Edgar Degas
Biography
Themes in Their Work
Featured in Essays

Essay
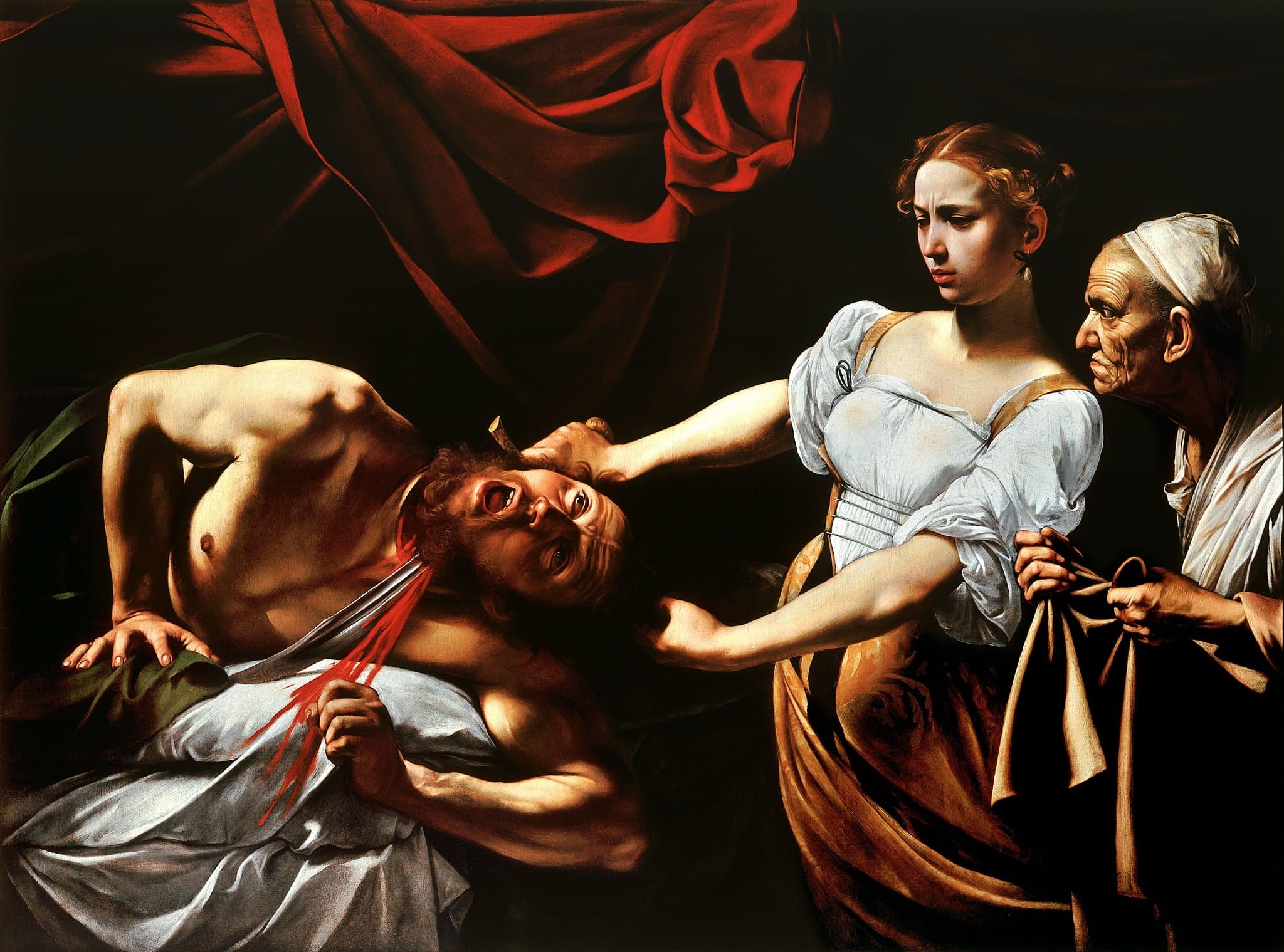
The Courtesan Behind the Sword
Start in a rented room with a curtain pulled high. A banker is waiting for a deliverable; a patronage network is watching a comet of a painter. Caravaggio steps to the canvas and chooses his Judith — not a saint from a sermon, but a woman Rome’s police could name. “And she smote twice upon his neck, and cut off his head.” The Book of Judith gives the script. Caravaggio turns it into live theater.

Essay
The Day Manet Took a Knife to His Own Painting
Paris, 1864. The Salon is the arena. A painting can knight you or end you. Manet, already bruised by scandal the year before, bets big on spectacle: a sweeping bullfight scene, Spanish costume, blood and bravado. He hangs it for the crowd. The critics circle. The verdict is icy. He can’t afford another public drubbing; every jeer dents his chances of becoming more than a punchline. The stakes are career, pride, and Paris itself. Here’s the twist sitting in plain sight: the famous close‑up of the fallen matador you know as The Dead Toreador — you can see it here [link](/artworks/edouard-manet/the-dead-toreador)[1] — started life as just one corner of that doomed panorama.

