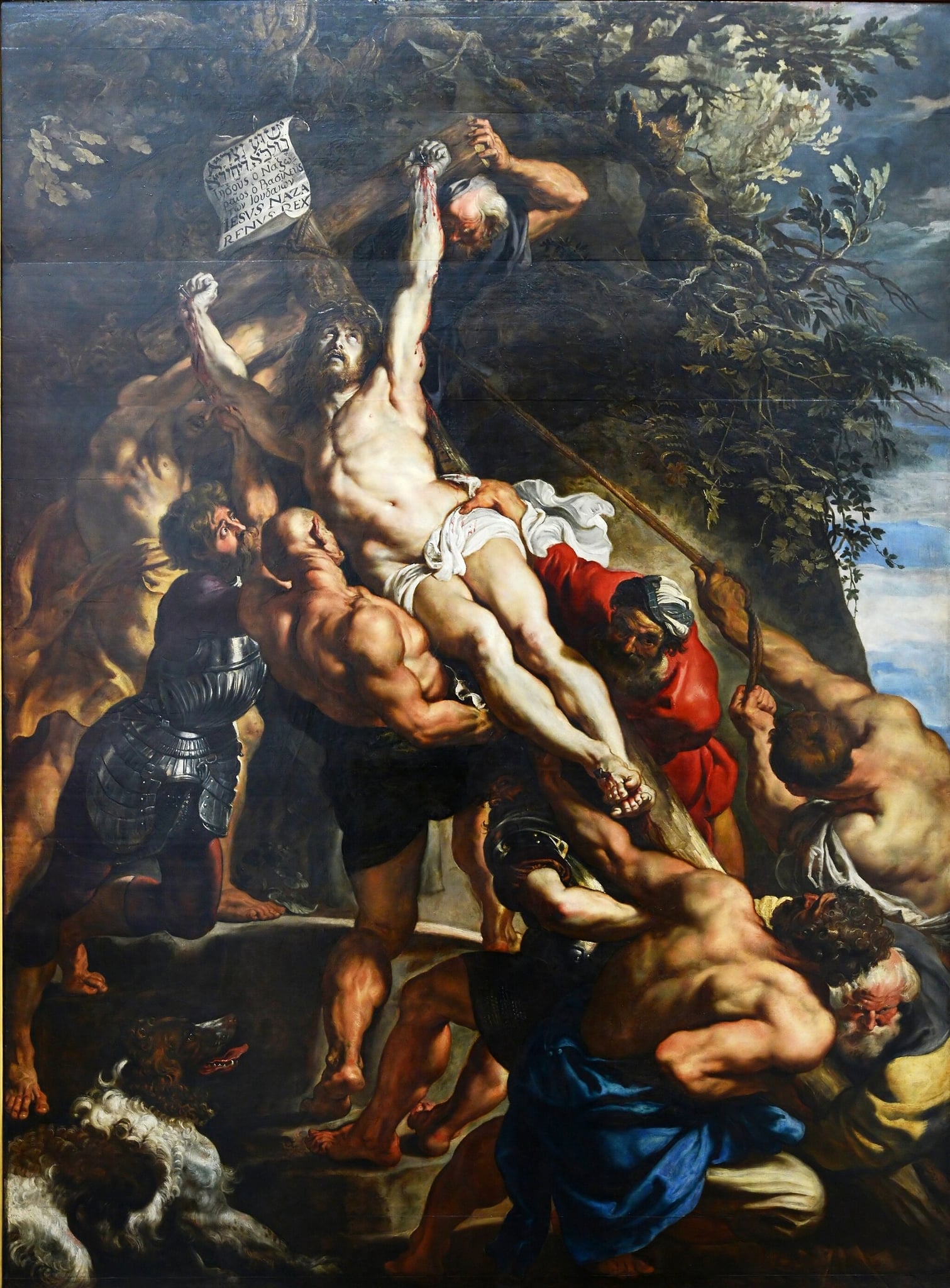

The Elevation of the Cross
Peter Paul Rubens (1609–1610)
A single, surging diagonal drives The Elevation of the Cross as straining executioners heave the timber while Christ’s pale body becomes the calm, radiant fulcrum. Rubens fuses muscular anatomy, flashing armor, taut ropes, and storm-dark landscape into a Baroque crescendo where <strong>divine light</strong> confronts <strong>human violence</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Assumption of the Virgin
Titian (1516–1518)
Titian’s The Assumption of the Virgin stages a three-tier ascent—apostles below, Mary rising on clouds, and God the Father above—fused by radiant light and Venetian <strong>colorito</strong>. Mary’s red and blue drapery, open <strong>orant</strong> hands, and the vortex of putti visualize grace lifting humanity toward the divine. The painting’s scale and kinetic design turned a doctrinal mystery into a public, liturgical drama for Venice. <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>
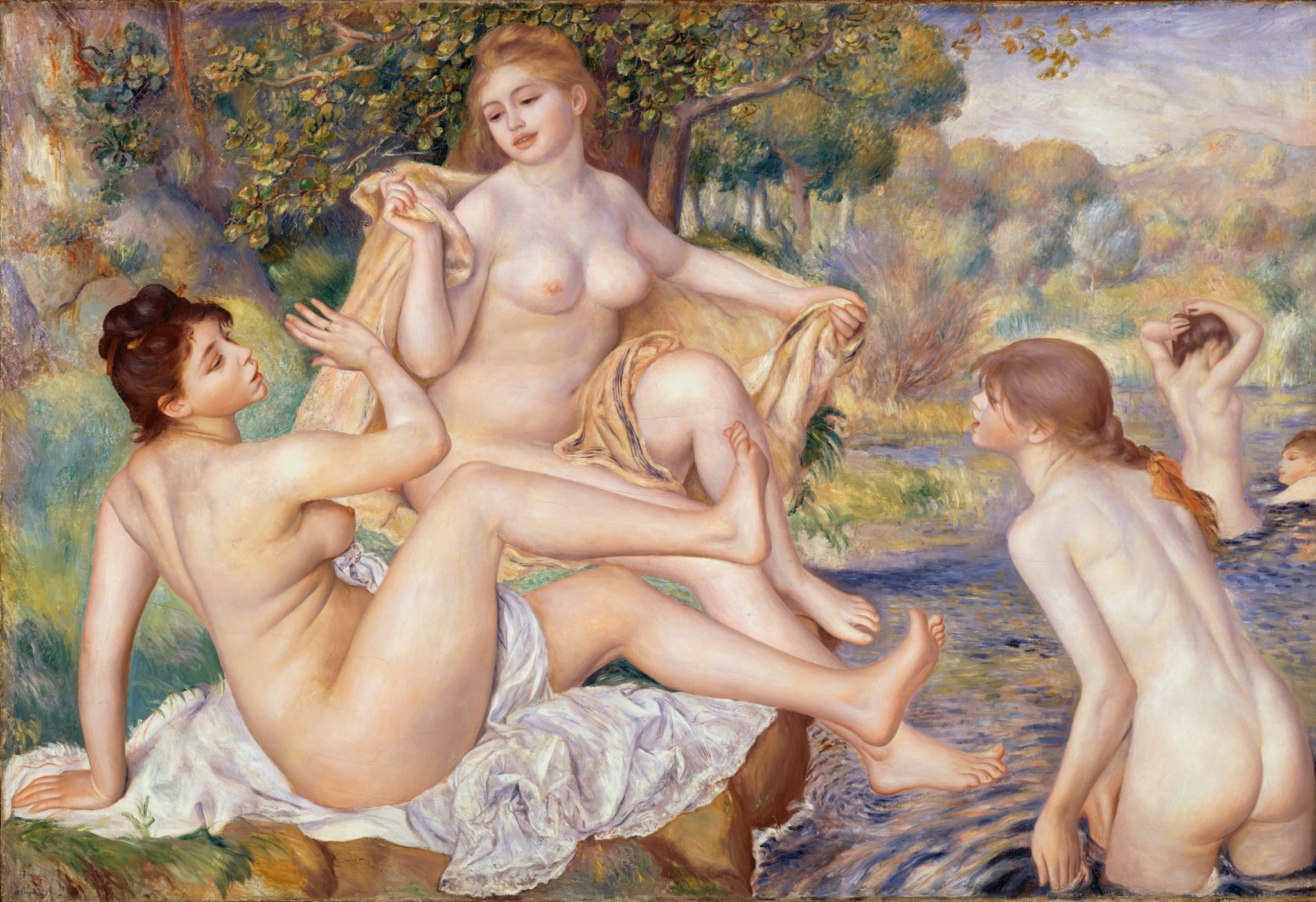

The Large Bathers
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1884–1887)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir’s The Large Bathers unites modern bodies with a pastoral grove to stage an <strong>Arcadian ideal</strong>. Three monumental nudes form interlocking curves and triangles while two background figures splash and groom, fusing <strong>sensual warmth</strong> with <strong>classical order</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Grand Canal
Claude Monet (1908)
Claude Monet’s The Grand Canal turns Venice into <strong>pure atmosphere</strong>: the domes of Santa Maria della Salute waver at right while a regiment of <strong>pali</strong> stands at left, their verticals reverberating in the water. The scene asserts <strong>light over architecture</strong>, transforming stone into memory and time into color <sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

San Giorgio Maggiore at Dusk
Claude Monet (1908–1912)
Claude Monet’s San Giorgio Maggiore at Dusk fuses the Benedictine church’s dark silhouette with a sky flaming from apricot to cobalt, turning architecture into atmosphere. The campanile’s vertical and its wavering reflection anchor a sea of trembling color, staging a meditation on <strong>permanence</strong> and <strong>flux</strong>.
