Class & inequality
Featured Artworks

Woman in Black at the Opera
Mary Cassatt (1878)
Mary Cassatt’s Woman in Black at the Opera stages a taut drama of vision and visibility. A woman in <strong>black attire</strong> raises <strong>opera glasses</strong> while a distant man aims his own at her, setting off a chain of looks that makes public leisure a site of <strong>power, agency, and surveillance</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman with a Hat
Henri Matisse (1905)
In Woman with a Hat, Henri Matisse turns portraiture into a laboratory for <strong>pure color</strong> and <strong>modern identity</strong>. Jagged greens and violets carve the face; the hat detonates into a crown of brushstrokes; a fan slices the torso into bright planes. The result declares Fauvism’s credo: <strong>feeling over description</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Tea
Mary Cassatt (about 1880)
Mary Cassatt’s The Tea stages a poised, interior <strong>drama of manners</strong>: two women sit close yet feel apart, one thoughtful, the other raising a cup that <strong>veils her face</strong>. A gleaming, oversized <strong>silver tea service</strong> commands the foreground, its reflections turning ritual objects into actors in the scene <sup>[1]</sup>. The shallow, cropped room—striped wall, gilt mirror, marble mantel—compresses the atmosphere into <strong>intimacy edged by restraint</strong>.

Breakfast in Bed
Mary Cassatt (1897)
Breakfast in Bed distills a <strong>tender modern intimacy</strong> into a tightly cropped sanctuary of rumpled white linens, protective embrace, and interrupted routine. Mary Cassatt uses <strong>cool light</strong> against <strong>warm flesh</strong> to anchor attention on the mother’s encircling arm and the child’s outward gaze, fusing care, curiosity, and the rhythms of <strong>everyday modern life</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Boating
Claude Monet (1887)
Monet’s Boating crystallizes modern leisure as a drama of perception, setting a slim skiff and two pale dresses against a field of dark, mobile water. Bold cropping, a thrusting oar, and the complementary flash of hull and foliage convert a quiet outing into an experiment in <strong>modern vision</strong> and the <strong>materiality of water</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Venus of Urbino
Titian (1538)
Titian’s Venus of Urbino turns the mythic goddess into an ideal bride, merging frank <strong>eroticism</strong> with the codes of <strong>marital fidelity</strong>. In a Venetian bedroom, the nude’s direct gaze, roses, sleeping lapdog, and attendants at a cassone bind desire to domestic virtue and fertility <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Children Playing on the Beach
Mary Cassatt (1884)
In Children Playing on the Beach, Mary Cassatt brings the viewer down to a child’s eye level, granting everyday play the weight of <strong>serious, self-contained work</strong>. The cool horizon and tiny boats open onto <strong>modern space and possibility</strong>, while the cropped, tilted foreground seals us inside the children’s focused world <sup>[1]</sup>.

Women in the Garden
Claude Monet (1866–1867)
Claude Monet’s Women in the Garden choreographs four figures in a sunlit bower to test how <strong>white dresses</strong> register <strong>dappled light</strong> and shadow. The path, parasol, and clipped flowers frame a modern ritual of leisure while turning fashion into an instrument of <strong>perception</strong>. The scene reads less as portraiture than as a manifesto for painting the <strong>momentary</strong> outdoors <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

A Woman and a Girl Driving
Mary Cassatt (1881)
Cassatt stages a modern scene of <strong>female control</strong> in motion: a woman grips the reins and whip while a girl beside her mirrors the pose, and a groom seated behind looks away. The cropped horse and diagonal harness thrust the carriage forward, placing viewers inside a public outing in the Bois de Boulogne—an arena where visibility signaled status and autonomy <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Young Girls at the Piano
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1892)
Renoir’s Young Girls at the Piano turns a quiet lesson into a scene of <strong>attunement</strong> and <strong>bourgeois grace</strong>. Two adolescents—one seated at the keys, the other leaning to guide the score—embody harmony between discipline and delight, rendered in Renoir’s late, <strong>luminous</strong> touch <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Tub
Edgar Degas (1886)
In The Tub (1886), Edgar Degas turns a routine bath into a study of <strong>modern solitude</strong> and <strong>embodied labor</strong>. From a steep, overhead angle, a woman kneels within a circular basin, one hand braced on the rim while the other gathers her hair; to the right, a tabletop packs a ewer, copper pot, comb/brush, and cloth. Degas’s layered pastel binds skin, water, and objects into a single, breathing field of <strong>warm flesh tones</strong> and blue‑greys, collapsing distance between body and still life <sup>[1]</sup>.
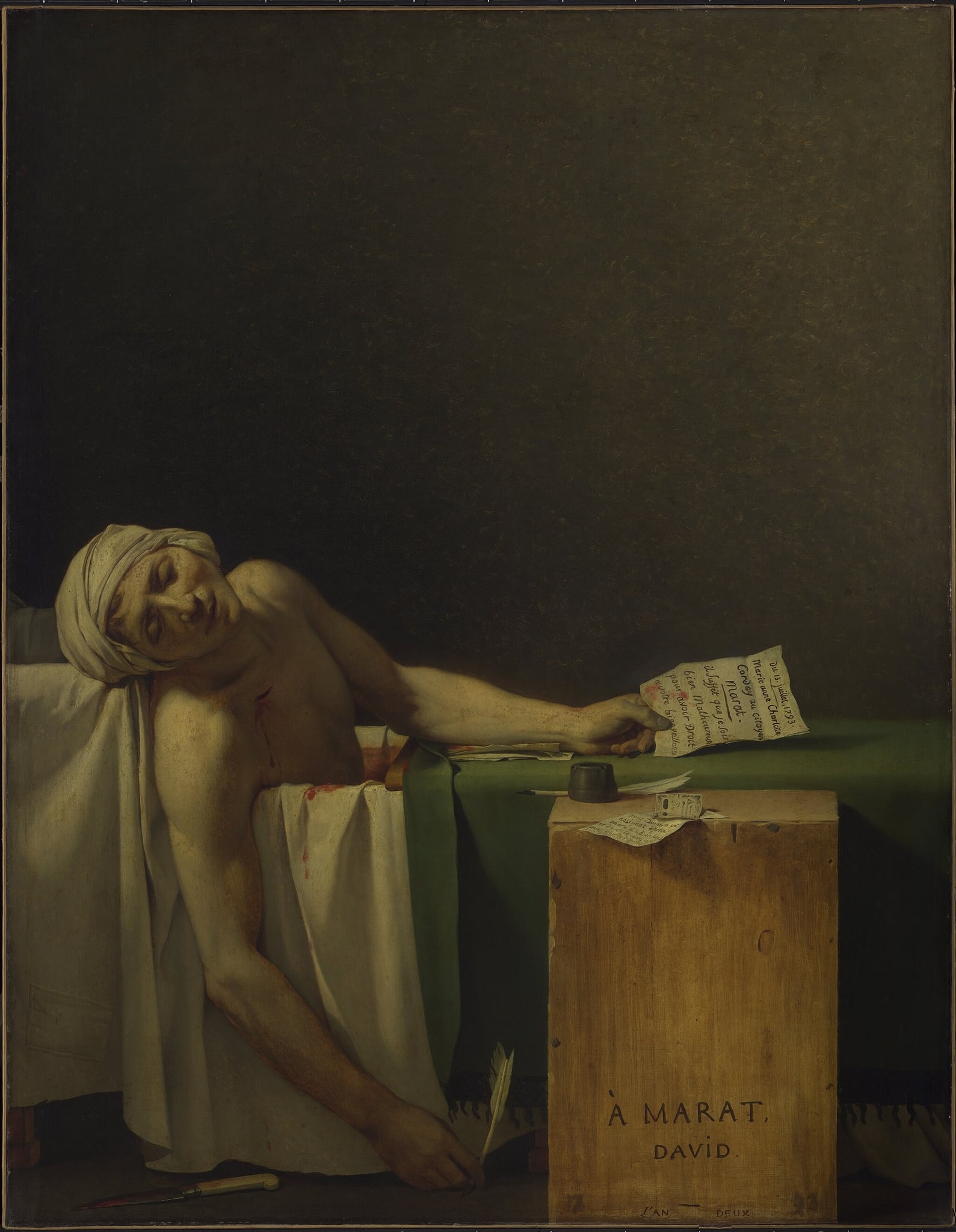

The Death of Marat
Jacques-Louis David (1793)
<strong>The Death of Marat</strong> turns a private murder into a <strong>secular martyrdom</strong>: Marat’s idealized body slumps in a bath, a pleading letter in his hand, a quill slipping from the other beside a bloodied knife and inkwell. Against a vast dark void, David’s calm light and austere geometry elevate humble objects—the green baize plank and the crate inscribed “À MARAT, DAVID, L’AN DEUX”—into civic emblems <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Pont Neuf Paris
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1872)
In Pont Neuf Paris, Pierre-Auguste Renoir turns the oldest bridge in Paris into a stage where <strong>light</strong> and <strong>movement</strong> bind a city back together. From a high perch, he orchestrates crowds, carriages, gas lamps, the rippling Seine, and a fluttering <strong>tricolor</strong> so that everyday bustle reads as civic grace <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Hermitage at Pontoise
Camille Pissarro (ca. 1867)
Camille Pissarro’s The Hermitage at Pontoise shows a hillside village interlaced with <strong>kitchen gardens</strong>, stone houses, and workers bent to their tasks under a <strong>low, cloud-laden sky</strong>. The painting binds human labor to place, staging a quiet counterpoint between <strong>architectural permanence</strong> and the <strong>seasonal flux</strong> of fields and weather <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.