Essay
The Iron and the Eye: Degas Against the Glare
By the mid‑1870s, collectors wanted Degas for ballet: satin shoes, mirrored studios, the sellable dream. Instead, he kept showing up in steam and starch. Over and over, he painted laundresses—women who boiled, beat, and pressed other people’s clothes for pennies in rooms as hot as kilns. The choice wasn’t neutral; it could stall sales and annoy patrons who preferred dancers to drudgery. But Degas wouldn’t look away. The Musée d’Orsay calls this an obsession, tracing versions of ironers across the decade, including the famous yawning pair in Repasseuses [1].

Essay
The Blue Armchair Rebellion
Paris, 1878. An American woman is fighting for entry into the most controversial circle in art. Reputation on the line, money scarce, critics circling. Her next move must land. She paints… a kid who won’t behave. A small girl slumps diagonally across a vast sea of turquoise upholstery, socks rumpled, gaze elsewhere, a terrier comatose on a neighboring chair. It looks unbothered, even rude. And that’s the point. In a market that rewarded sugarcoated childhood, Mary Cassatt risked everything on a portrait that shrugs at adult decorum [1]. Cassatt had just thrown in with the outsiders—at Degas’s urging—and was preparing for her first Impressionist exhibition the following year. It wasn’t a club you entered softly. “I accepted with joy,” she later said of the invitation, because the Salon “crushed all originality” [3]. If this picture failed, the doubters would say she didn’t belong.

Essay
The Balcony That Started a Riot
Picture the stakes. Paris still bowed to the Salon, a jury that could mint careers or erase them. Monet had a young family, debts, and a dwindling market. So he and a handful of friends did the unthinkable: rent the grand studio of star photographer Nadar at 35 Boulevard des Capucines and hang their own show—no permission, no jury, all risk. The vantage in this painting is that balcony, that window, that leap.[2][7]

Essay
Degas’s Vanished Paris: The Painting That Went to War and Came Back With a Secret
Start in 1875: a man strides, girls in gray keep pace, a dog scouts the pavement. No one looks at each other. A city square yawns like a stage. Edgar Degas freezes it all with brutal cuts at the frame, the visual grammar of a world too fast for eye contact. Today the canvas lives at the State Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg, a long way from the Paris square it depicts—and even farther from where it was last seen before the war [State Hermitage Museum](https://hermitagemuseum.org/digital-collection/29681?lng=en)[1].

Essay
The Audition in Blue: Renoir’s Gamble Behind Girl with a Watering Can
Picture Renoir at 35, debts circling, reputation wobbling after the second Impressionist show. The critics mocked his circle; the market yawned. Portrait commissions — the cash engine of Paris — kept going to establishment names. He had to change that or sink. [National Gallery, London](https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/artists/pierre-auguste-renoir) [2].

Essay
The Picnic That Made an Emperor Blink
Start with the stakes: the Paris Salon decided an artist’s fate. Win the jury, you get buyers, critics, immortality. Lose, you vanish. That year, the jury rejected an unusually high number of submissions. Among the refusés was a picnic with a stare that wouldn’t look away—Édouard Manet’s Le Déjeuner sur l’herbe, then called Le Bain. The museum that owns it now says flatly: it “caused a scandal.” [Musée d’Orsay](https://www.musee-orsay.fr/en/artworks/le-dejeuner-sur-lherbe-904) [1].

Essay
She Put Down the Fan
Look closely: the props of flirtation lie useless in the grass. The fan is shut. The green parasol is abandoned. A carriage blurs by in the distance, but the figure never looks up. She reads, and the world waits. Morisot painted this in 1873, her surface quick and alive, the scene almost dissolving around the reader’s concentration. The Cleveland Museum of Art calls it Reading; it’s small, disarming, and dangerously calm [2].

Essay
Renoir’s Fake Date Night
Picture the stakes: Renoir is thirty-three, broke, and rolling the dice on a renegade show the Salon has snubbed—the first Impressionist exhibition. If this painting doesn’t spark attention, he’s not just unfashionable; he’s finished.

Essay
The Sunniest Monet Was Painted in a Storm
First glance: a perfect day. Parasols tilt. White sails cut the Channel. Sun freckles the water like confetti. It looks like a rich man’s postcard. That’s the trap.

Essay
Monet’s Pink Parasol, and the Secret It Was Hiding
Start at the edge. In 1882 Monet escaped to a fishing village on the Normandy coast and worked like a man trying to outrun gossip. He had fallen in love with Alice Hoschedé, the wife of his former patron Ernest, whose finances had collapsed. Two households had fused into one. The art world was watching, and not kindly [4].

Essay
The Night Pissarro Learned to See Again
He was in his mid‑sixties, the elder statesman of Impressionism with bills to pay and younger stars sprinting past. Critics loved the myth of Pissarro the tireless outdoor painter. But his reality was uglier: an infection had made bright, dusty daylight brutal. So he moved indoors and up—into a rented high window on the Boulevard Montmartre—staking his reputation on whether a man who couldn’t face the sun could still paint light.[5]

Essay
The Mirror That Said No: Berthe Morisot’s Quiet Rebellion
Look at the setup: a woman in satin, arm lifted, powders and jars within reach. Paris, late 1870s. It reads like flirtation. But the reflection is a smear, the face withheld. Morisot built a trap for the viewer and sprung it with a brush.

Essay
The Pink Portrait the Revolution Seized
Start in 1877. Renoir is broke, ambitious, and tired of being called a lightweight. He paints a young actress from the Comédie‑Française—Jeanne Samary—with a coral-pink atmosphere and a sea‑green dress, a portrait designed to charm the Salon and the paying classes. The picture glows like a debutante’s rumor. It still does. See it up close on our artwork page: /artworks/pierre-auguste-renoir/portrait-of-jeanne-samary.