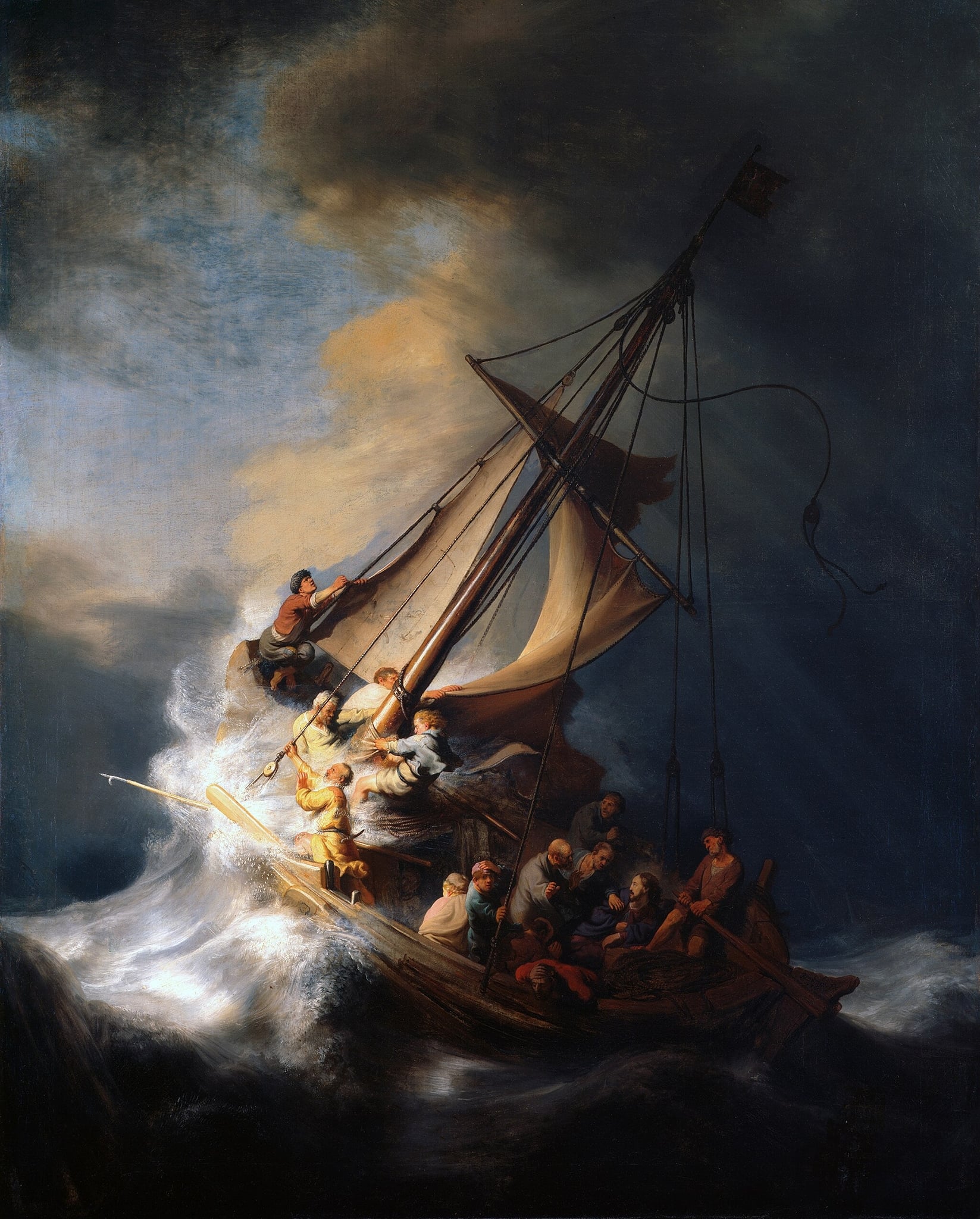

The Storm on the Sea of Galilee
Rembrandt van Rijn (1633)
Rembrandt van Rijn’s The Storm on the Sea of Galilee stages a clash of <strong>human panic</strong> and <strong>divine composure</strong> at the instant before the miracle. A torn mainsail whips across a steeply tilted boat as terrified disciples scramble, while a <strong>serenely lit Christ</strong> anchors a pocket of calm—an image of faith holding within chaos <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. It is Rembrandt’s only painted seascape, intensifying its dramatic singularity in his oeuvre <sup>[2]</sup>.
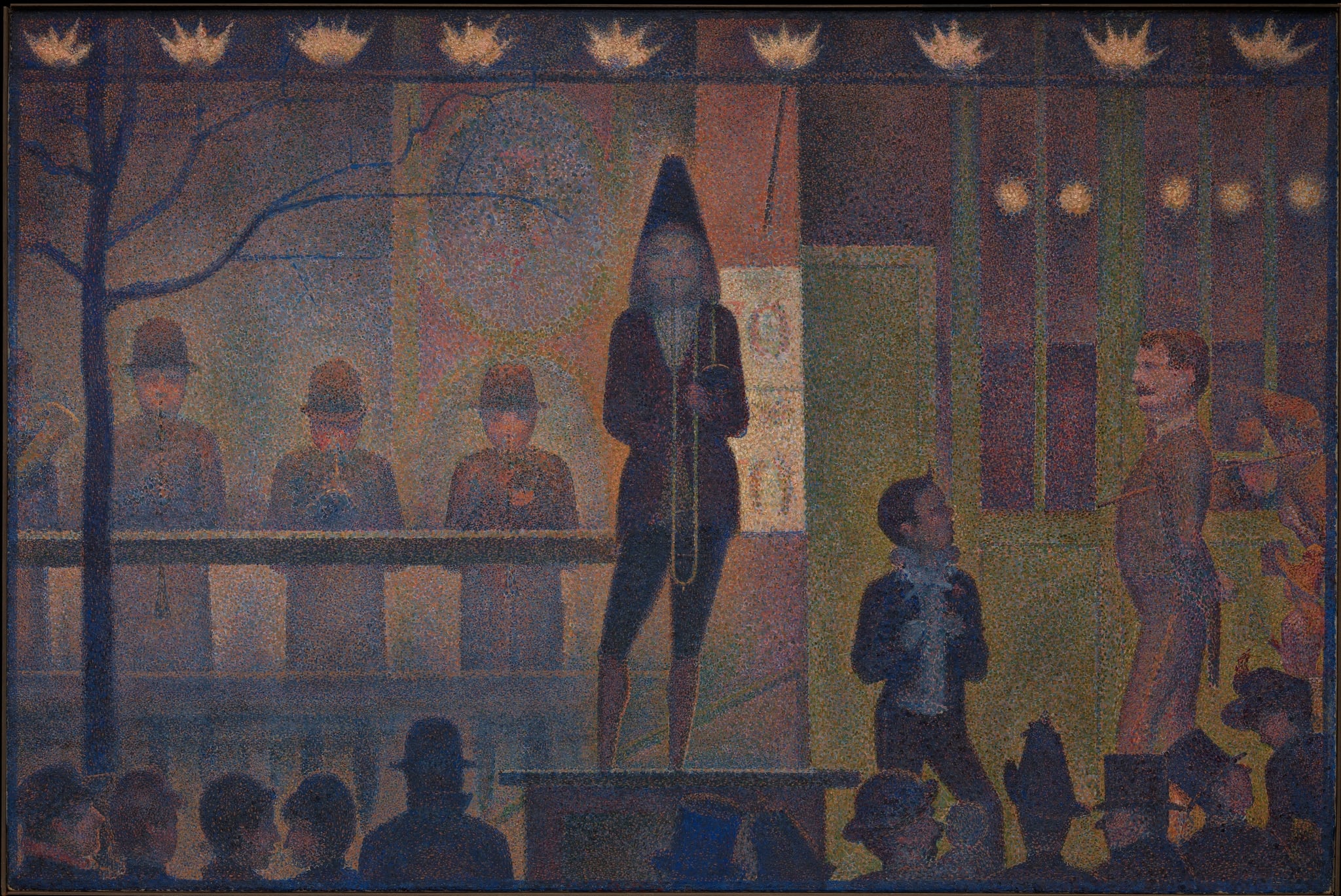

Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque)
Georges Seurat (1887–88)
Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque) distills a bustling Paris fairground into a cool, ritualized <strong>threshold</strong> between street and spectacle. Under nine crownlike <strong>gaslights</strong>, a barker, musicians, and attendants align with geometric restraint while the crowd remains a band of silhouettes, held at the edge. Seurat’s <strong>Neo‑Impressionist</strong> dots make the night hum yet stay eerily still, turning publicity into a modern icon of order and mood <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Church at Moret
Alfred Sisley (1894)
Alfred Sisley’s The Church at Moret turns a Flamboyant Gothic façade into a living barometer of light, weather, and time. With <strong>cool blues, lilacs, and warm ochres</strong> laid in broken strokes, the stone seems to breathe as tiny townspeople drift along the street. The work asserts <strong>permanence meeting transience</strong>: a communal monument held steady while the day’s atmosphere endlessly remakes it <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
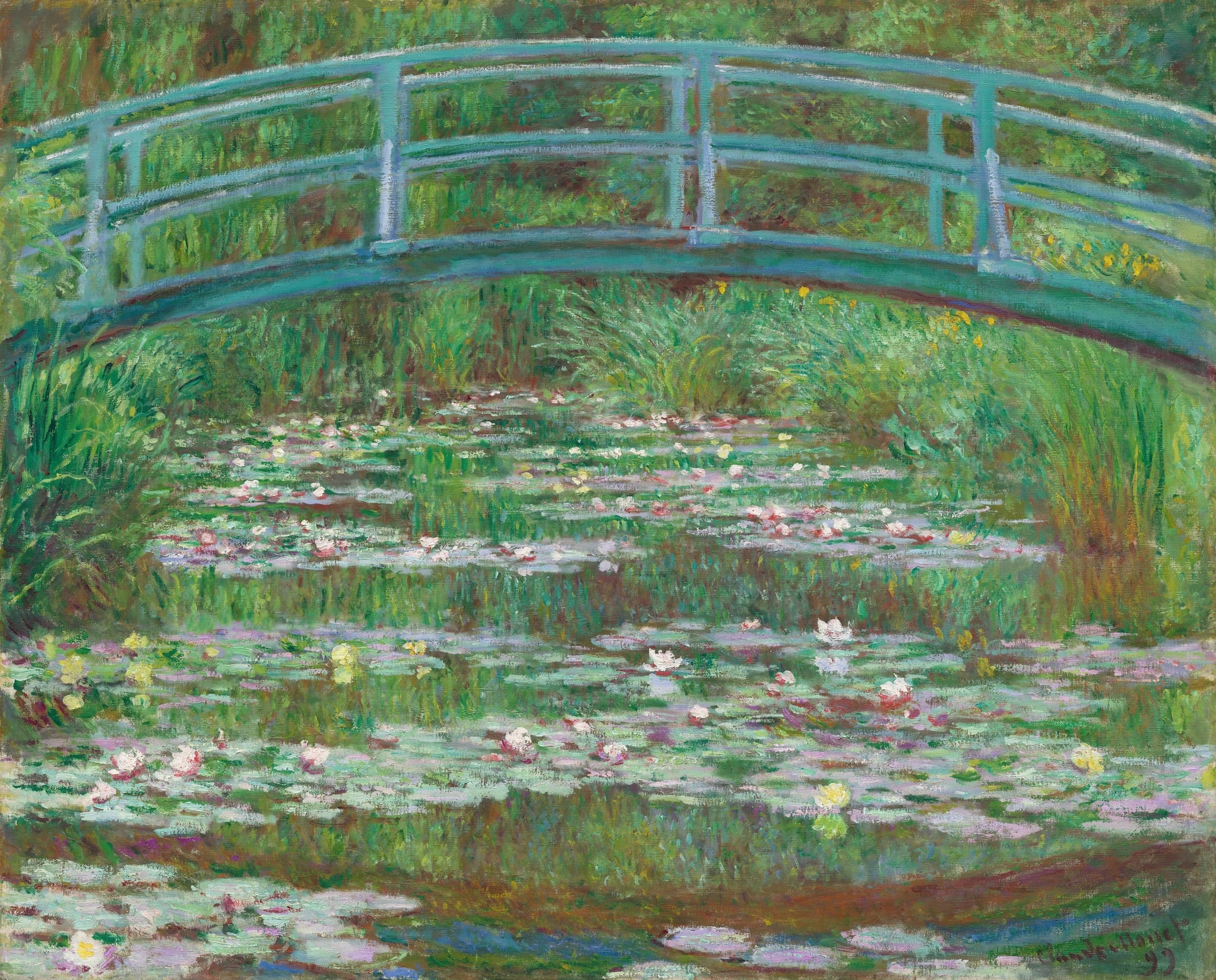

The Japanese Bridge
Claude Monet (1899)
Claude Monet’s The Japanese Bridge centers a pale <strong>blue‑green arch</strong> above a horizonless pond, where water‑lily pads and blossoms punctuate a field of