Laundresses Carrying Linen in Town
Camille Pissarro (1879)
In Laundresses Carrying Linen in Town, two working women strain under <strong>white bundles</strong> that flare against a <strong>flat yellow ground</strong> and a <strong>dark brown band</strong>. The abrupt cropping and opposing diagonals turn anonymous labor into a <strong>monumental, modern frieze</strong> of effort and motion.

The Loge
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s The Loge (1874) turns an opera box into a <strong>stage of looking</strong>, where a woman meets our gaze while her companion scans the crowd through binoculars. The painting’s <strong>frame-within-a-frame</strong> and glittering fashion make modern Parisian leisure both alluring and self-conscious, turning spectators into spectacles <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman Reading
Édouard Manet (1880–82)
Manet’s Woman Reading distills a fleeting act into an emblem of <strong>modern self-possession</strong>: a bundled figure raises a journal-on-a-stick, her luminous profile set against a brisk mosaic of greens and reds. With quick, loaded strokes and a deliberately cropped <strong>beer glass</strong> and paper, Manet turns perception itself into subject—asserting the drama of a private mind within a public café world <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman Ironing
Edgar Degas (c. 1876–1887)
In Woman Ironing, Degas builds a modern icon of labor through <strong>contre‑jour</strong> light and a forceful diagonal from shoulder to iron. The worker’s silhouette, red-brown dress, and the cool, steamy whites around her turn repetition into <strong>ritualized transformation</strong>—wrinkled cloth to crisp order <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Madame Monet and Her Son
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s 1874 canvas Madame Monet and Her Son crystallizes <strong>modern domestic leisure</strong> and <strong>plein‑air immediacy</strong> in Argenteuil. A luminous white dress pools into light while a child in a pale‑blue sailor suit reclines diagonally; a strutting rooster punctuates the greens with warm color. The brushwork fuses figure and garden so the moment reads as <strong>lived, not staged</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The Floor Scrapers
Gustave Caillebotte (1875)
Gustave Caillebotte’s The Floor Scrapers stages three shirtless workers planing a parquet floor as shafts of light pour through an ornate balcony door. The painting fuses <strong>rigorous perspective</strong> with <strong>modern urban labor</strong>, turning curls of wood and raking light into a ledger of time and effort <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. Its cool, gilded interior makes visible how bourgeois elegance is built on bodily work.

Paris Street; Rainy Day
Gustave Caillebotte (1877)
Gustave Caillebotte’s Paris Street; Rainy Day renders a newly modern Paris where <strong>Haussmann’s geometry</strong> meets the <strong>anonymity of urban life</strong>. Umbrellas punctuate a silvery atmosphere as a <strong>central gas lamp</strong> and knife-sharp façades organize the space into measured planes <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Rehearsal of the Ballet Onstage
Edgar Degas (ca. 1874)
Degas’s The Rehearsal of the Ballet Onstage turns a moment of practice into a modern drama of work and power. Under <strong>harsh footlights</strong>, clustered ballerinas stretch, yawn, and repeat steps as a <strong>ballet master/conductor</strong> drives the tempo, while <strong>abonnés</strong> lounge in the wings and a looming <strong>double bass</strong> anchors the labor of music <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.

Regatta at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
On a brilliant afternoon at the Normandy coast, a diagonal <strong>pebble beach</strong> funnels spectators with parasols toward a bay scattered with <strong>white-sailed yachts</strong>. Monet’s quick, broken strokes set <strong>wind, water, and light</strong> in synchrony, turning a local regatta into a modern scene of leisure held against the vastness of sea and sky <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Dance at Bougival
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1883)
In Dance at Bougival, Pierre-Auguste Renoir turns a crowded suburban dance into a <strong>private vortex of intimacy</strong>. Rose against ultramarine, skin against shade, and a flare of the woman’s <strong>scarlet bonnet</strong> concentrate the scene’s energy into a single turning moment—modern leisure made palpable as <strong>touch, motion, and light</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Beach at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
In The Beach at Sainte-Adresse, Claude Monet stages a modern shore where <strong>labor and leisure intersect</strong> under a broad, changeable sky. The bright <strong>blue beached boat</strong> and the flotilla of <strong>rust-brown working sails</strong> punctuate a turquoise channel, while a fashionably dressed pair sits mid-beach, spectators to the traffic of the port. Monet’s brisk, broken strokes make the scene feel <strong>caught between tides and weather</strong>, a momentary balance of work, tourism, and atmosphere <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
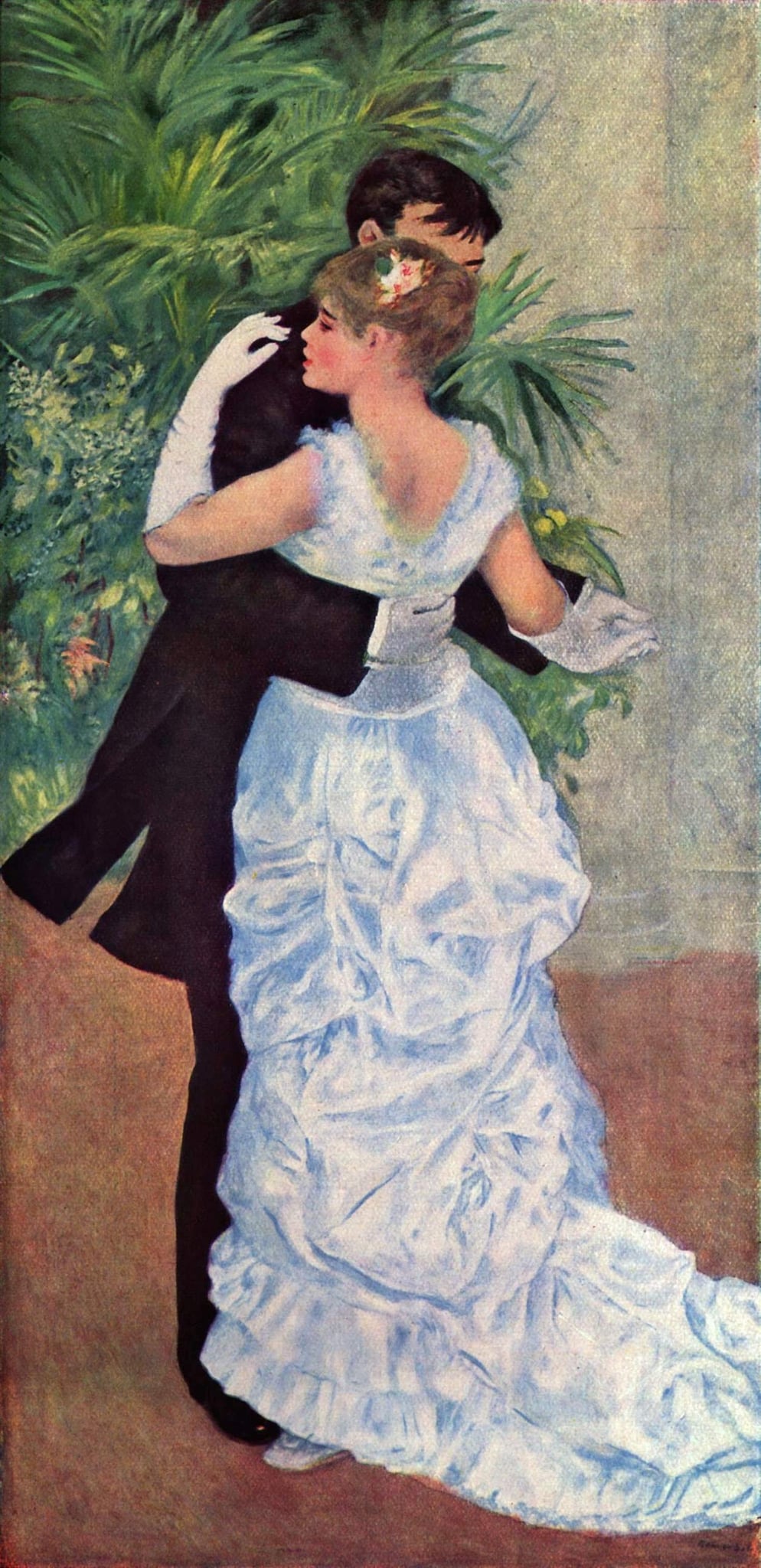