Essay
The Prettiest SOS on the Seine
Picture Renoir at thirty-four, rent due, reputation wobbling. He’s fresh from the first Impressionist shockwaves and a Paris press that mocked his friends as incompetents. One reviewer sneered that Renoir painted a woman’s body like “a mass of decomposing flesh with green and purple spots.”[4] The message was clear: stop, or starve.

Essay
The Wheatfield Myth: Van Gogh’s Stormiest Painting Isn’t a Suicide Note
Scroll any feed and you’ll meet this image: a blasted-blue sky, a road that forks and dies, black birds like shrapnel. The caption is almost always the same: his last canvas, his farewell. Our shiver becomes the story.

Essay
Renoir’s Sweetest Breakup
You know this image: a couple under a living arbor, hands grazing over a café table. Soft light. Soft edges. Soft story. Except the year is 1885, and Pierre‑Auguste Renoir is in crisis. The painter who helped spark Impressionism is suddenly telling friends he no longer knows how to paint. The romance on canvas hides a rupture off it.[3][10]

Essay
The Day Monet Turned a Picnic into a Comeback
Start here: a hill at Argenteuil, a flash of white dress, a boy blinking in the wind. The painting feels tossed-off and weightless. That’s the trick. Because months earlier, the money and the mood were brutal. In 1875, fresh from the first Impressionist exhibition’s ridicule, Monet and friends tried an auction at Hôtel Drouot. The crowd jeered, prices collapsed, and police were called. His name became shorthand for recklessness with paint, not value. The family’s comfort—rent, food, even paint—was on the line. The parasol wasn’t shade; it was cover. Monet needed an image that could flip the narrative: not starving bohemians, but modern life, bright and breathable, the very leisure new suburban rail lines were selling. Argenteuil was Paris’s weekend playground—sailboats, strolls, picnics, and status on display—exactly the world collectors fancied seeing on their walls.

Essay
The Cradle Was a Warning, Not a Lullaby
Paris, 1874. A young painter stakes her reputation on a domestic scene while her comrades hang boats, boulevards, and fog. Berthe Morisot chooses a nursery. Money, credibility, and a seat at the table are on the line—because if the public writes her off as merely “feminine,” she’s finished.

Essay
The Cathedral That Took Monet Hostage
The postcard version is easy: stone lace, soft color, Impressionism behaving. But Monet’s cathedral wasn’t decor. It was a duel with the sun, run on minutes and panic, with a dealer betting that the public would finally understand what Impressionism had been saying all along.

Essay
The Woman Paris Refused to See
The Salon was the only career ladder that mattered. Manet needed it. Respectability, buyers, a future—hung on a wall in 1865. Then the crowd arrived, and the painting that wouldn’t behave drew jeers so thick the museum put up a cord to protect it. The Musée d’Orsay is blunt about the reception: scandal, fury, and a guard between public and paint.

Essay
The $65 Million Spring
Christie’s, New York, 2014. Phones light up. The bidding climbs past the price of many houses, then many museums’ annual acquisitions budgets. When the hammer falls, Manet’s Jeanne (Spring) shatters a record and the Getty wins the picture for $65.1 million—a new pinnacle for the artist at auction [3][1].

Essay
The Night Degas Put the Ballerinas in the Back Row
Picture Paris in the late 1860s: velvet boxes, diamonded patrons, ballerinas floating like chandeliers. And then an unknown painter plants his easel where no one is looking—down in the orchestra pit. Why risk it? Because reputation was on the line. Degas was switching gears, ditching history painting for modern life, and the Opéra was the city’s most ruthless stage: art, money, and gossip in a single address.[1] If he chose wrong, he’d stay a nobody. He also had a personal stake. The man gripping that diagonal bassoon is Désiré Dihau—a real friend, a working musician whose salary depended on staying visible to an audience that never looked his way.[2][3] Degas knew the rules of this house, and he was about to break them on canvas.

Essay
Monet’s Quiet Bridge, Built on Noise
In 1893, Monet walked into local bureaucracy with a radical request: let me reroute a stream and build a lily pond in my backyard. Farmers objected, fearing floods and foreign plants. The painter pushed through anyway, secured permission, and set about reshaping the land at Giverny. The tranquil bridge you know was born out of paperwork and protests, not Zen stillness. [1] Money and reputation were on the line. Monet had finally bought his home in 1890 after years of financial precarity; now he was risking cash and goodwill to turn a garden into a studio—and a studio into a legacy. He wasn’t just planting; he was betting his name. He staged the scene with precision: a curved wooden span, no horizon, and a pond thick with lilies. This wasn’t picturesque chance—it was design. The bridge, lifted from the era’s mania for Japan, signaled a fashionable cool while tightening the composition like a drum. As the National Gallery in London notes, the structure arrived alongside Paris’s craze for Japanese art and prints, which Monet collected obsessively. [2] Then came the first payoff: in 1899, he painted it. If you think the image recorded a walk in the park, consider how hard he worked to make the park exist. The Japanese Footbridge compresses space, removes the sky, and turns reflection into theater, a trick he could repeat at will from his doorstep. [1] [5]

Essay
The Prettiest Sunset in Art Was Air Pollution
He arrived not for Parliament’s Gothic drama but for the weather report. From a window on the south bank, Monet lined up the towers and waited for the sky to burn through the haze. The National Gallery of Art notes he finished the canvas in 1903, after returning to Giverny to tune the color of the Thames like a violin string—then unveiled the London series in 1904, betting his mature reputation on a city that barely wanted to be seen at all. [NGA link][1]

Essay
Monet Booked the Steam
Monet was in his late thirties and still not a sure thing. The Impressionists had split with the Salon, but the public wasn’t buying in bulk. He needed a subject that felt undeniable—modern, popular, unmistakably Paris. He picked the engine room of the city itself: the Gare Saint-Lazare, the Western Railway’s iron-and-glass cathedral of departures.

