Leisure & recreation
Featured Artworks

Woman in Black at the Opera
Mary Cassatt (1878)
Mary Cassatt’s Woman in Black at the Opera stages a taut drama of vision and visibility. A woman in <strong>black attire</strong> raises <strong>opera glasses</strong> while a distant man aims his own at her, setting off a chain of looks that makes public leisure a site of <strong>power, agency, and surveillance</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Tea
Mary Cassatt (about 1880)
Mary Cassatt’s The Tea stages a poised, interior <strong>drama of manners</strong>: two women sit close yet feel apart, one thoughtful, the other raising a cup that <strong>veils her face</strong>. A gleaming, oversized <strong>silver tea service</strong> commands the foreground, its reflections turning ritual objects into actors in the scene <sup>[1]</sup>. The shallow, cropped room—striped wall, gilt mirror, marble mantel—compresses the atmosphere into <strong>intimacy edged by restraint</strong>.

Boating
Claude Monet (1887)
Monet’s Boating crystallizes modern leisure as a drama of perception, setting a slim skiff and two pale dresses against a field of dark, mobile water. Bold cropping, a thrusting oar, and the complementary flash of hull and foliage convert a quiet outing into an experiment in <strong>modern vision</strong> and the <strong>materiality of water</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Children Playing on the Beach
Mary Cassatt (1884)
In Children Playing on the Beach, Mary Cassatt brings the viewer down to a child’s eye level, granting everyday play the weight of <strong>serious, self-contained work</strong>. The cool horizon and tiny boats open onto <strong>modern space and possibility</strong>, while the cropped, tilted foreground seals us inside the children’s focused world <sup>[1]</sup>.

Women in the Garden
Claude Monet (1866–1867)
Claude Monet’s Women in the Garden choreographs four figures in a sunlit bower to test how <strong>white dresses</strong> register <strong>dappled light</strong> and shadow. The path, parasol, and clipped flowers frame a modern ritual of leisure while turning fashion into an instrument of <strong>perception</strong>. The scene reads less as portraiture than as a manifesto for painting the <strong>momentary</strong> outdoors <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

A Woman and a Girl Driving
Mary Cassatt (1881)
Cassatt stages a modern scene of <strong>female control</strong> in motion: a woman grips the reins and whip while a girl beside her mirrors the pose, and a groom seated behind looks away. The cropped horse and diagonal harness thrust the carriage forward, placing viewers inside a public outing in the Bois de Boulogne—an arena where visibility signaled status and autonomy <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Bacchus
Caravaggio (c. 1598)
Caravaggio’s Bacchus stages a human-scaled god who offers wine with disarming immediacy, yoking <strong>sensual invitation</strong> to <strong>vanitas</strong> warning. The tilted goblet, blemished fruit, and wilting leaves insist that abundance and youth are <strong>precarious</strong>. A private Roman milieu under Cardinal del Monte shaped this refined, provocative image <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

In the Garden
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1885)
In the Garden presents a charged pause in modern leisure: a young couple at a café table under a living arbor of leaves. Their lightly clasped hands and the bouquet on the tabletop signal courtship, while her calm, front-facing gaze checks his lean. Renoir’s flickering brushwork fuses figures and foliage, rendering love as a <strong>transitory, luminous sensation</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Café Terrace at Night
Vincent van Gogh (1888)
In Café Terrace at Night, Vincent van Gogh turns nocturne into <strong>luminous color</strong>: a gas‑lit terrace glows in yellows and oranges against a deep <strong>ultramarine sky</strong> pricked with stars. By building night “<strong>without black</strong>,” he stages a vivid encounter between human sociability and the vastness overhead <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
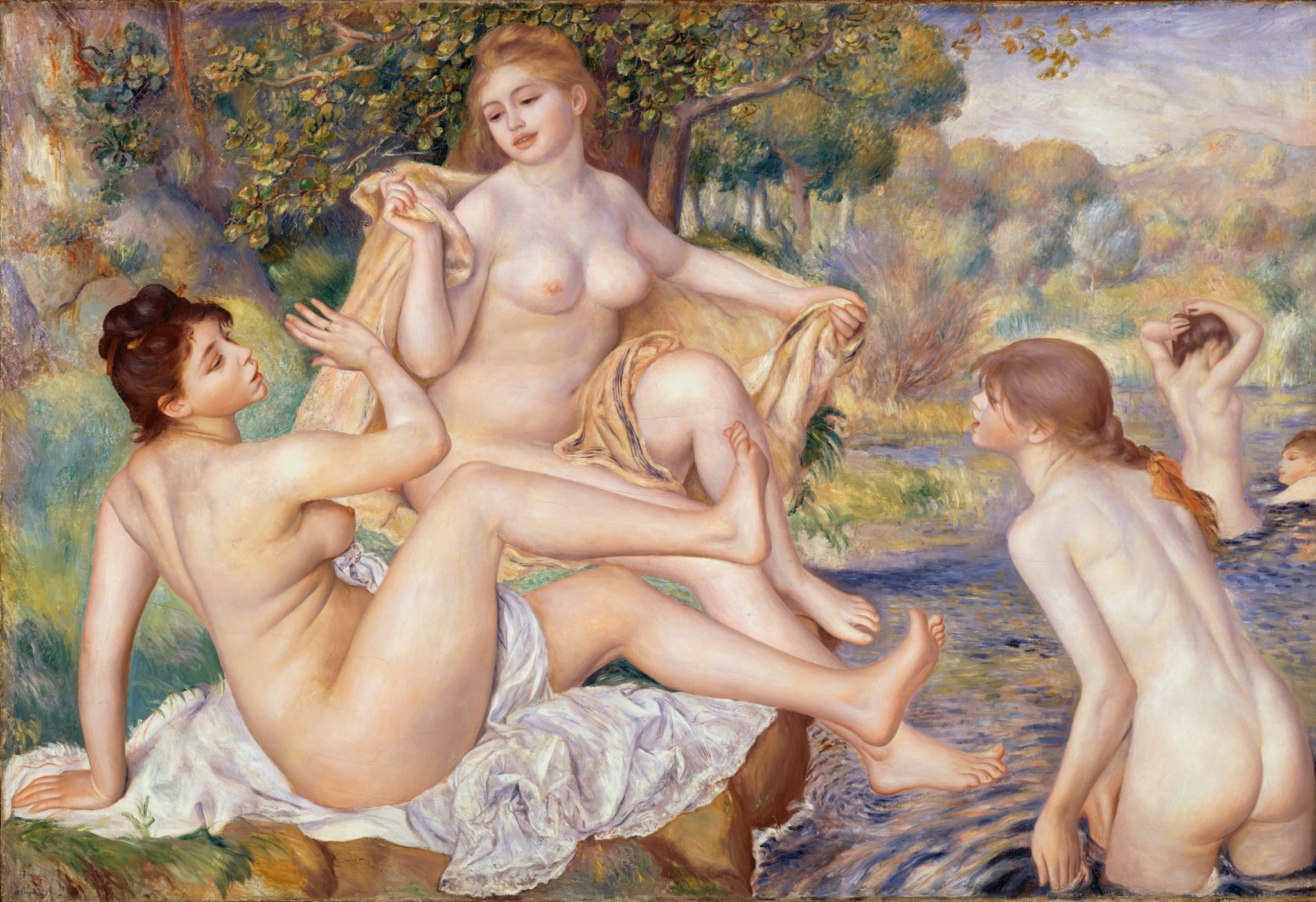

The Large Bathers
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1884–1887)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir’s The Large Bathers unites modern bodies with a pastoral grove to stage an <strong>Arcadian ideal</strong>. Three monumental nudes form interlocking curves and triangles while two background figures splash and groom, fusing <strong>sensual warmth</strong> with <strong>classical order</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

After the Luncheon
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1879)
After the Luncheon crystallizes a <strong>suspended instant</strong> of Parisian leisure: coffee finished, glasses dappled with light, and a cigarette just being lit. Renoir’s <strong>shimmering brushwork</strong> and the trellised spring foliage turn the scene into a tapestry of conviviality where time briefly pauses.

Summertime
Mary Cassatt (1894)
Mary Cassatt’s Summertime (1894) stages a quiet drama of <strong>attentive looking</strong>: a woman and a girl lean from a cropped boat toward two ducks as the lake flickers with broken color. Cassatt fuses <strong>Impressionism</strong> and <strong>Japonisme</strong>—no horizon, tipped perspective, and abrupt cropping—to press our gaze downward into light-spattered water. The result is an image of <strong>modern leisure</strong> that is also a study of perception itself <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Loge
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s The Loge (1874) turns an opera box into a <strong>stage of looking</strong>, where a woman meets our gaze while her companion scans the crowd through binoculars. The painting’s <strong>frame-within-a-frame</strong> and glittering fashion make modern Parisian leisure both alluring and self-conscious, turning spectators into spectacles <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Beach at Trouville
Claude Monet (1870)
Beach at Trouville turns the Normandy resort into a stage where <strong>modern leisure</strong> meets <strong>restless weather</strong>. Monet’s diagonal boardwalk, wind-whipped <strong>red flags</strong>, and white <strong>parasols</strong> marshal the eye through a day animated by light and air rather than by individual stories <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. The work asserts Impressionism’s claim to immediacy—there is even <strong>sand embedded in the paint</strong> from working on site <sup>[1]</sup>.