Dance in the City
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1883)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir’s Dance in the City stages an urban waltz where decorum and desire briefly coincide. A couple’s close embrace—his black tailcoat enclosing her luminous white satin gown—creates a <strong>cool, elegant</strong> harmony against potted palms and marble. Renoir’s refined, post‑Impressionist touch turns social ritual into <strong>sensual modernity</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
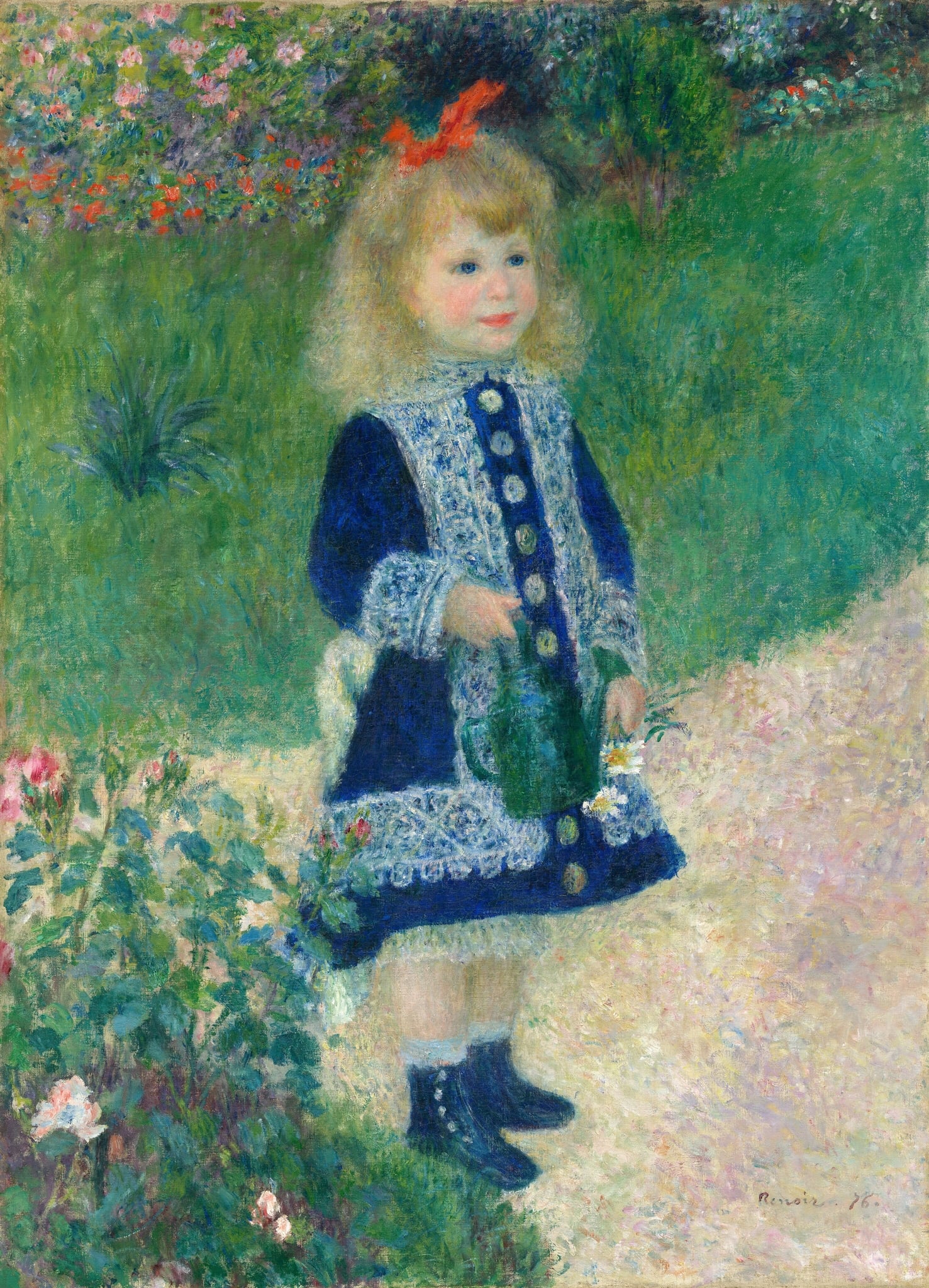
Girl with a Watering Can
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1876)
Renoir’s 1876 Girl with a Watering Can fuses a crisply perceived child with a dissolving garden atmosphere, using <strong>prismatic color</strong> and <strong>controlled facial modeling</strong> to stage innocence within modern leisure <sup>[1]</sup>. The cobalt dress, red bow, and green can punctuate a haze of pinks and greens, making nurture and growth the scene’s quiet thesis.
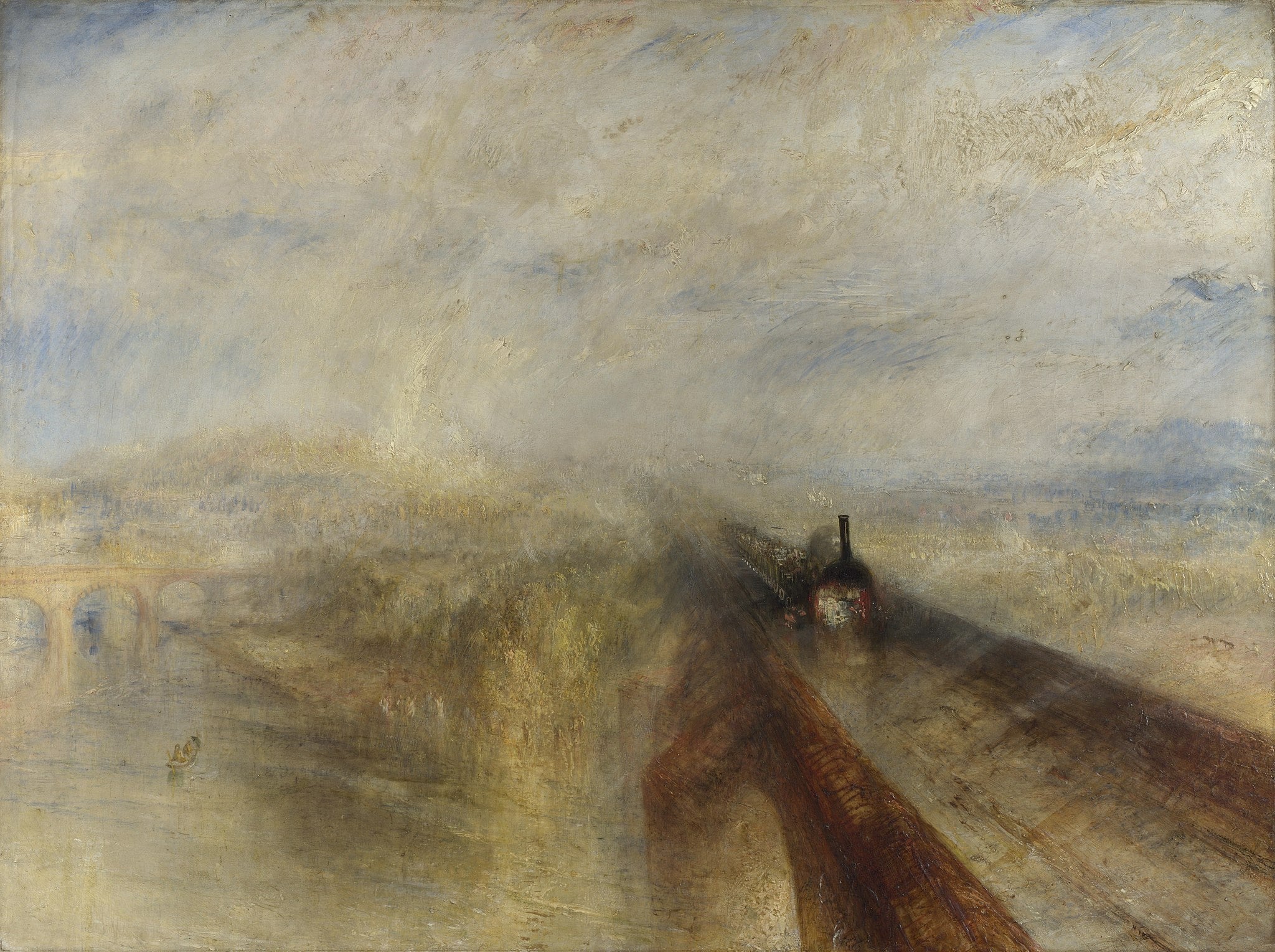