Essay
Grit in the Light: Monet’s Trouville, Captured Not Just Seen
Stand before the National Gallery’s Beach at Trouville and the composition immediately leans into you: a boardwalk pulled taut on the diagonal, parasols opening like sails, and a regiment of red flags firing toward the Channel. The confection of hotels to the right—anchored by the fashionable Hôtel des Roches Noires—presses the promenade into a stage for modern leisure, a Second Empire theater of strolling and display. Monet painted it on site in the summer of 1870, a blustery day made legible by architecture and cloth rather than narrative incident, as the museum’s entry for the work recounts ([The Beach at Trouville](https://www.nationalgallery.org.uk/paintings/claude-monet-the-beach-at-trouville) [1]). [Image: Beach at Trouville (1870) — /artworks/claude-monet/beach-at-trouville] That slanted boardwalk does more than guide the eye: it sets a vector. From left surf to right-hand steps, every stroke queues to the wind’s push, a coastal physics lesson rendered in broken blues and bleached ochres.
Essay
The Wind Is the Protagonist: Monet’s Beach at Trouville as a Pre-Digital Live Feed
Beach at Trouville looks, at first glance, like a souvenir of a fashionable afternoon: sun-struck planks, white parasols, genteel promenaders. But every element is drafted into a single task—measuring the air. The diagonal boardwalk hurries the eye past the figures; a volley of red flags snaps mid-gust; skirts and veils flare into vectors. In Monet’s 1870 season at the Normandy resort, modern leisure had met meteorology—tourism built to be felt in motion [2][4]. [Artwork: /artworks/claude-monet/beach-at-trouville] That sense of motion anchors the canvas in a specific place and moment. Trouville had exploded into a Second Empire playground, its grand hotels and villas marching right up to the sand. Monet painted those very facades elsewhere that same season, including the newly fashionable Hôtel des Roches Noires—a statement of seaside modernity still rising from the dunes [1].
Featured Artworks

The Opera Orchestra by Edgar Degas | Analysis
Edgar Degas
In The Opera Orchestra, Degas flips the theater’s hierarchy: the black-clad pit fills the frame while the ballerinas appear only as cropped tutus and legs, glittering above. The diagonal <strong>bassoon</strong> and looming <strong>double bass</strong> marshal a dense field of faces lit by footlights, turning backstage labor into the subject and spectacle into a fragment <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Tub
Edgar Degas (1886)
In The Tub (1886), Edgar Degas turns a routine bath into a study of <strong>modern solitude</strong> and <strong>embodied labor</strong>. From a steep, overhead angle, a woman kneels within a circular basin, one hand braced on the rim while the other gathers her hair; to the right, a tabletop packs a ewer, copper pot, comb/brush, and cloth. Degas’s layered pastel binds skin, water, and objects into a single, breathing field of <strong>warm flesh tones</strong> and blue‑greys, collapsing distance between body and still life <sup>[1]</sup>.
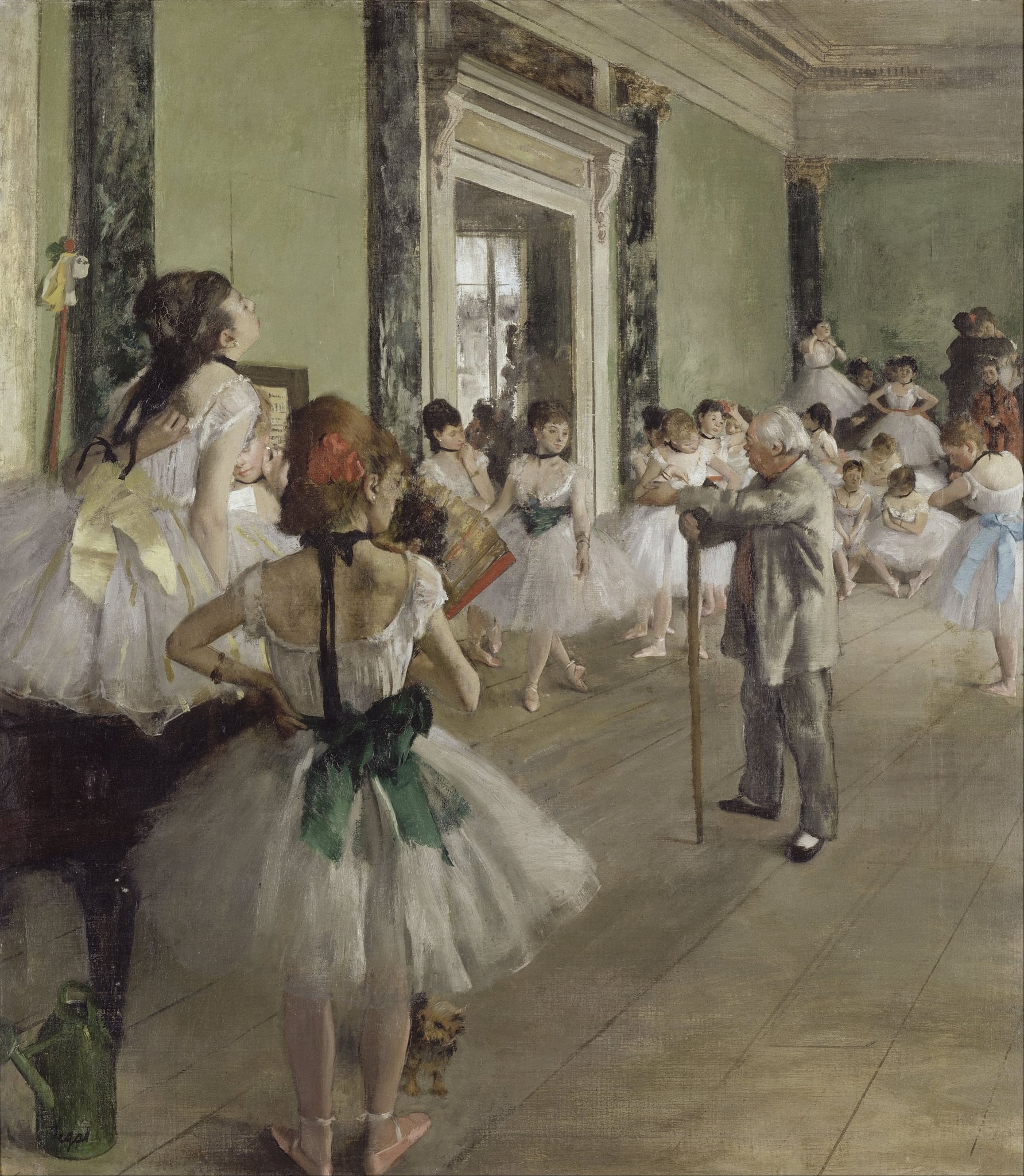