Woman Reading
Édouard Manet (1880–82)
Manet’s Woman Reading distills a fleeting act into an emblem of <strong>modern self-possession</strong>: a bundled figure raises a journal-on-a-stick, her luminous profile set against a brisk mosaic of greens and reds. With quick, loaded strokes and a deliberately cropped <strong>beer glass</strong> and paper, Manet turns perception itself into subject—asserting the drama of a private mind within a public café world <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Summer's Day
Berthe Morisot (about 1879)
Two women drift on a boat in the Bois de Boulogne, their dresses, hats, and a bright blue parasol fused with the lake’s flicker by Morisot’s swift, <strong>zig‑zag brushwork</strong>. The scene turns a brief outing into a poised study of <strong>modern leisure</strong> and <strong>female companionship</strong> in public space <sup>[1]</sup>.

Madame Monet and Her Son
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s 1874 canvas Madame Monet and Her Son crystallizes <strong>modern domestic leisure</strong> and <strong>plein‑air immediacy</strong> in Argenteuil. A luminous white dress pools into light while a child in a pale‑blue sailor suit reclines diagonally; a strutting rooster punctuates the greens with warm color. The brushwork fuses figure and garden so the moment reads as <strong>lived, not staged</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The Skiff (La Yole)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1875)
In The Skiff (La Yole), Pierre-Auguste Renoir stages a moment of modern leisure on a broad, vibrating river, where a slender, <strong>orange skiff</strong> cuts across a field of <strong>cool blues</strong>. Two women ride diagonally through the shimmer; an <strong>oar’s sweep</strong> spins a vortex of color as a sailboat, villa, and distant bridge settle the scene on the Seine’s suburban edge <sup>[1]</sup>. Renoir turns motion and light into a single sensation, using a high‑chroma, complementary palette to fuse human pastime with nature’s flux <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

On the Beach
Édouard Manet (1873)
On the Beach captures a paused interval of modern leisure: two fashionably dressed figures sit on pale sand before a <strong>banded, high-horizon sea</strong>. Manet’s <strong>economical brushwork</strong>, restricted greys and blacks, and radical cropping stage a scene of absorption and wind‑tossed motion that feels both intimate and detached <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Cliff Walk at Pourville
Claude Monet (1882)
Claude Monet’s The Cliff Walk at Pourville renders wind, light, and sea as interlocking forces through <strong>shimmering, broken brushwork</strong>. Two small walkers—one beneath a pink parasol—stand near the <strong>precipitous cliff edge</strong>, their presence measuring the vastness of turquoise water and bright sky dotted with white sails. The scene fuses leisure and the <strong>modern sublime</strong>, making perception itself the subject <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Plum Brandy
Édouard Manet (ca. 1877)
Manet’s Plum Brandy crystallizes a modern pause—an urban <strong>interval of suspended action</strong>—through the idle tilt of a woman’s head, an <strong>unlit cigarette</strong>, and a glass cradling a <strong>plum in amber liquor</strong>. The boxed-in space—marble table, red banquette, and decorative grille—turns a café moment into a stage for <strong>solitude within public life</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Regatta at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
On a brilliant afternoon at the Normandy coast, a diagonal <strong>pebble beach</strong> funnels spectators with parasols toward a bay scattered with <strong>white-sailed yachts</strong>. Monet’s quick, broken strokes set <strong>wind, water, and light</strong> in synchrony, turning a local regatta into a modern scene of leisure held against the vastness of sea and sky <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Dance at Bougival
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1883)
In Dance at Bougival, Pierre-Auguste Renoir turns a crowded suburban dance into a <strong>private vortex of intimacy</strong>. Rose against ultramarine, skin against shade, and a flare of the woman’s <strong>scarlet bonnet</strong> concentrate the scene’s energy into a single turning moment—modern leisure made palpable as <strong>touch, motion, and light</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Beach at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
In The Beach at Sainte-Adresse, Claude Monet stages a modern shore where <strong>labor and leisure intersect</strong> under a broad, changeable sky. The bright <strong>blue beached boat</strong> and the flotilla of <strong>rust-brown working sails</strong> punctuate a turquoise channel, while a fashionably dressed pair sits mid-beach, spectators to the traffic of the port. Monet’s brisk, broken strokes make the scene feel <strong>caught between tides and weather</strong>, a momentary balance of work, tourism, and atmosphere <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
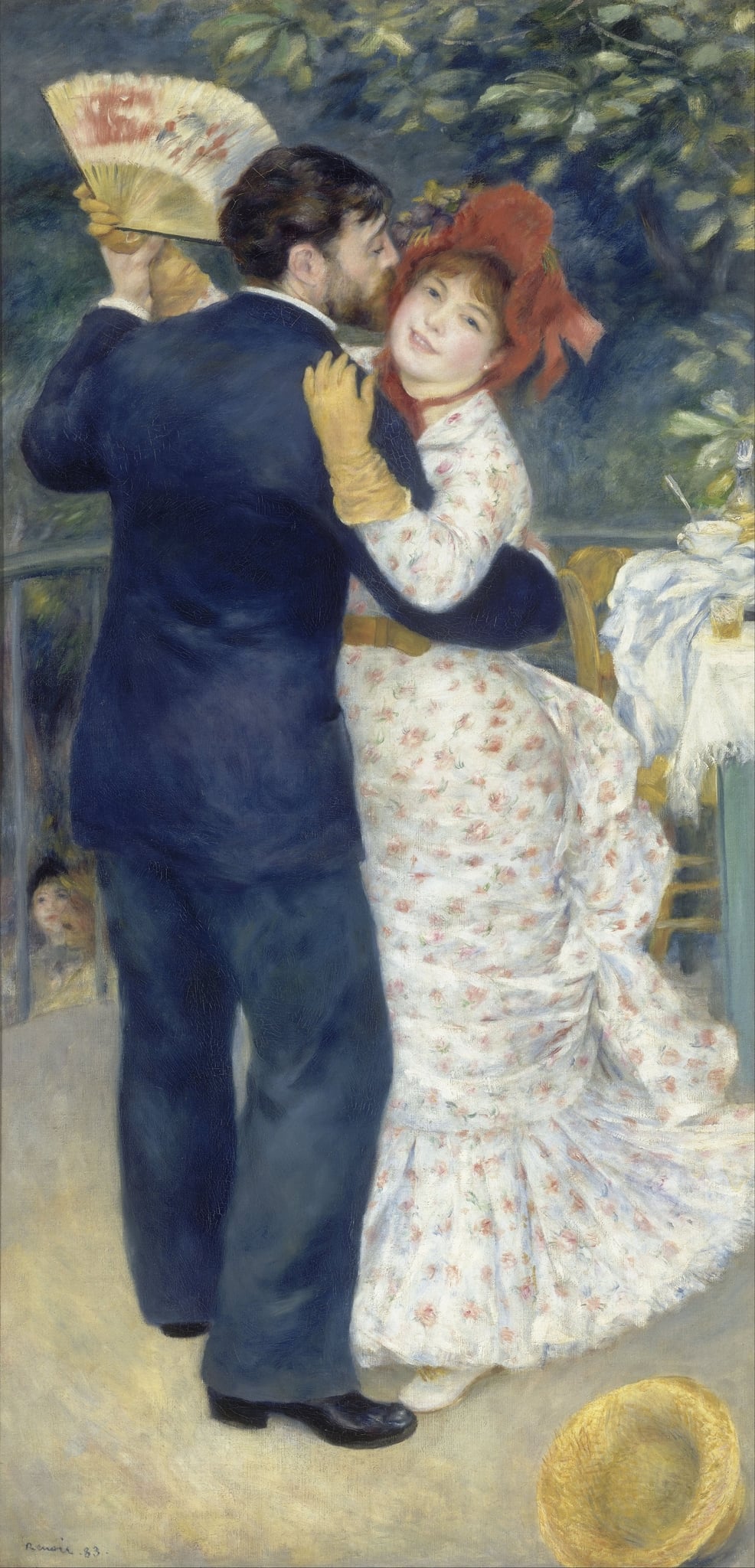