Rain, Steam and Speed
J. M. W. Turner (1844)
In Rain, Steam and Speed, J. M. W. Turner fuses weather and industry into a single onrushing vision, as a dark locomotive thrusts along the diagonal of Brunel’s Maidenhead Railway Bridge through veils of rain and light. The blurred fields, river, and town dissolve into a charged atmosphere where <strong>rain</strong>, <strong>steam</strong>, and <strong>speed</strong> become the true subjects. Counter-motifs—a small boat beneath pale arches and a near-invisible hare ahead of the train—stage a drama between pre‑industrial life and modern velocity <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Place de la Concorde
Edgar Degas (1875)
Degas’s Place de la Concorde turns a famous Paris square into a study of <strong>modern isolation</strong> and <strong>instantaneous vision</strong>. Figures stride past one another without contact, their bodies abruptly <strong>cropped</strong> and adrift in a wide, airless plaza—an urban stage where elegance masks estrangement <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
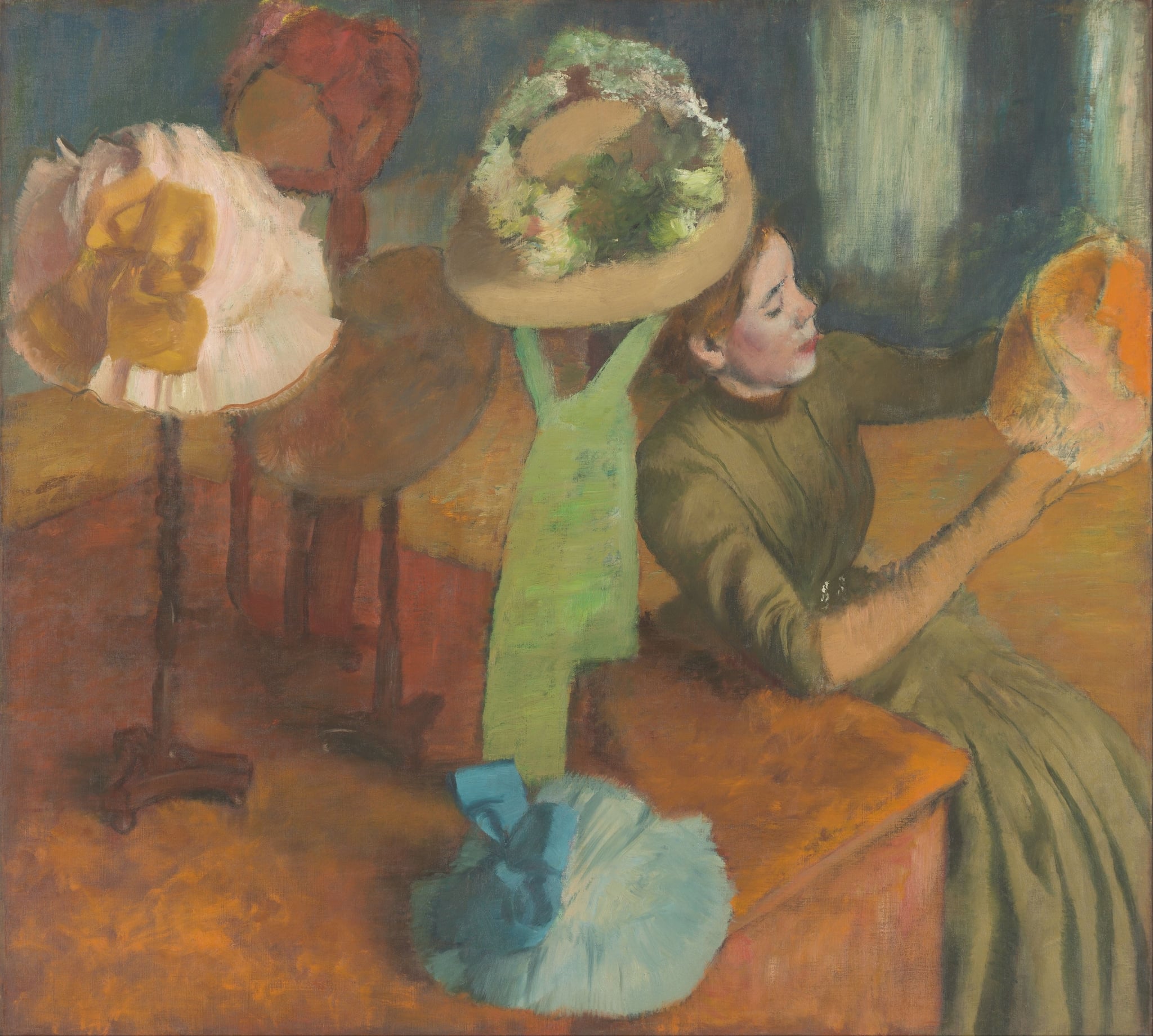

The Millinery Shop
Edgar Degas (1879–1886)
Edgar Degas’s The Millinery Shop stages modern Paris through a quiet act of <strong>work</strong> rather than display. A young woman, cropped in profile, studies a glowing <strong>orange hat</strong> while faceless stands crowned with ribbons and plumes press toward the picture plane. Degas turns a boutique into a meditation on <strong>labor, commodities, and identity</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
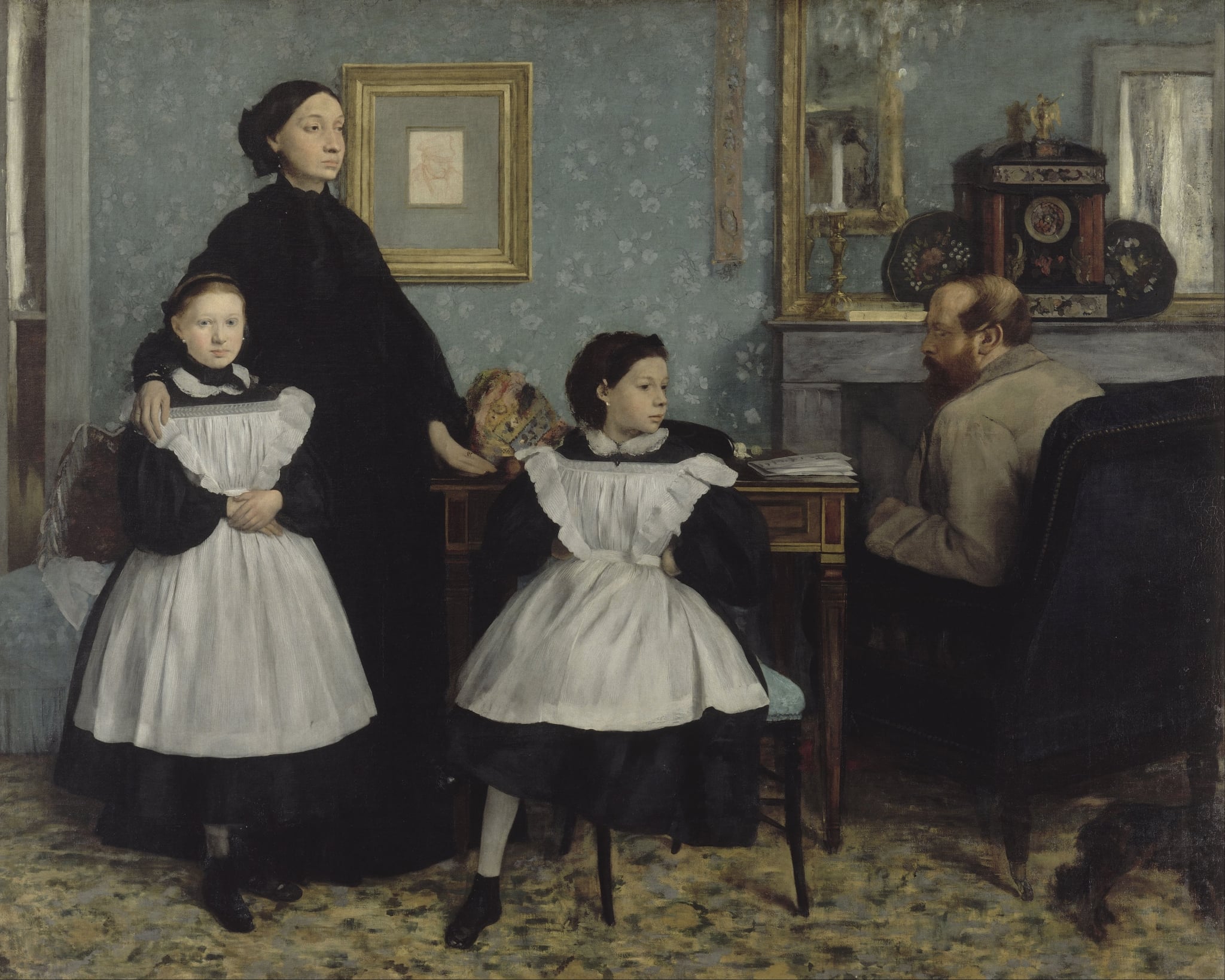
The Bellelli Family
Edgar Degas (1858–1869)
In The Bellelli Family, Edgar Degas orchestrates a poised domestic standoff, using the mother’s column of <strong>mourning black</strong>, the daughters’ <strong>mediating whiteness</strong>, and the father’s turned-away profile to script roles and distance. Rigid furniture lines, a gilt <strong>clock</strong>, and the ancestor’s red-chalk portrait create a stage where time, duty, and inheritance press on a family held in uneasy equilibrium.
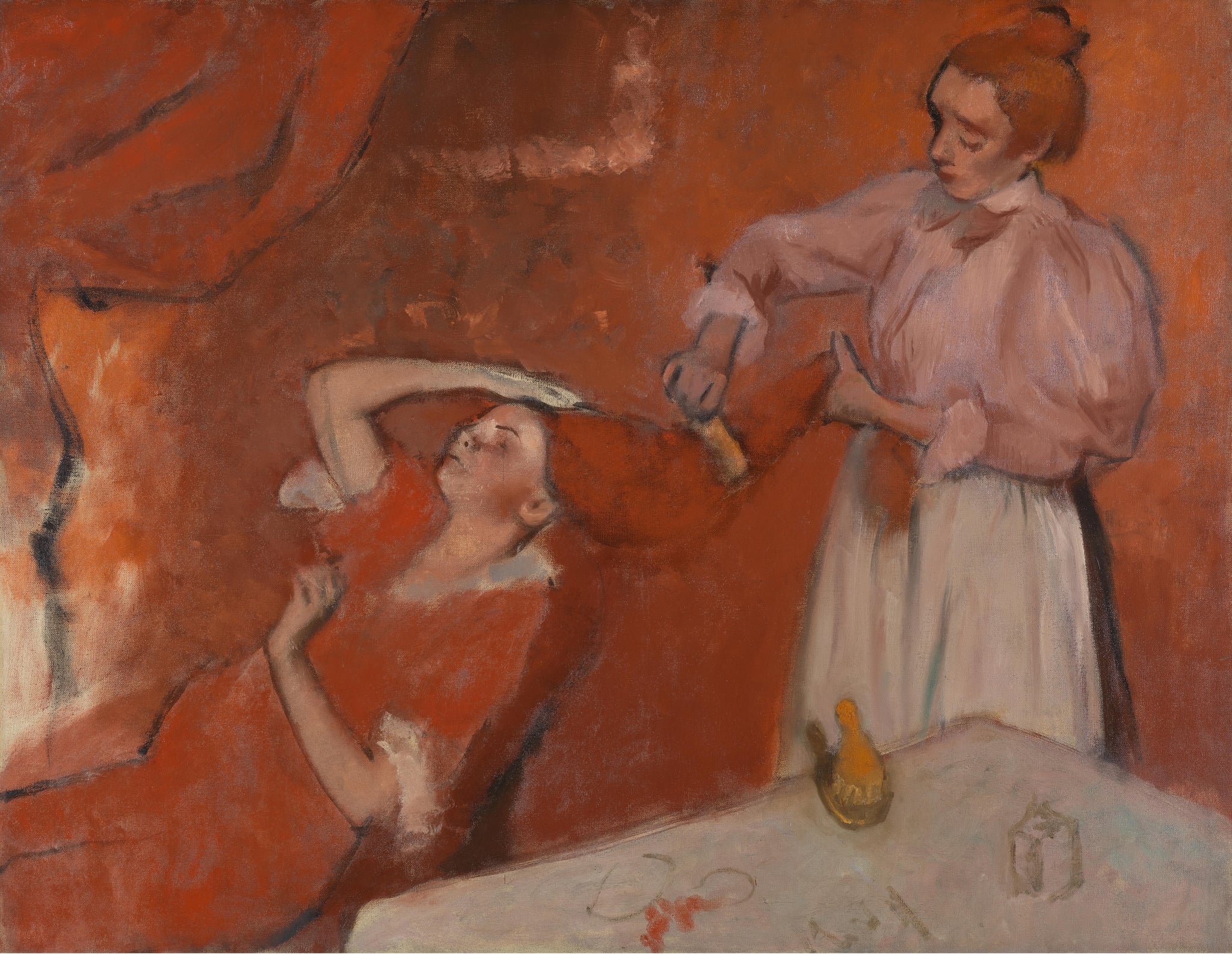