shifting reflections. The bridge reads as both structure and <strong>contemplative threshold</strong>, suspending the eye between surface shimmer and mirrored depths <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
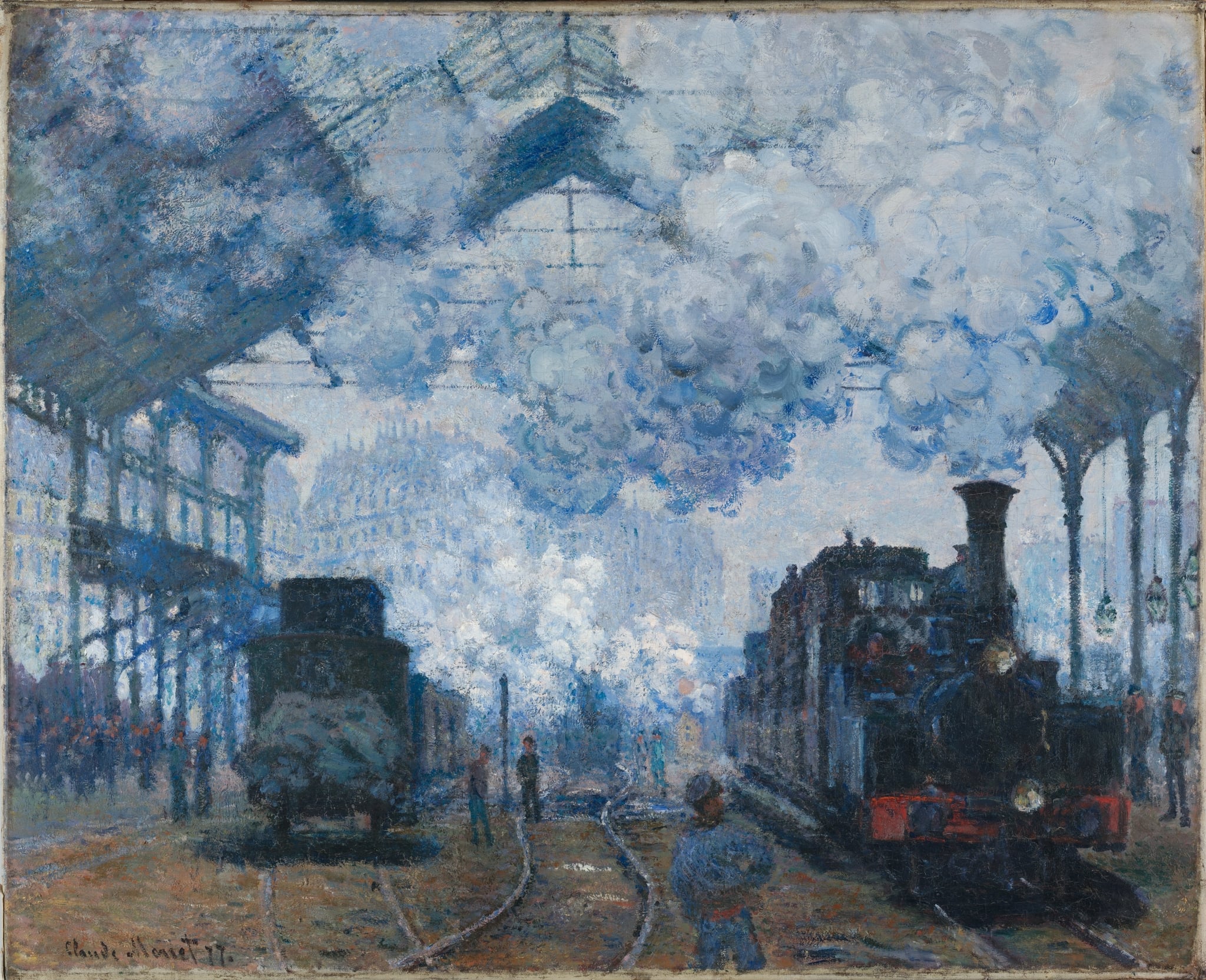

The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train
Claude Monet (1877)
Claude Monet’s The Gare Saint-Lazare: Arrival of a Train plunges viewers into a <strong>vapor-filled nave of iron and glass</strong>, where billowing steam, hot lamps, and converging rails forge a drama of industrial modernity. The right-hand locomotive, its red buffer beam glowing, materializes out of a <strong>blue-gray atmospheric