Dance in the Country
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1883)
Dance in the Country shows a couple swept into a close embrace on a café terrace, their bodies turning in a soft spiral as foliage and sunlight dissolve into <strong>dappled color</strong>. Renoir orchestrates <strong>bourgeois leisure</strong>—the tossed straw boater, a small table with glass and napkin, the woman’s floral dress and red bonnet—to stage a moment where decorum and desire meet. The result is a modern emblem of shared pleasure, poised between Impressionist shimmer and a newly <strong>firm, linear touch</strong>.
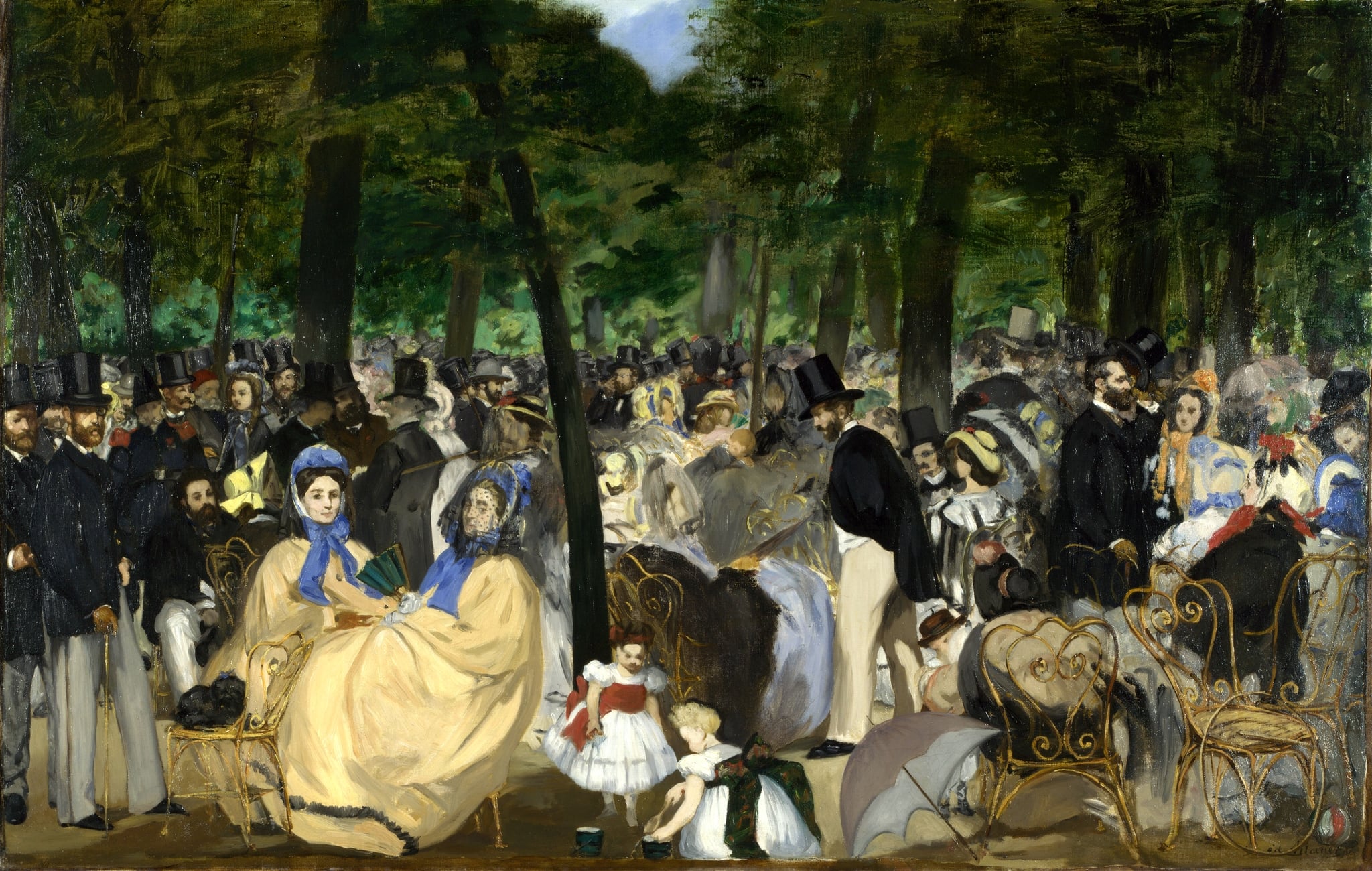

Music in the Tuileries
Édouard Manet (1862)
Édouard Manet’s Music in the Tuileries turns a Sunday concert into a manifesto of <strong>modern life</strong>: a frieze of top hats, crinolines, and iron chairs flickering beneath <strong>toxic green</strong> foliage. Instead of a hero or center, the painting disperses attention across a restless crowd, making <strong>looking itself</strong> the drama of the scene <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
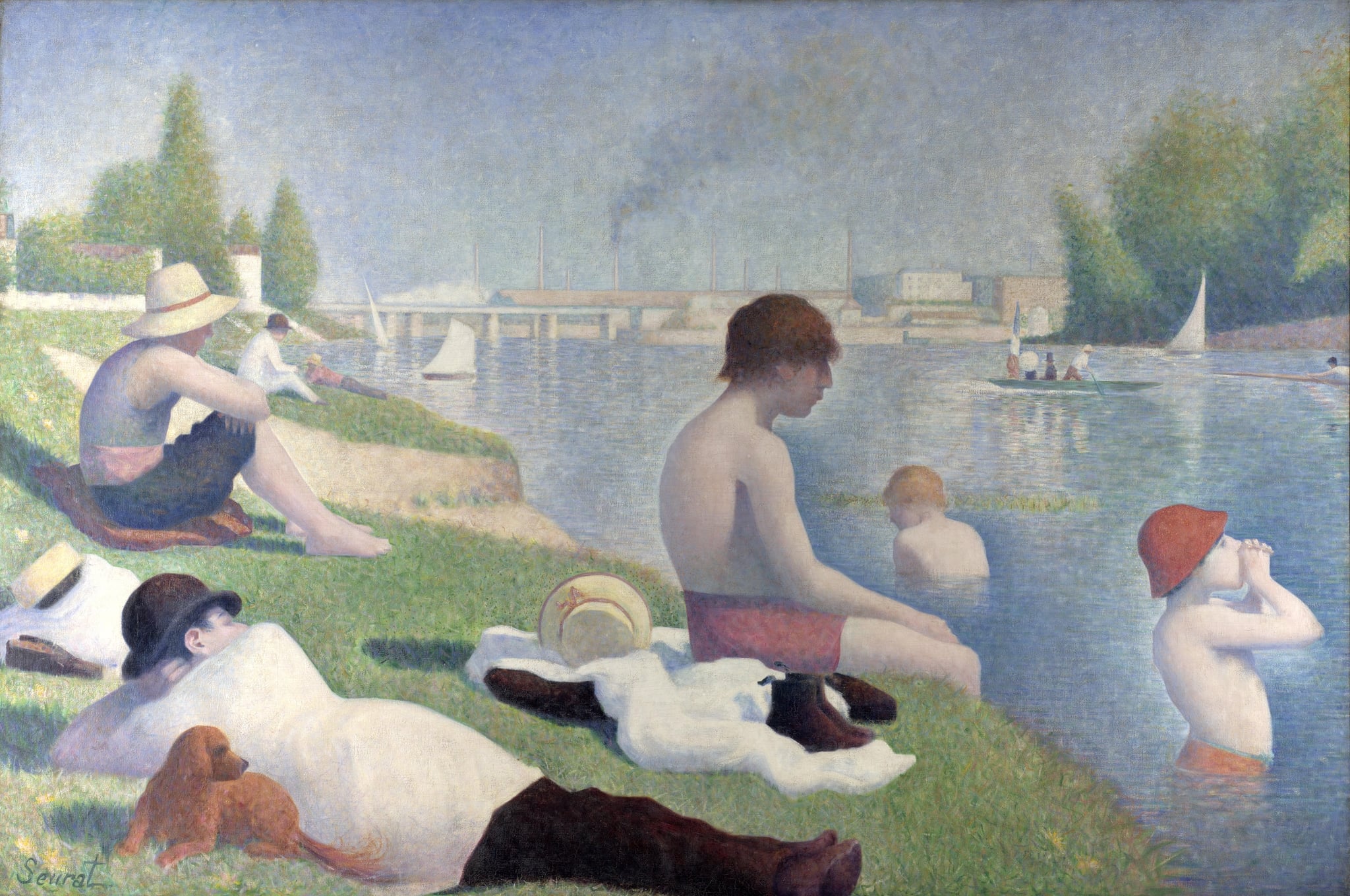