The Ballet Class
Edgar Degas (1873–1876)
<strong>The Ballet Class</strong> shows the work behind grace: a green-walled studio where young dancers in white tutus rest, fidget, and stretch while the gray-suited master stands with his cane. Degas’s diagonal floorboards, cropped viewpoints, and scattered props—a watering can, a music stand, even a tiny dog—stage a candid vision of routine rather than spectacle. The result is a modern image of discipline, hierarchy, and fleeting poise.

Woman Ironing
Edgar Degas (c. 1876–1887)
In Woman Ironing, Degas builds a modern icon of labor through <strong>contre‑jour</strong> light and a forceful diagonal from shoulder to iron. The worker’s silhouette, red-brown dress, and the cool, steamy whites around her turn repetition into <strong>ritualized transformation</strong>—wrinkled cloth to crisp order <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Rehearsal of the Ballet Onstage
Edgar Degas (ca. 1874)
Degas’s The Rehearsal of the Ballet Onstage turns a moment of practice into a modern drama of work and power. Under <strong>harsh footlights</strong>, clustered ballerinas stretch, yawn, and repeat steps as a <strong>ballet master/conductor</strong> drives the tempo, while <strong>abonnés</strong> lounge in the wings and a looming <strong>double bass</strong> anchors the labor of music <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