envelope</strong>, turning motion and time into visible substance <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
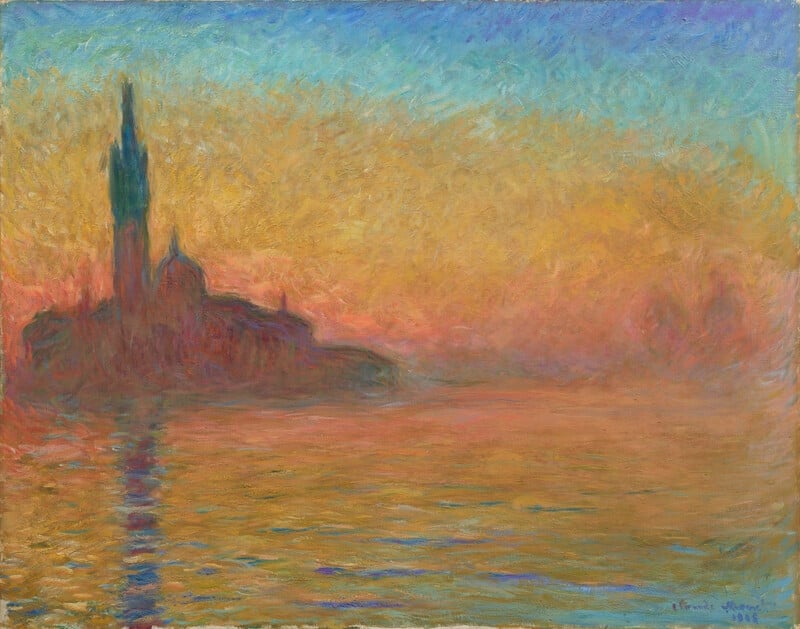
San Giorgio Maggiore by Twilight
Claude Monet (1908)
Claude Monet’s San Giorgio Maggiore by Twilight turns Venice into a <strong>luminous threshold</strong> where stone, air, and water merge. The dark, melting silhouette of the church and its vertical reflection anchor a field of <strong>apricot–rose–violet</strong> light that drifts into cool turquoise, making permanence feel provisional <sup>[1]</sup>. Monet’s subject is not the monument, but the <strong>enveloppe</strong> of atmosphere that momentarily creates it <sup>[4]</sup>.