Bathers at Asnières
Georges Seurat (1884)
Bathers at Asnières stages a scene of <strong>modern leisure</strong> on the Seine, where workers recline and wade beneath a hazy, unified light. Seurat fuses <strong>classicizing stillness</strong> with an <strong>industrial backdrop</strong> of chimneys, bridges, and boats, turning ordinary rest into a monumental, ordered image of urban life <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The canvas balances soft greens and blues with geometric structures, producing a calm yet charged harmony.
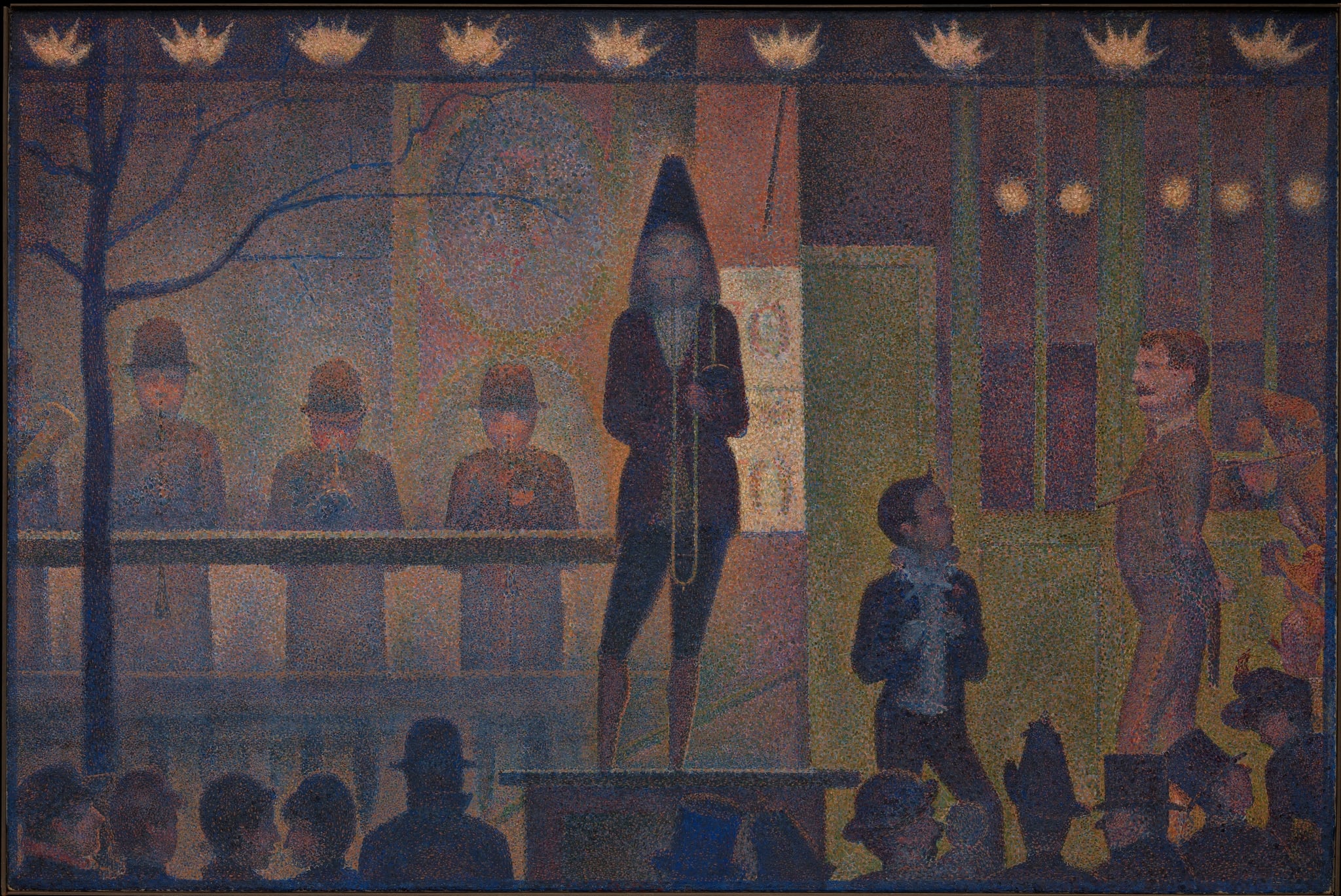

Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque)
Georges Seurat (1887–88)
Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque) distills a bustling Paris fairground into a cool, ritualized <strong>threshold</strong> between street and spectacle. Under nine crownlike <strong>gaslights</strong>, a barker, musicians, and attendants align with geometric restraint while the crowd remains a band of silhouettes, held at the edge. Seurat’s <strong>Neo‑Impressionist</strong> dots make the night hum yet stay eerily still, turning publicity into a modern icon of order and mood <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

At the Moulin Rouge
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (1892–1895)
At the Moulin Rouge plunges us into the churn of Paris nightlife, staging a crowded room where spectacle and fatigue coexist. A diagonal banister and abrupt croppings create <strong>off‑kilter immediacy</strong>, while harsh artificial light turns faces <strong>masklike</strong> and cool. Mirrors multiply the crowd, amplifying a mood of allure tinged with <strong>urban alienation</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.
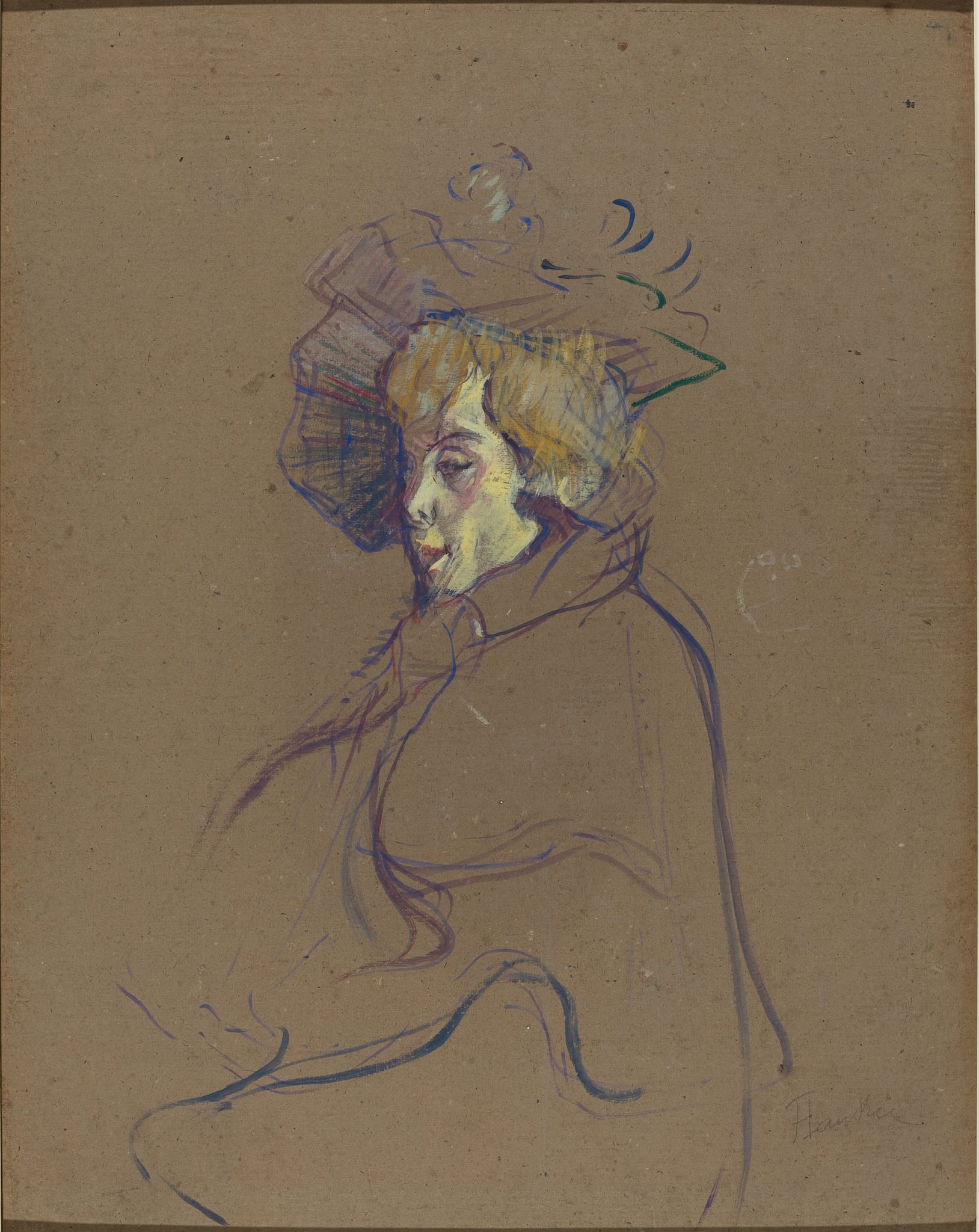

Jane Avril
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec (c. 1891–1892)
In Jane Avril, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec crystallizes a public persona from a few <strong>urgent, chromatic strokes</strong>: violet and blue lines whirl into a cloak, while green and indigo dashes crown a buoyant hat. Her face—sharply keyed in <strong>lemon yellow, lilac, and carmine</strong>—hovers between mask and likeness, projecting poise edged with fatigue. The raw brown ground lets her <strong>whiplash silhouette</strong> materialize like smoke from Montmartre’s nightlife.