Place de la Concorde
Edgar Degas (1875)
Degas’s Place de la Concorde turns a famous Paris square into a study of <strong>modern isolation</strong> and <strong>instantaneous vision</strong>. Figures stride past one another without contact, their bodies abruptly <strong>cropped</strong> and adrift in a wide, airless plaza—an urban stage where elegance masks estrangement <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
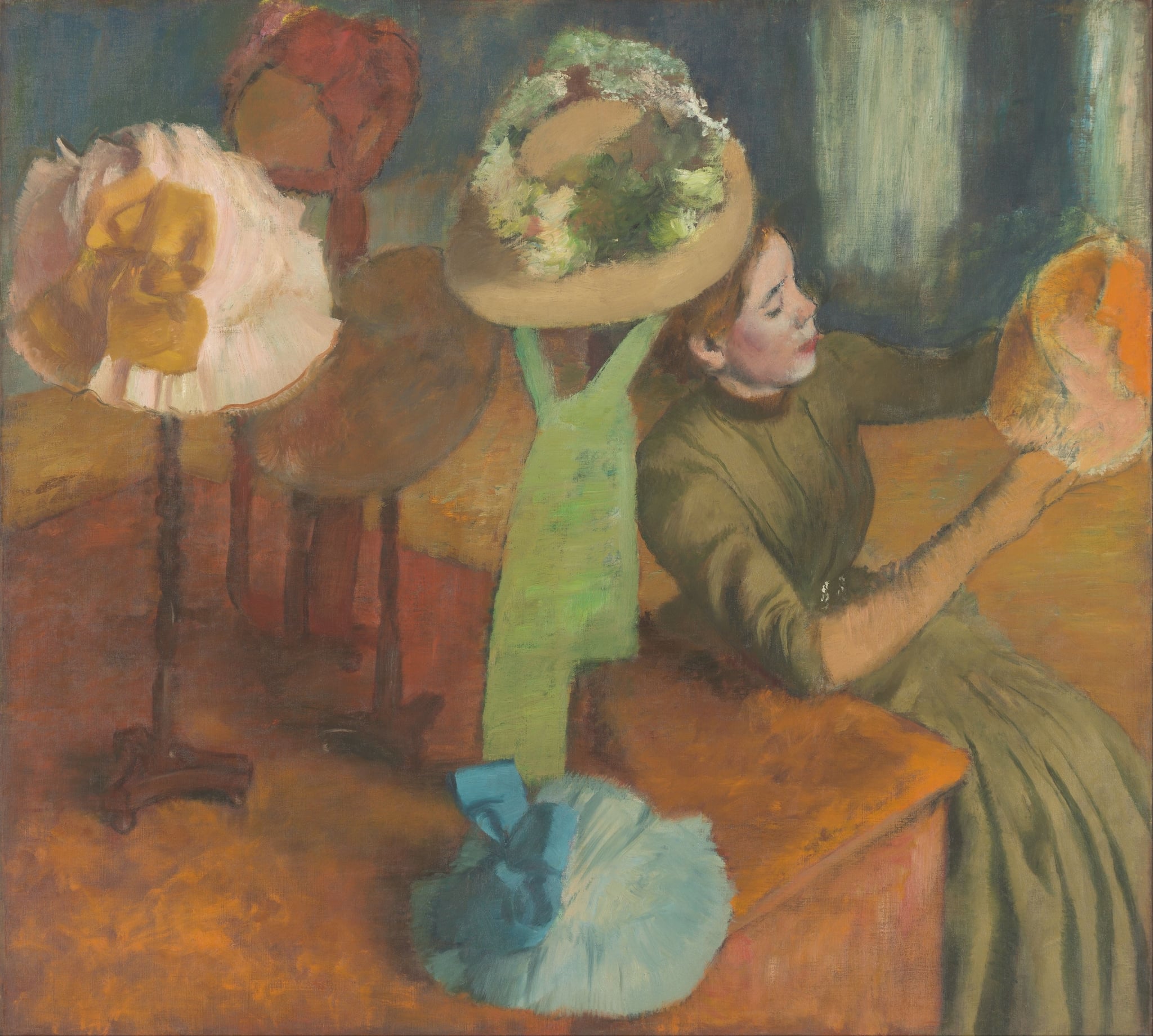

The Millinery Shop
Edgar Degas (1879–1886)
Edgar Degas’s The Millinery Shop stages modern Paris through a quiet act of <strong>work</strong> rather than display. A young woman, cropped in profile, studies a glowing <strong>orange hat</strong> while faceless stands crowned with ribbons and plumes press toward the picture plane. Degas turns a boutique into a meditation on <strong>labor, commodities, and identity</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
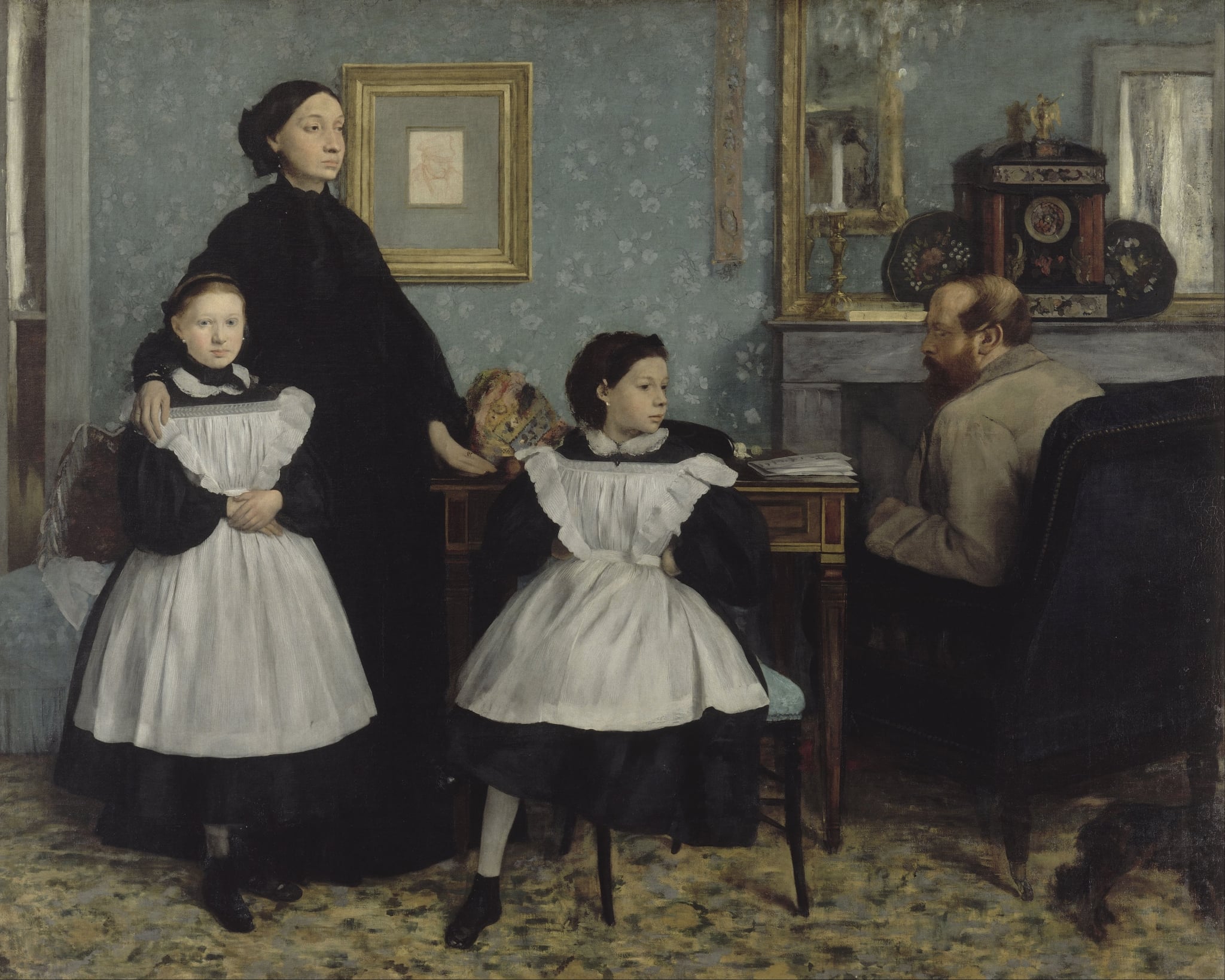
The Bellelli Family
Edgar Degas (1858–1869)
In The Bellelli Family, Edgar Degas orchestrates a poised domestic standoff, using the mother’s column of <strong>mourning black</strong>, the daughters’ <strong>mediating whiteness</strong>, and the father’s turned-away profile to script roles and distance. Rigid furniture lines, a gilt <strong>clock</strong>, and the ancestor’s red-chalk portrait create a stage where time, duty, and inheritance press on a family held in uneasy equilibrium.