The Piazza San Marco, Venice
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1881)
Renoir’s The Piazza San Marco, Venice redefines St. Mark’s Basilica as <strong>atmosphere</strong> rather than architecture, fusing domes, mosaics, and crowd into vibrating color. Blue‑violet shadows sweep the square while pigeons and passersby resolve into <strong>daubs of light</strong>, declaring modern vision as the true subject <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Creation of Adam
Michelangelo (c.1511–1512)
Michelangelo’s The Creation of Adam crystallizes the instant before life is conferred, staging a charged interval between two nearly touching hands. The fresco turns Genesis into a study of <strong>imago Dei</strong>, bodily perfection, and the threshold between inert earth and <strong>active spirit</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Kiss
Gustav Klimt (1908 (completed 1909))
The Kiss stages human love as a <strong>sacred union</strong>, fusing two figures into a single, gold-clad form against a timeless field. Klimt opposes <strong>masculine geometry</strong> (black-and-white rectangles) to <strong>feminine organic rhythm</strong> (spirals, circles, flowers), then resolves them in radiant harmony <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The School of Athens
Raphael (1509–1511)
Raphael’s The School of Athens orchestrates a grand debate on knowledge inside a perfectly ordered, classical hall whose one-point perspective converges on the central pair, <strong>Plato</strong> and <strong>Aristotle</strong>. Their opposed gestures—one toward the heavens, one level to the earth—establish the fresco’s governing dialectic between <strong>ideal forms</strong> and <strong>empirical reason</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. Around them, mathematicians, scientists, and poets cluster under statues of <strong>Apollo</strong> and <strong>Athena/Minerva</strong>, turning the room into a temple of <strong>Renaissance humanism</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Third of May 1808
Francisco Goya (1814)
Francisco Goya’s The Third of May 1808 turns a specific reprisal after Madrid’s uprising into a universal indictment of <strong>state violence</strong>. A lantern’s harsh glare isolates a civilian who raises his arms in a <strong>cruciform</strong> gesture as a faceless firing squad executes prisoners, transforming reportage into <strong>modern anti-war testimony</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Arnolfini Portrait
Jan van Eyck (1434)
In The Arnolfini Portrait, Jan van Eyck stages a poised encounter between a richly dressed couple whose joined hands, a single burning candle, and a convex mirror transform a domestic interior into a scene of <strong>status and sanctity</strong>. The painting asserts the artist’s own <strong>presence</strong>—"Johannes de eyck fuit hic 1434"—as if to validate the moment while showcasing oil painting’s power to make belief tangible through light, texture, and reflection <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Wanderer above the Sea of Fog
Caspar David Friedrich (ca. 1817)
Caspar David Friedrich’s The Wanderer above the Sea of Fog distills the Romantic encounter with nature into a single <strong>Rückenfigur</strong> poised on jagged rock above a rolling <strong>sea of mist</strong>. The cool, receding vista and the figure’s still stance convert landscape into an <strong>inner drama of contemplation</strong> and the <strong>sublime</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

The Jewish Bride
Rembrandt van Rijn (c. 1665–1669)
The Jewish Bride by Rembrandt van Rijn stages an intimate covenant: two figures, read today as <strong>Isaac and Rebecca</strong>, seal their union through touch rather than spectacle. Light concentrates on faces and hands, while the man’s glittering <strong>gold sleeve</strong> and the woman’s <strong>coral-red gown</strong> turn paint itself into a metaphor for fidelity and tenderness <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. This late masterpiece embodies Rembrandt’s <strong>material eloquence</strong>—impasto as feeling—within a hushed, dark setting <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Manneporte near Étretat
Claude Monet (1886)
Monet’s The Manneporte near Étretat turns the colossal sea arch into a <strong>threshold of light</strong>: rock, sea, and air interlock as shifting color rather than fixed form. Dense lilac–ochre strokes make the cliff feel massive yet <strong>dematerialized</strong> by illumination, while the arch’s opening stages a quiet, glimmering horizon <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Tree of Life
Gustav Klimt (1910–1911 (design; mosaic installed 1911))
Gustav Klimt’s The Tree of Life crystallizes a <strong>cosmological axis</strong> in a gilded ornamental language: a rooted trunk erupts into <strong>endless spirals</strong>, embedded with <strong>eye-like rosettes</strong> and shadowed by a black, red‑eyed bird. Designed as part of the Stoclet dining‑room frieze, it fuses <strong>symbolism and luxury materials</strong> to link earthly abundance with timeless transcendence <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.