The Cup of Tea
Mary Cassatt (ca. 1880–81)
Mary Cassatt’s The Cup of Tea distills a moment of bourgeois leisure into a study of <strong>poise</strong>, <strong>etiquette</strong>, and <strong>private reflection</strong>. A woman in a rose‑pink dress and bonnet, white‑gloved, balances a gold‑rimmed cup against the shimmer of <strong>Impressionist</strong> brushwork, while a green planter of pale blossoms echoes her pastel palette <sup>[1]</sup>. The work turns an ordinary ritual into a modern emblem of women’s experience.
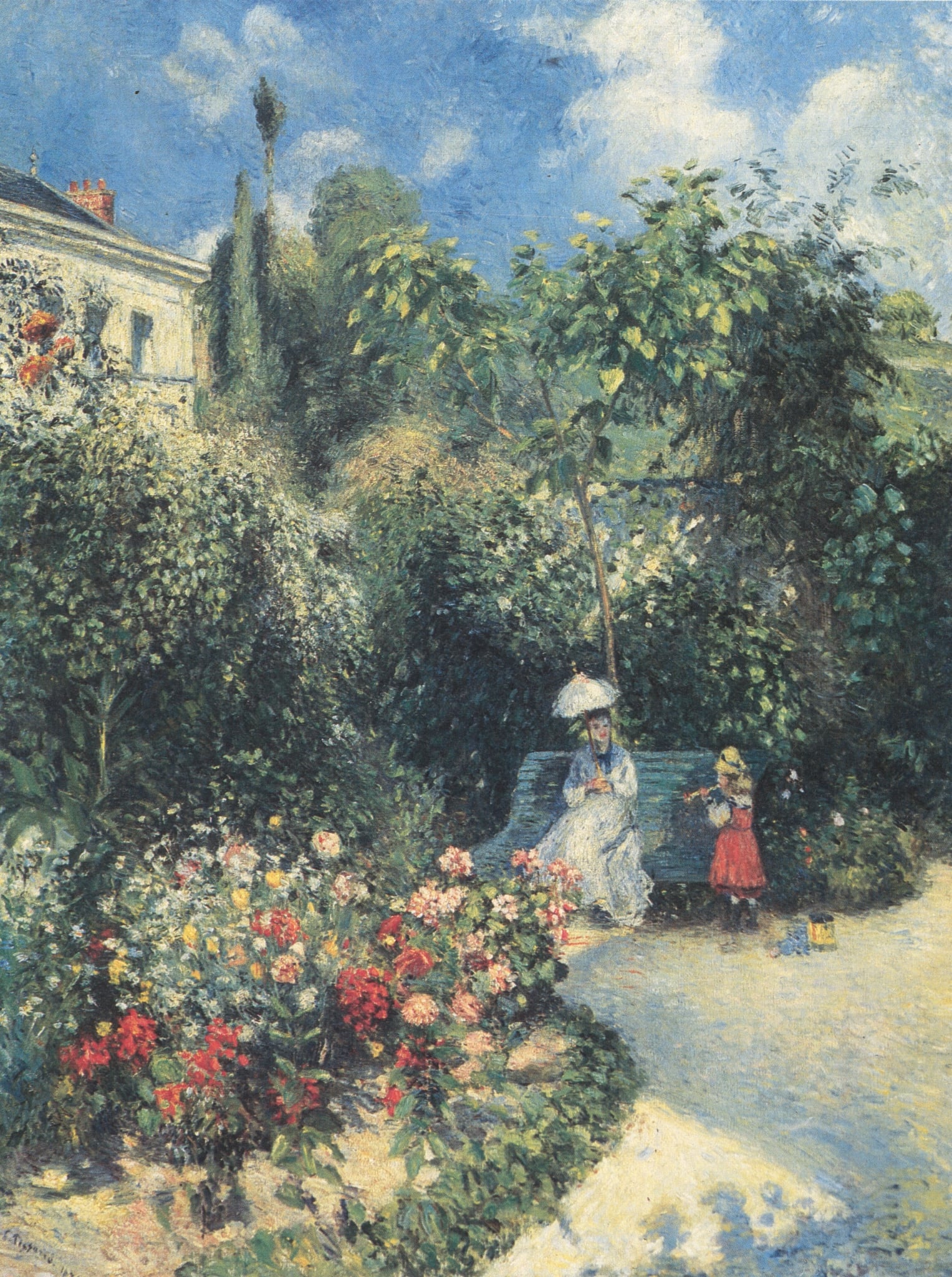
The Garden of Pontoise
Camille Pissarro (1874)
In The Garden of Pontoise, Camille Pissarro turns a modest suburban plot into a stage for <strong>modern leisure</strong> and <strong>fugitive light</strong>. A woman shaded by a parasol and a child in a bright red skirt punctuate the deep greens, while a curving sand path and beds of red–pink blossoms draw the eye toward a pale house and cloud‑flecked sky. The painting asserts that everyday, cultivated nature can be a <strong>modern Eden</strong> where time, season, and social ritual quietly unfold <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
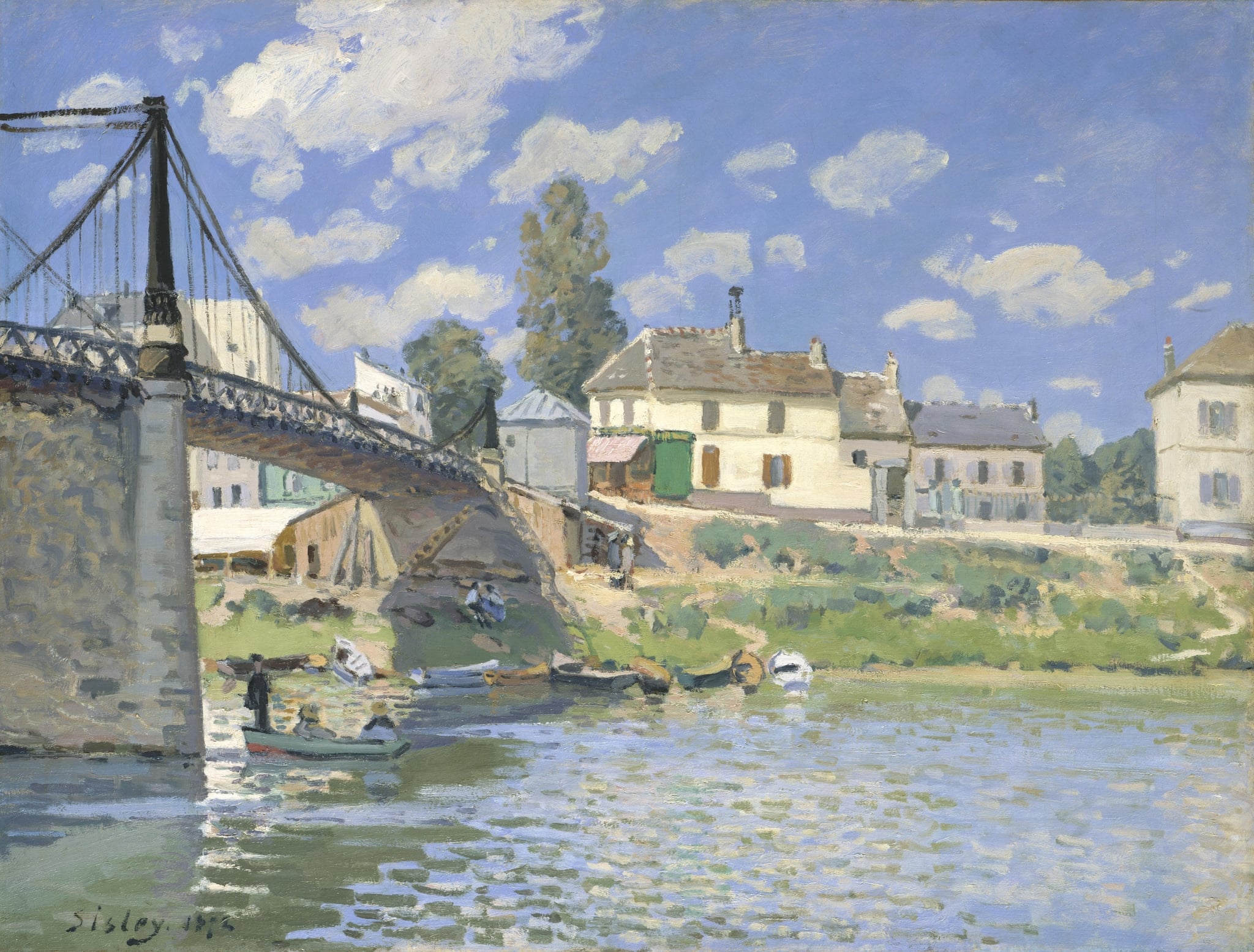