The Star
Edgar Degas (c. 1876–1878)
Edgar Degas’s The Star shows a prima ballerina caught at the crest of a pose, her tutu a <strong>vaporous flare</strong> against a <strong>murky, tilted stage</strong>. Diagonal floorboards rush beneath her single pointe, while pale, ghostlike dancers linger in the wings, turning triumph into a scene of <strong>radiant isolation</strong> <sup>[2]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.
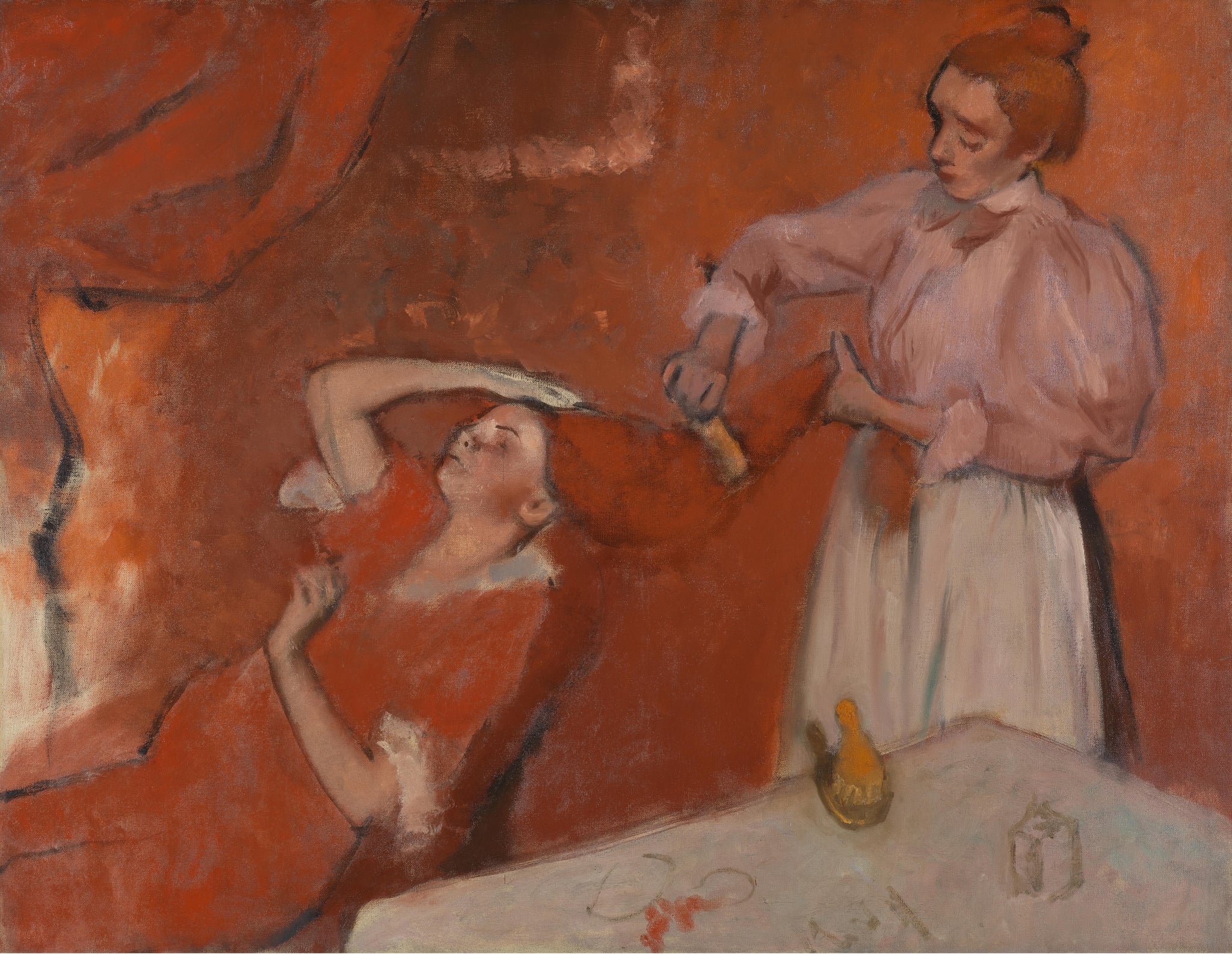