Combing the Hair
Edgar Degas (c.1896)
Edgar Degas’s Combing the Hair crystallizes a private ritual into a scene of <strong>compressed intimacy</strong> and <strong>classed labor</strong>. The incandescent field of red fuses figure and room, turning the hair into a <strong>binding ribbon</strong> between attendant and sitter <sup>[1]</sup>.

The Umbrellas
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (about 1881–86)
A sudden shower turns a Paris street into a lattice of <strong>slate‑blue umbrellas</strong>, knitting strangers into a single moving frieze. A bareheaded young woman with a <strong>bandbox</strong> strides forward while a bourgeois mother and children cluster at right, their <strong>hoop</strong> echoing the umbrellas’ arcs <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.
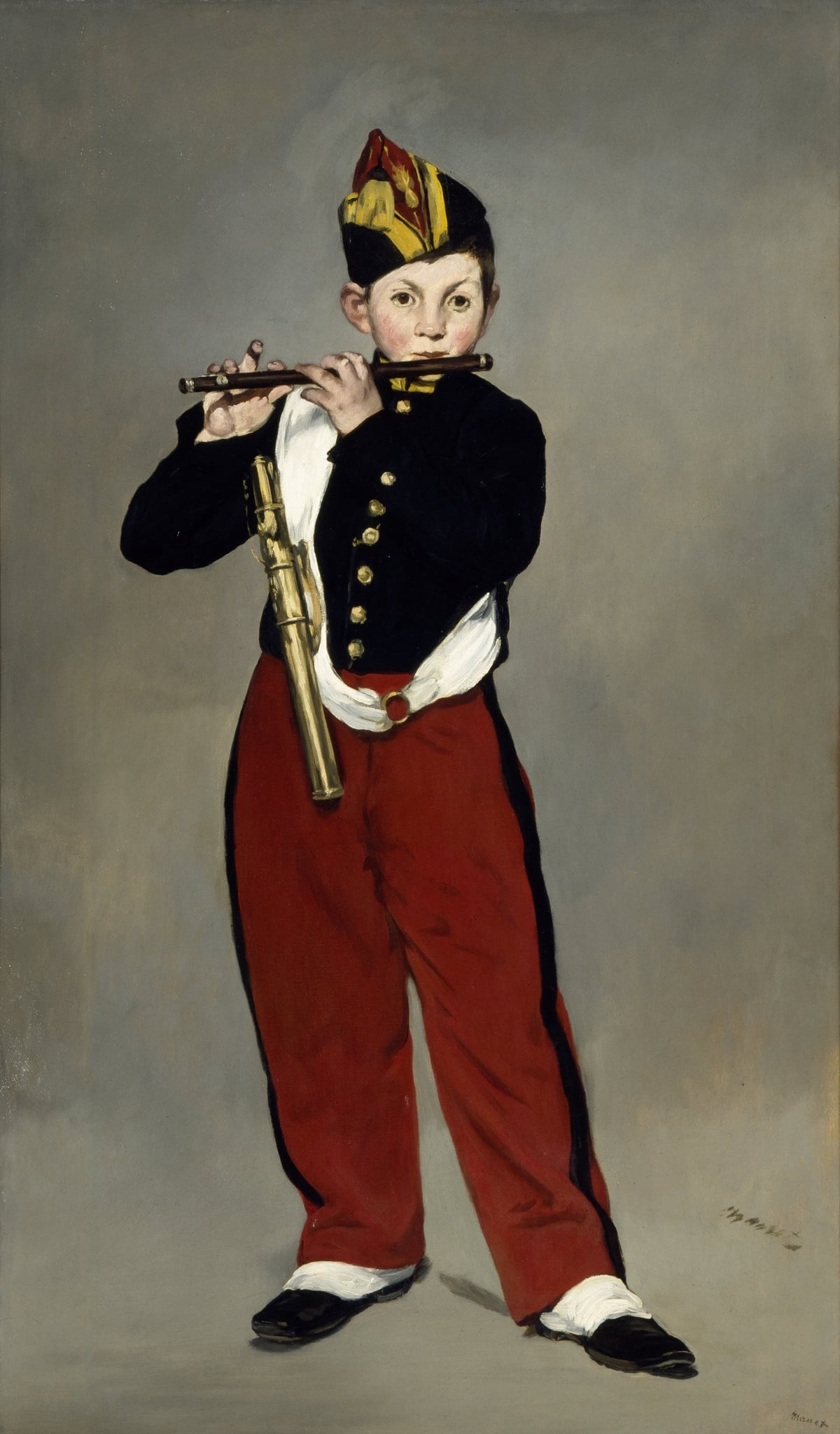