The Bridge at Villeneuve-la-Garenne
Alfred Sisley (1872)
Alfred Sisley's The Bridge at Villeneuve-la-Garenne crystallizes the encounter between <strong>modern engineering</strong> and <strong>riverside leisure</strong> under <strong>Impressionist light</strong>. The diagonal suspension bridge, dark pylons, and filigreed truss command the left foreground while small boats skim the Seine, their wakes breaking into shimmering strokes that echo the sky.
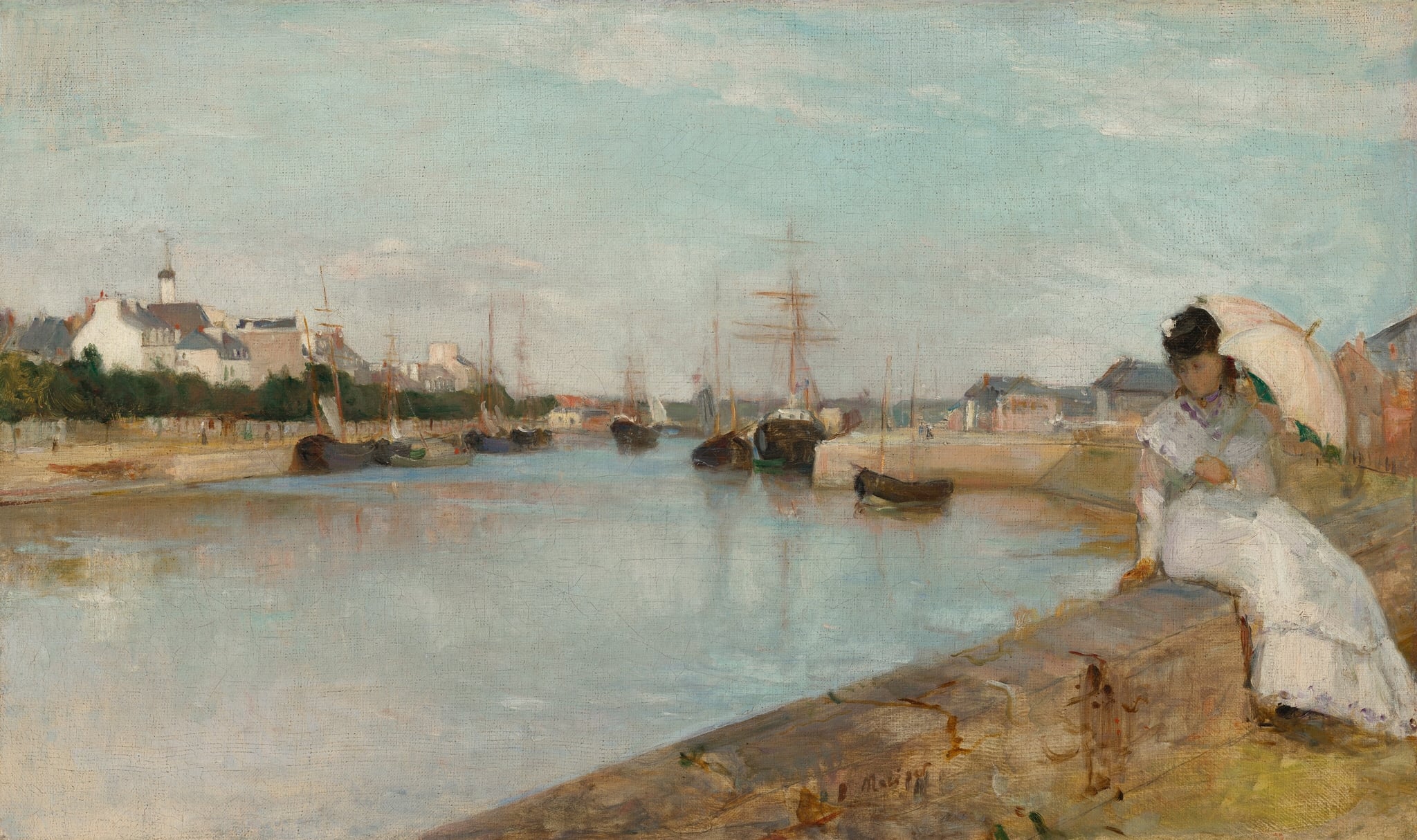

The Harbour at Lorient
Berthe Morisot (1869)
Berthe Morisot’s The Harbour at Lorient stages a quiet tension between <strong>private reverie</strong> and <strong>public movement</strong>. A woman under a pale parasol sits on the quay’s stone lip while a flotilla of masted boats idles across a silvery basin, their reflections dissolving into light. Morisot’s <strong>pearly palette</strong> and brisk brushwork make the water read as time itself, holding stillness and departure in the same breath <sup>[1]</sup>.

Reading
Berthe Morisot (1873)
In Berthe Morisot’s <strong>Reading</strong> (1873), a woman in a pale, patterned dress sits on the grass, absorbed in a book while a <strong>green parasol</strong> and <strong>folded fan</strong> lie nearby. Morisot’s quick, luminous brushwork dissolves the landscape into <strong>atmospheric greens</strong> as a distant carriage passes, turning an outdoor scene into a study of interior life. The work makes <strong>female intellectual absorption</strong> its true subject, aligning modern leisure with private thought.

In the Loge
Mary Cassatt (1878)
Mary Cassatt’s In the Loge (1878) stages modern spectatorship as a drama of <strong>mutual looking</strong>. A woman in dark dress leans forward with <strong>opera glasses</strong>, her <strong>fan closed</strong> on her lap, as a man in the distance raises his own glasses toward her—turning the theater into a circuit of gazes <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman with a Pearl Necklace in a Loge
Mary Cassatt (1879)
Mary Cassatt’s Woman with a Pearl Necklace in a Loge (1879) stages modern <strong>spectatorship</strong> inside a plush opera box, where a young woman in pink satin, pearls, and gloves occupies the red velvet seat while a mirror multiplies the chandeliers and balconies. Cassatt fuses <strong>intimacy</strong> and <strong>public display</strong>, using luminous brushwork to place her sitter within the social theater of Parisian leisure <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
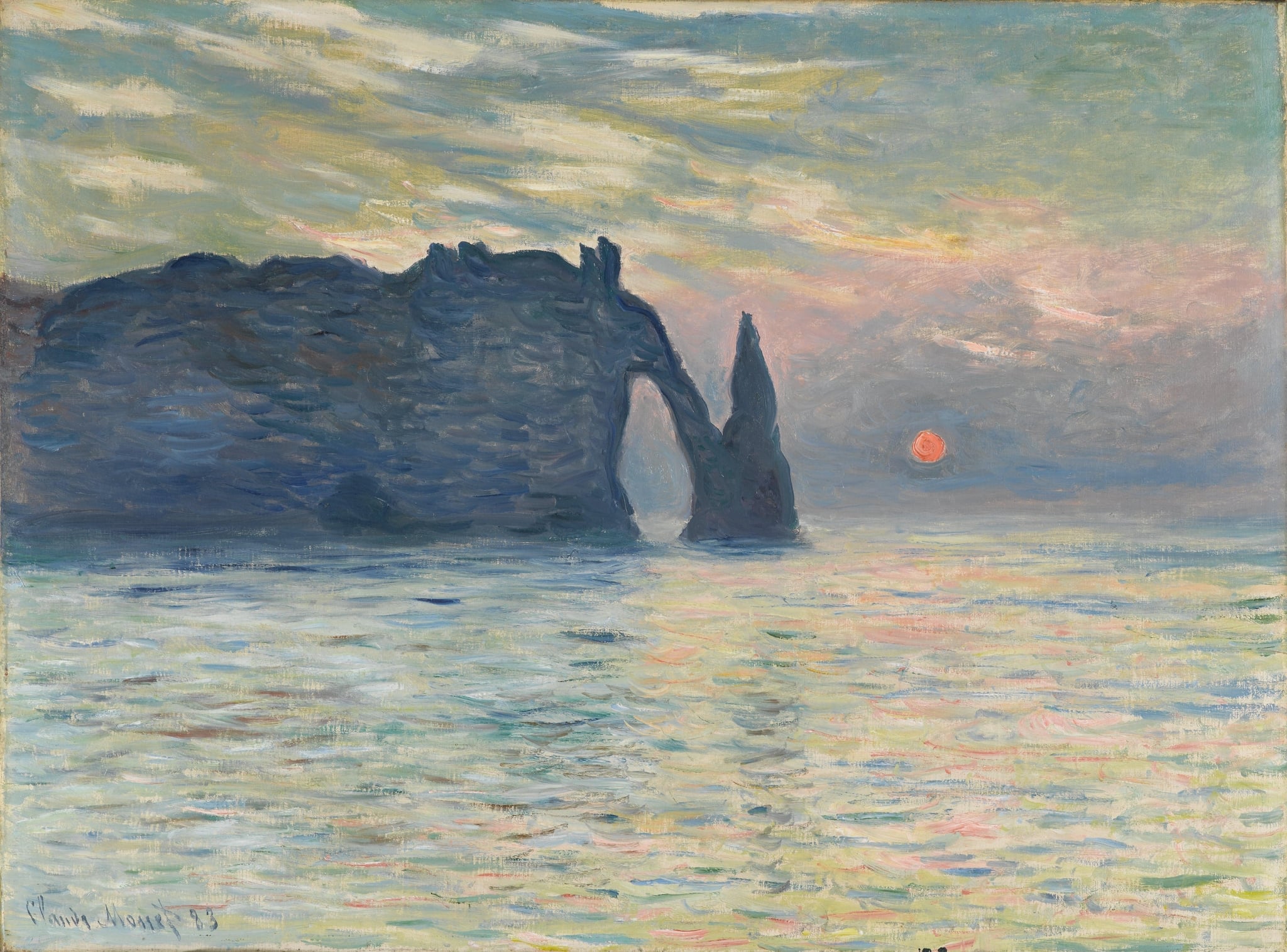