Combing the Hair
Edgar Degas (c.1896)
Edgar Degas’s Combing the Hair crystallizes a private ritual into a scene of <strong>compressed intimacy</strong> and <strong>classed labor</strong>. The incandescent field of red fuses figure and room, turning the hair into a <strong>binding ribbon</strong> between attendant and sitter <sup>[1]</sup>.
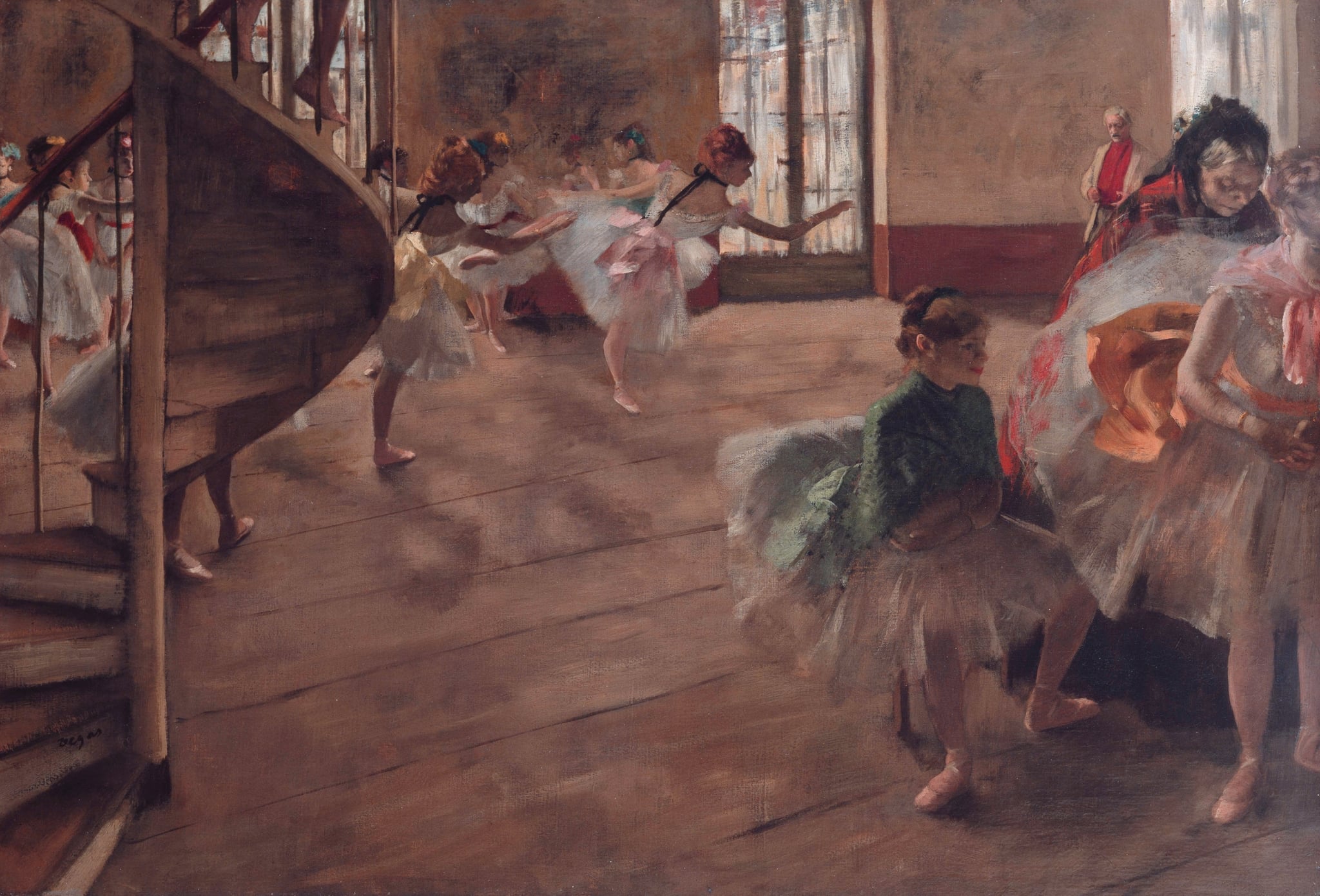

The Ballet Rehearsal
Edgar Degas (c. 1874)
In The Ballet Rehearsal, Edgar Degas turns a practice room into a modern drama where <strong>discipline and desire</strong> collide. A dark <strong>spiral staircase</strong> slices the space, scuffed floorboards yawn open, and clusters of dancers oscillate between poised effort and weary waiting <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.