The Fifer
Édouard Manet (1866)
In The Fifer, <strong>Édouard Manet</strong> monumentalizes an anonymous military child by isolating him against a flat, gray field, converting everyday modern life into a subject of high pictorial dignity. The crisp <strong>silhouette</strong>, blocks of <strong>unmodulated color</strong> (black tunic, red trousers, white gaiters), and glints on the brass case make sound and discipline palpable without narrative scaffolding <sup>[1]</sup>. Drawing on <strong>Velázquez’s single-figure-in-air</strong> formula yet inflected by japonisme’s flatness, Manet forges a new modern image that the Salon rejected in 1866 <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
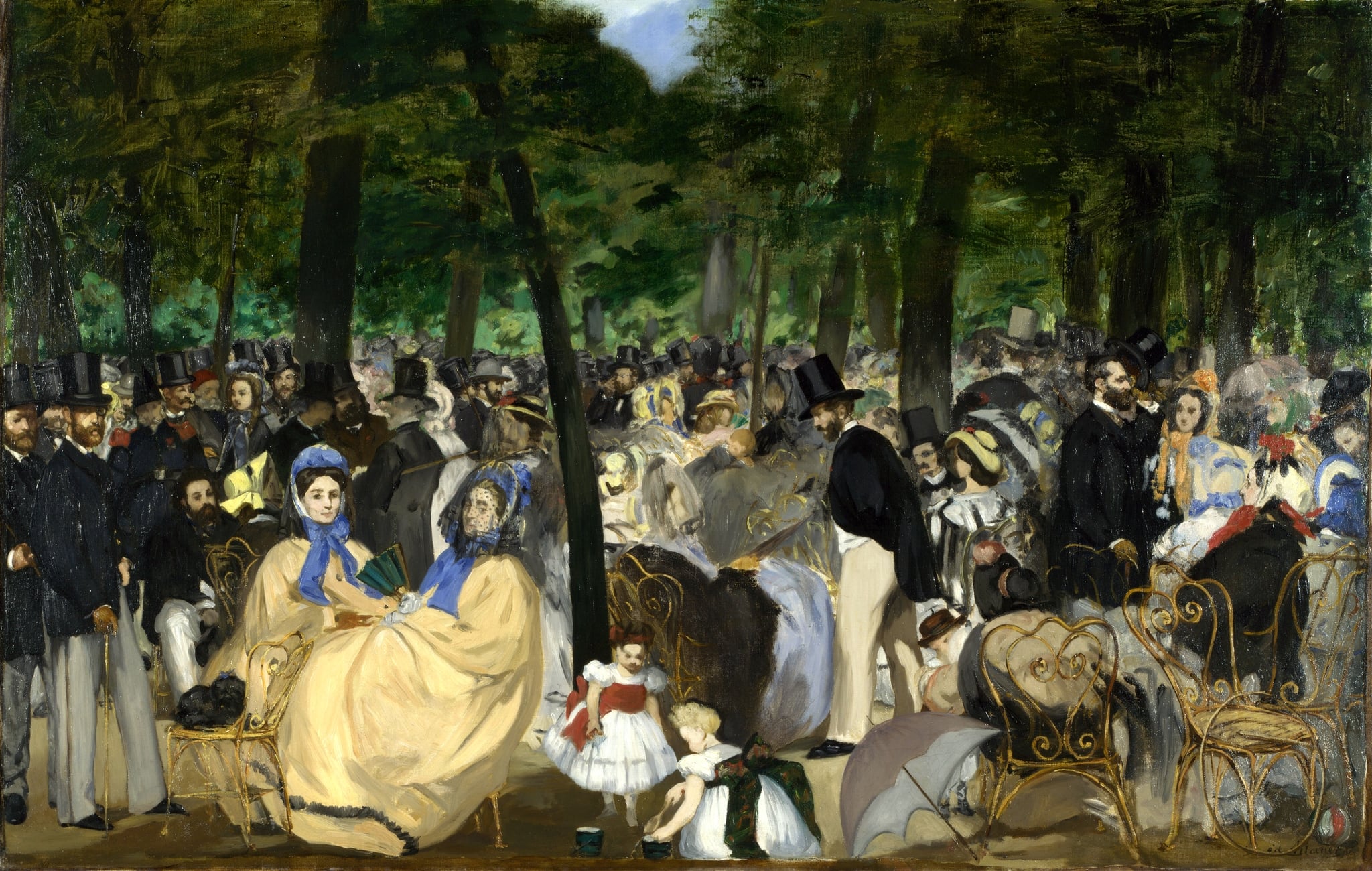

Music in the Tuileries
Édouard Manet (1862)
Édouard Manet’s Music in the Tuileries turns a Sunday concert into a manifesto of <strong>modern life</strong>: a frieze of top hats, crinolines, and iron chairs flickering beneath <strong>toxic green</strong> foliage. Instead of a hero or center, the painting disperses attention across a restless crowd, making <strong>looking itself</strong> the drama of the scene <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
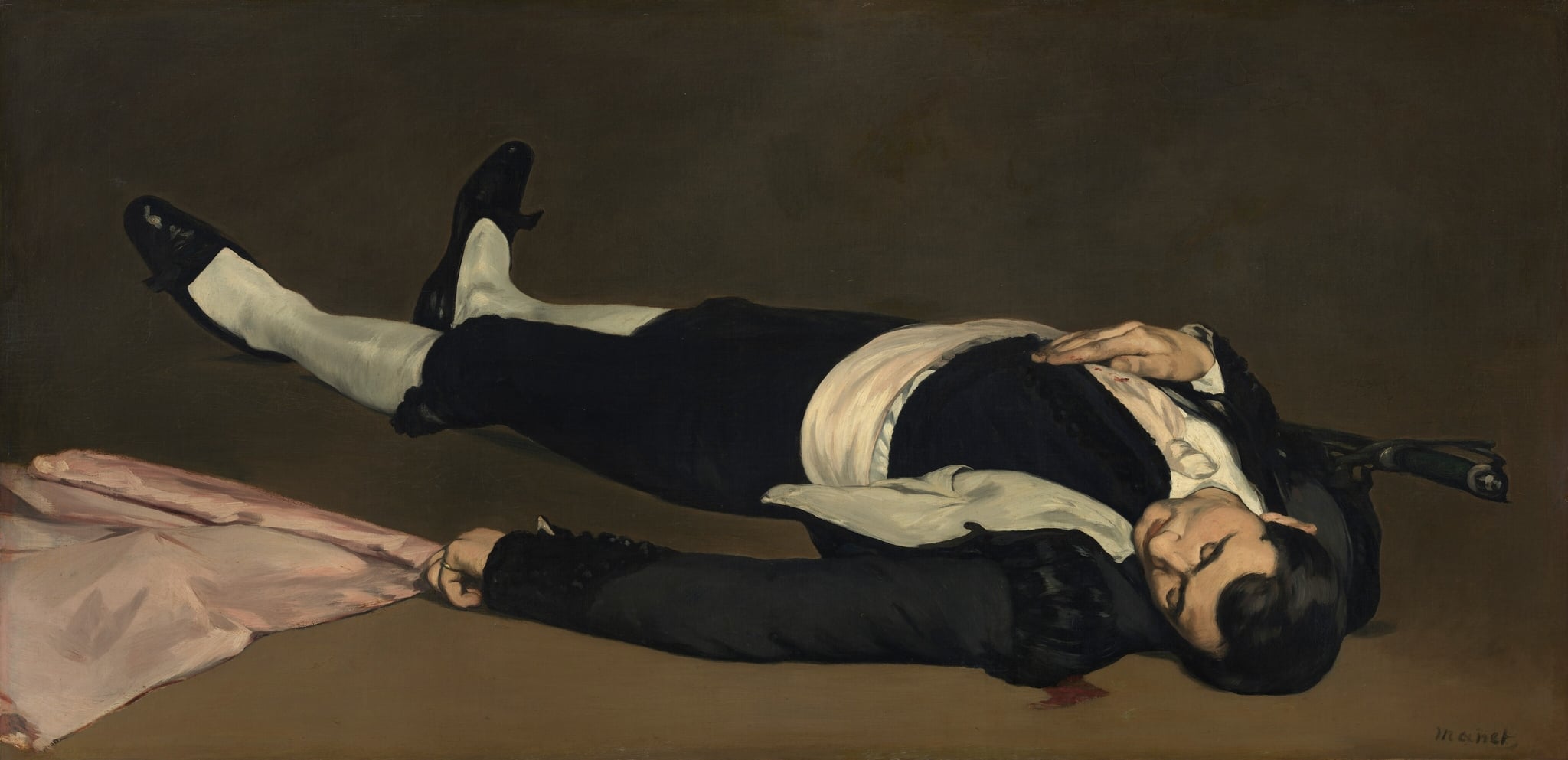