The Cliff, Etretat
Claude Monet (1882–1883)
<strong>The Cliff, Etretat</strong> stages a confrontation between <strong>permanence and flux</strong>: the dark mass of the arch and needle holds like a monument while ripples of coral, green, and blue light skate across the water. The low <strong>solar disk</strong> fixes the instant, and Monet’s fractured strokes make the sea and sky feel like time itself turning toward dusk. The arch reads as a <strong>threshold</strong>—an opening to the unknown that organizes vision and meaning <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
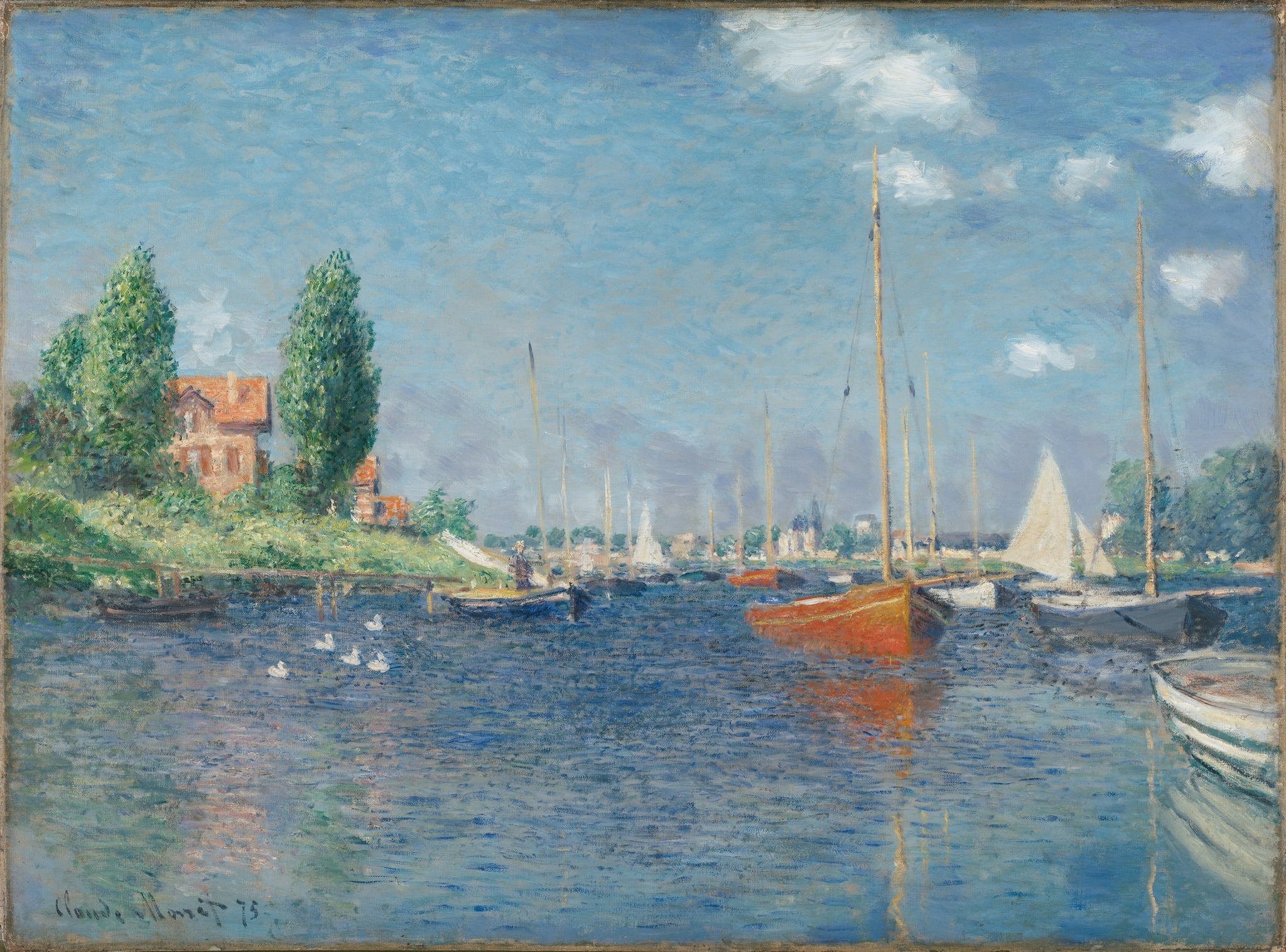

The Red Boats, Argenteuil
Claude Monet (1875)
Claude Monet’s The Red Boats, Argenteuil crystallizes a luminous afternoon on the Seine, where two <strong>vermilion hulls</strong> anchor a scene of leisure and light. The tremoring <strong>reflections</strong> and vertical <strong>masts/poplars</strong> weave nature and modern recreation into a single atmospheric field <sup>[1]</sup>.
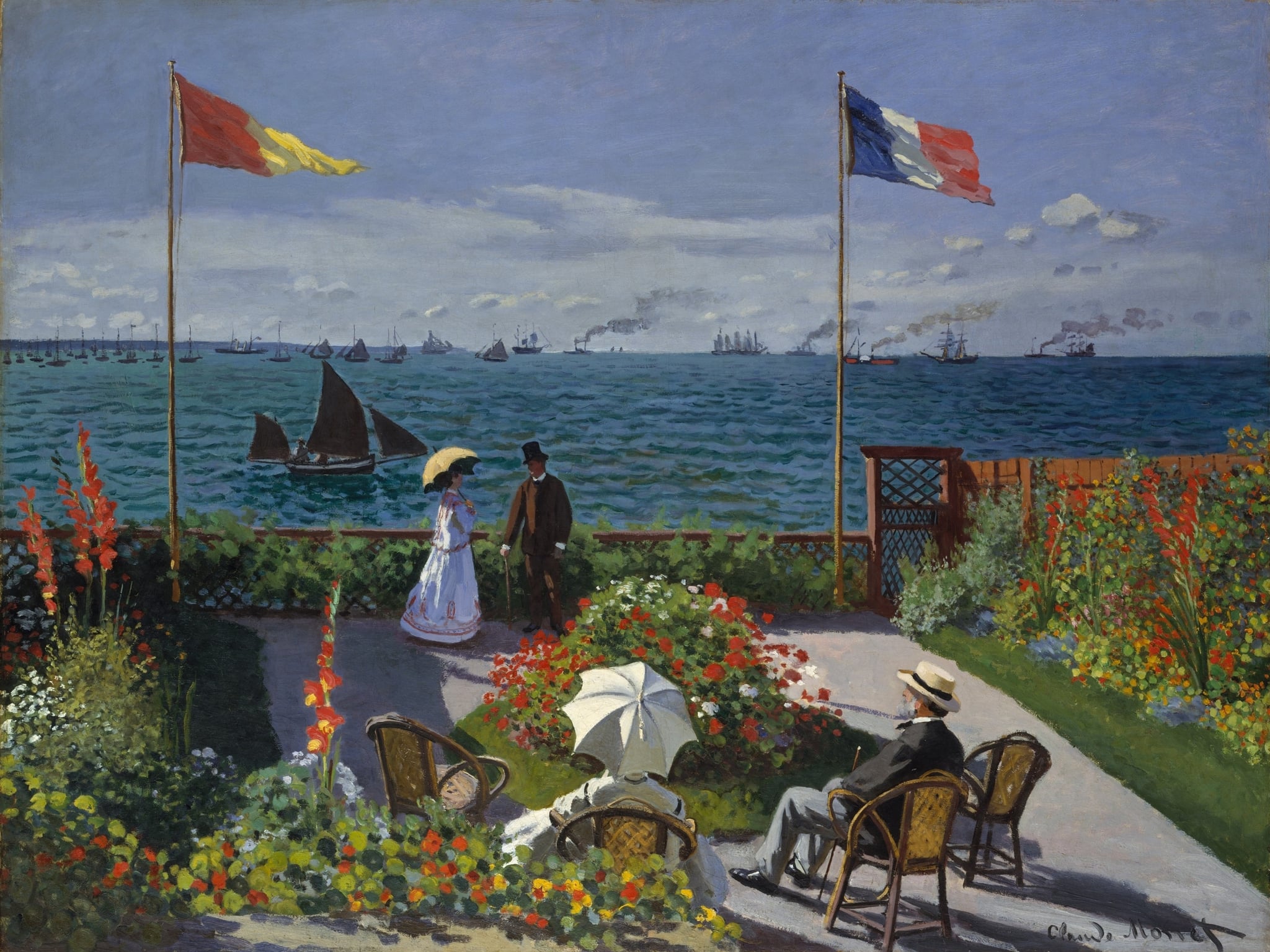

The Terrace at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
Claude Monet’s The Terrace at Sainte-Adresse stages a sunlit garden against the Channel, where <strong>bourgeois leisure</strong> unfolds between two wind-whipped flags and a horizon shared by <strong>sail and steam</strong>. Bright flowers, wicker chairs, and a white parasol form an ordered foreground, while the busy harbor and snapping tricolor project a confident, modern nation. The banded design—garden, sea, sky—reveals Monet’s early <strong>Japonisme</strong> and his drive to fuse fleeting light with a consciously structured composition <sup>[1]</sup>.

Boulevard des Capucines
Claude Monet (1873–1874)
From a high perch above Paris, Claude Monet turns the Haussmann boulevard into a living current of <strong>light, weather, and motion</strong>. Leafless trees web the view, crowds dissolve into <strong>flickering strokes</strong>, and a sudden <strong>pink cluster of balloons</strong> pierces the cool winter scale <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Theater Box
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s The Theater Box turns a plush loge into a stage where seeing becomes the performance. A luminous woman—pearls, pale gloves, black‑and‑white stripes—faces us, while her companion scans the auditorium through opera glasses. The painting crystallizes Parisian <strong>modernity</strong> and the choreography of the <strong>gaze</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

Seated Bather
Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Renoir’s Seated Bather stages a quiet pause between bathing and reverie, fusing the model’s pearly flesh with the flicker of stream and stone. The white drapery pooled around her hips and the soft, frontal gaze convert a simple toilette into a <strong>modern Arcadia</strong> where body and landscape dissolve into light. In this late-Impressionist idiom, Renoir refines the nude as a <strong>timeless ideal</strong> felt through color and touch <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
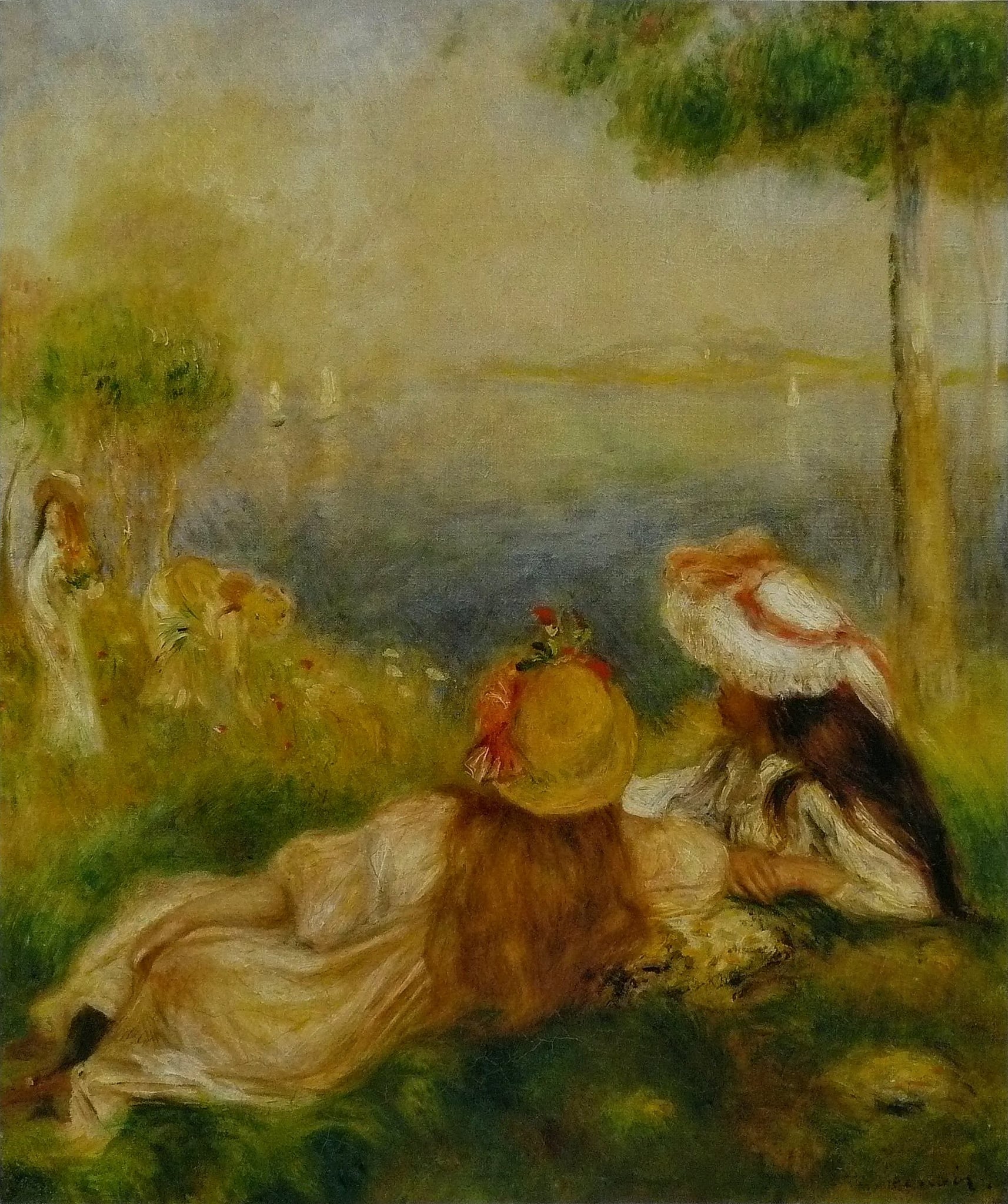

Girls at the Seashore
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (c.1890–1894)
Girls at the Seashore presents two young figures reclining on a grassy bank, their straw hats trimmed with flowers as they look toward a hazy waterway flecked with small sails. Renoir fuses figure and setting through soft, vaporous brushwork so that skin, fabric, foliage, and sea share the same light. The image is an ode to <strong>reverie</strong>, <strong>companionship</strong>, and the <strong>fleeting</strong> warmth of summer.

Children on the Seashore, Guernsey
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (about 1883)
Renoir’s Children on the Seashore, Guernsey crystallizes a wind‑bright moment of modern leisure with <strong>flickering brushwork</strong> and a gently choreographed group of children. The central girl in a white dress and black feathered hat steadies a toddler while a pink‑clad companion leans in and a sailor‑suited boy rests on the pebbles—an intimate triangle set against a <strong>shimmering, populated sea</strong>. The canvas makes light and movement the protagonists, dissolving edges into <strong>pearly surf and sun‑washed cliffs</strong>.

This is Not a Pipe
Rene Magritte (1929)
A crisply modeled tobacco pipe hovers over a blank beige field, while the cursive line "Ceci n’est pas une pipe" coolly denies what the eye assumes. The clash between image and sentence turns a familiar object into a <strong>thought experiment</strong> about signs and things. Magritte’s deadpan exactitude and ad‑like layout stage a <strong>philosophical trap</strong>: you can see a pipe, but you cannot smoke this picture. <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>