The Dead Toreador
Édouard Manet (probably 1864)
Manet’s The Dead Toreador isolates a matador’s corpse in a stark, horizontal close‑up, replacing the spectacle of the bullring with <strong>silence</strong> and <strong>abrupt finality</strong>. Black costume, white stockings, a pale pink cape, the sword’s hilt, and a small <strong>pool of blood</strong> become the painting’s cool, modern vocabulary of death <sup>[1]</sup>.
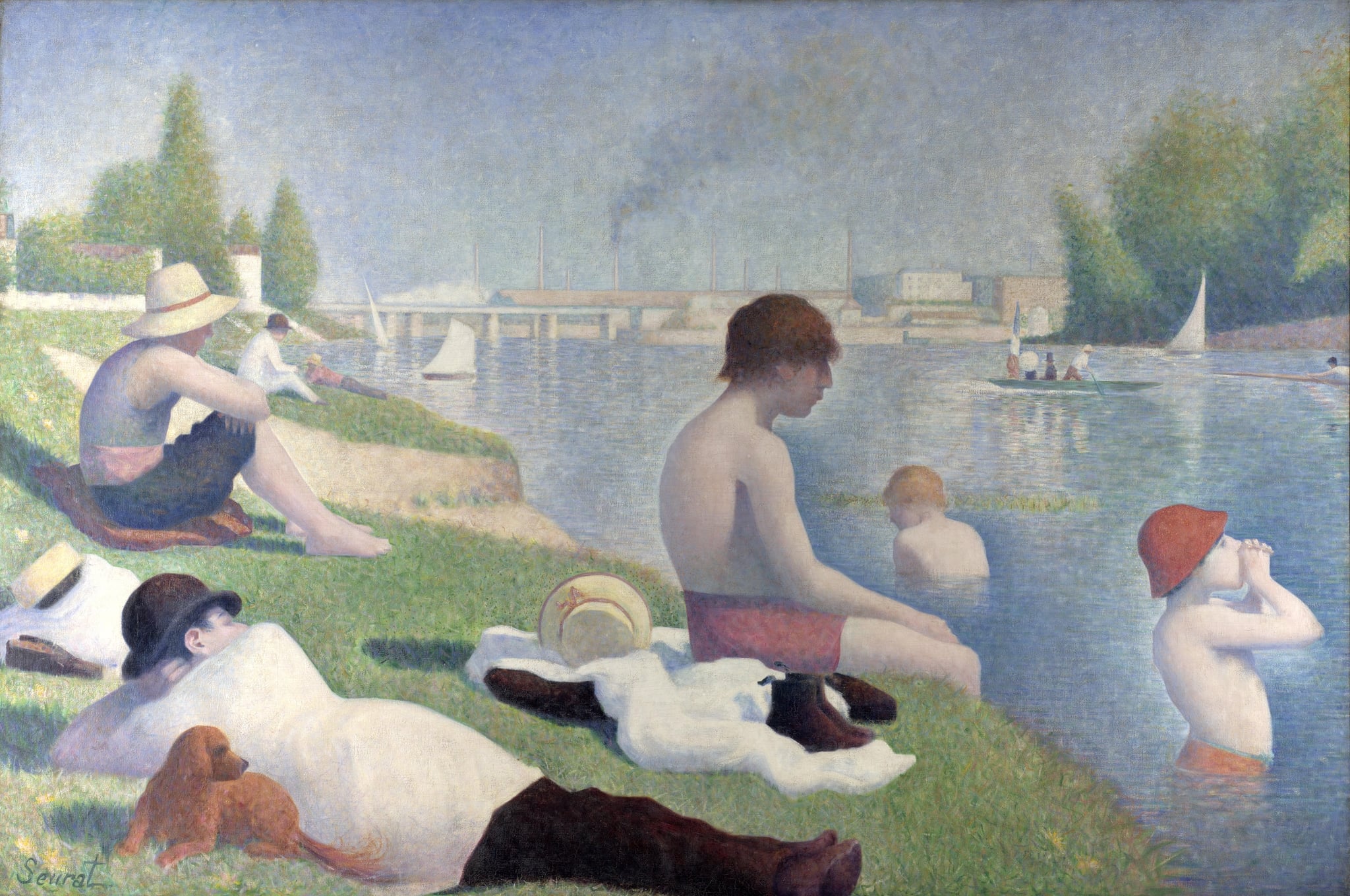

Bathers at Asnières
Georges Seurat (1884)
Bathers at Asnières stages a scene of <strong>modern leisure</strong> on the Seine, where workers recline and wade beneath a hazy, unified light. Seurat fuses <strong>classicizing stillness</strong> with an <strong>industrial backdrop</strong> of chimneys, bridges, and boats, turning ordinary rest into a monumental, ordered image of urban life <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. The canvas balances soft greens and blues with geometric structures, producing a calm yet charged harmony.
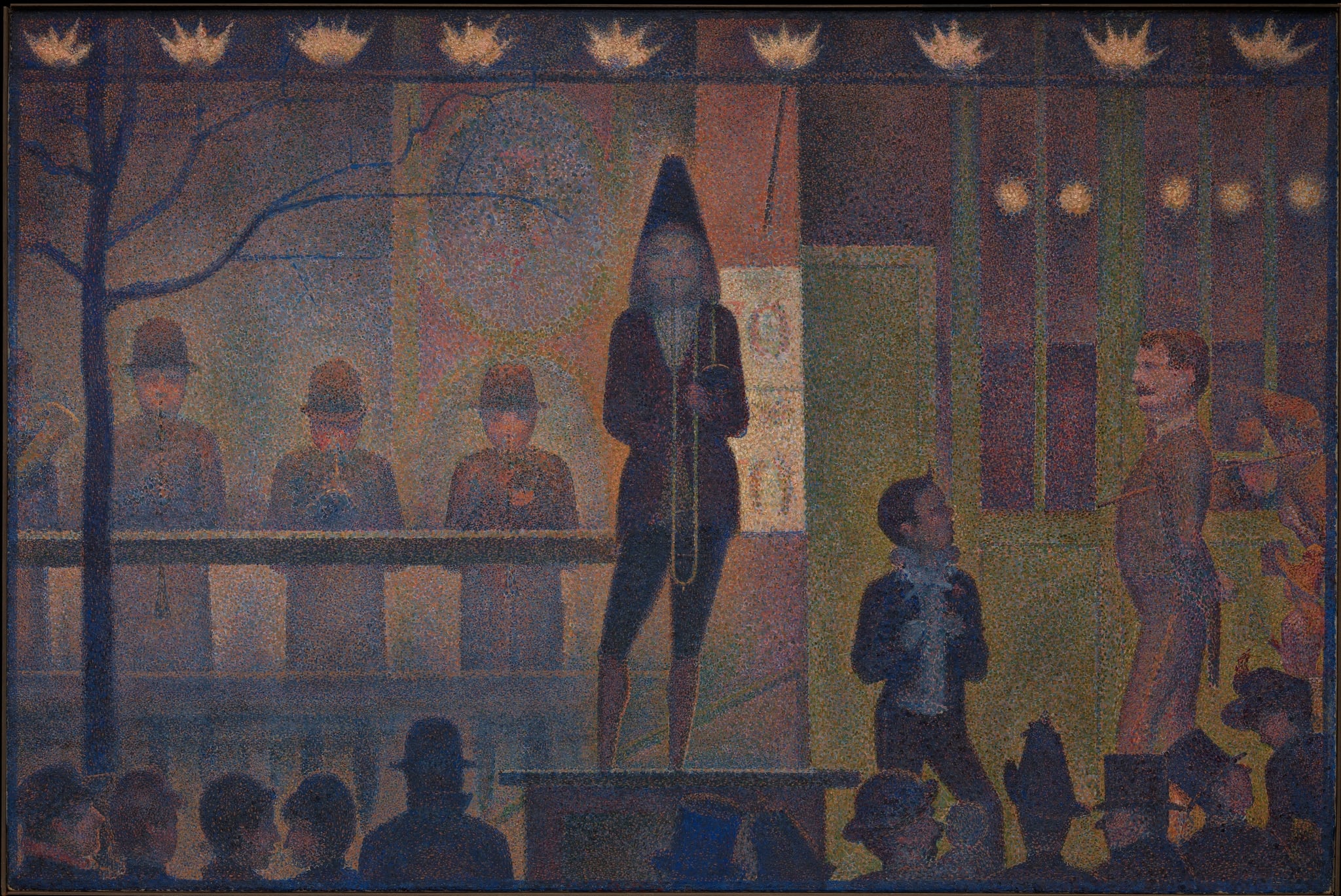

Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque)
Georges Seurat (1887–88)
Circus Sideshow (Parade de cirque) distills a bustling Paris fairground into a cool, ritualized <strong>threshold</strong> between street and spectacle. Under nine crownlike <strong>gaslights</strong>, a barker, musicians, and attendants align with geometric restraint while the crowd remains a band of silhouettes, held at the edge. Seurat’s <strong>Neo‑Impressionist</strong> dots make the night hum yet stay eerily still, turning publicity into a modern icon of order and mood <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Cup of Tea
Mary Cassatt (ca. 1880–81)
Mary Cassatt’s The Cup of Tea distills a moment of bourgeois leisure into a study of <strong>poise</strong>, <strong>etiquette</strong>, and <strong>private reflection</strong>. A woman in a rose‑pink dress and bonnet, white‑gloved, balances a gold‑rimmed cup against the shimmer of <strong>Impressionist</strong> brushwork, while a green planter of pale blossoms echoes her pastel palette <sup>[1]</sup>. The work turns an ordinary ritual into a modern emblem of women’s experience.
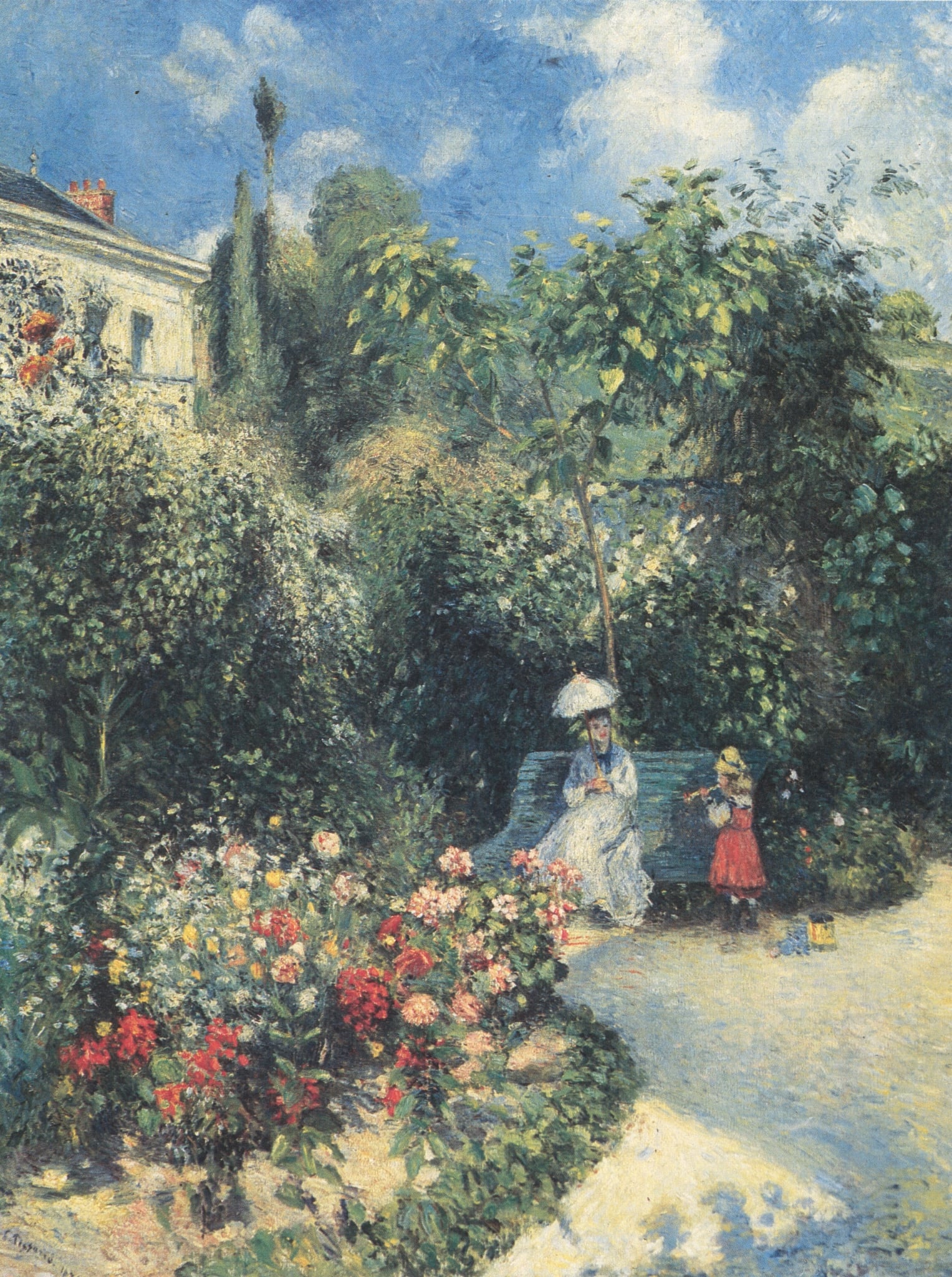
The Garden of Pontoise
Camille Pissarro (1874)
In The Garden of Pontoise, Camille Pissarro turns a modest suburban plot into a stage for <strong>modern leisure</strong> and <strong>fugitive light</strong>. A woman shaded by a parasol and a child in a bright red skirt punctuate the deep greens, while a curving sand path and beds of red–pink blossoms draw the eye toward a pale house and cloud‑flecked sky. The painting asserts that everyday, cultivated nature can be a <strong>modern Eden</strong> where time, season, and social ritual quietly unfold <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
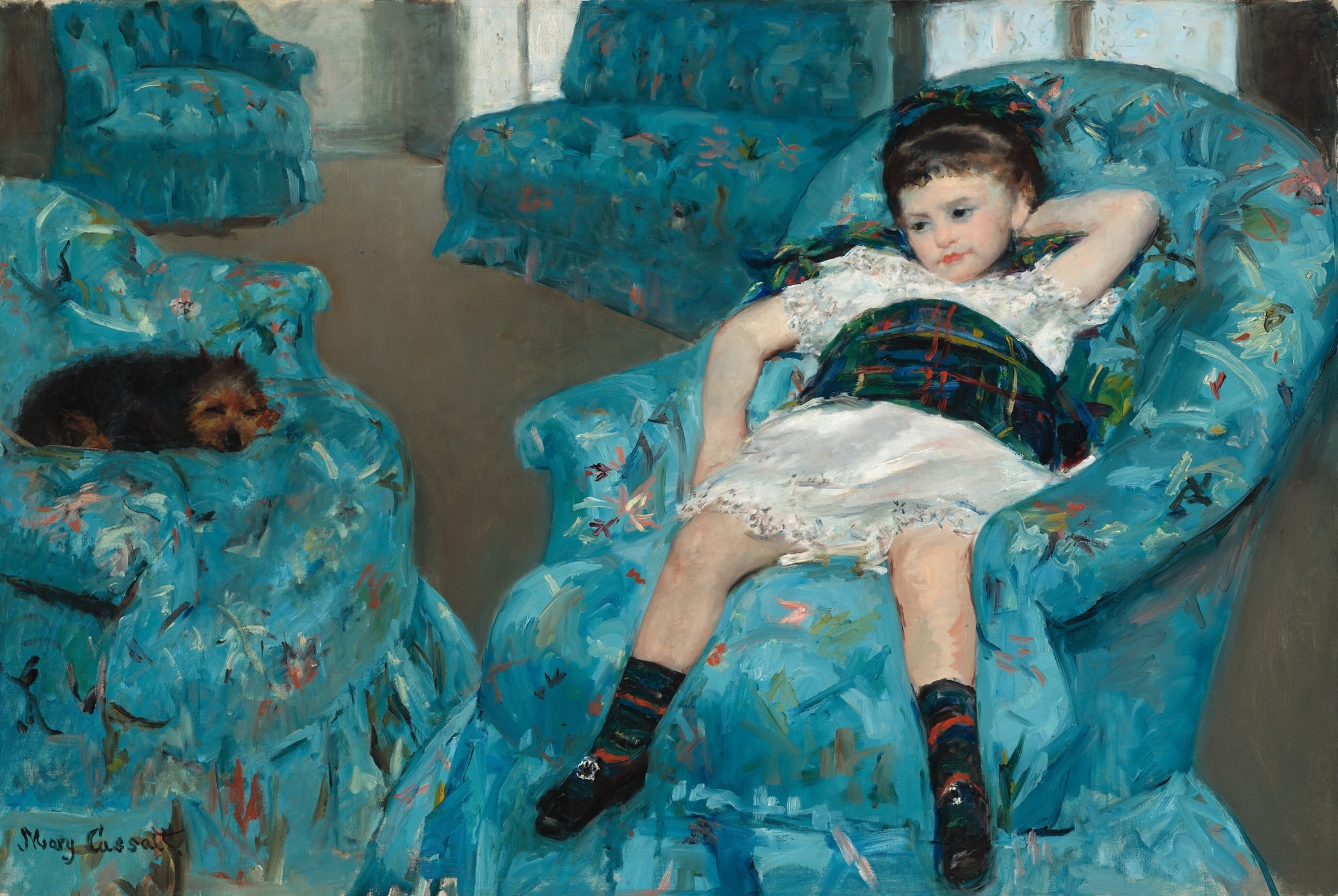

Little Girl in a Blue Armchair
Mary Cassatt (1878)
Mary Cassatt’s Little Girl in a Blue Armchair renders a child slumped diagonally across an oversized seat, surrounded by a flotilla of blue chairs and cool window light. With brisk, broken strokes and a skewed recession, Cassatt asserts a modern, unsentimental view of childhood—bored, autonomous, and <strong>out of step with adult decorum</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>. Subtle collaboration with <strong>Degas</strong> in the background design sharpens the picture’s daring spatial thrust <sup>[2]</sup>.

In the Loge
Mary Cassatt (1878)
Mary Cassatt’s In the Loge (1878) stages modern spectatorship as a drama of <strong>mutual looking</strong>. A woman in dark dress leans forward with <strong>opera glasses</strong>, her <strong>fan closed</strong> on her lap, as a man in the distance raises his own glasses toward her—turning the theater into a circuit of gazes <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Woman with a Pearl Necklace in a Loge
Mary Cassatt (1879)
Mary Cassatt’s Woman with a Pearl Necklace in a Loge (1879) stages modern <strong>spectatorship</strong> inside a plush opera box, where a young woman in pink satin, pearls, and gloves occupies the red velvet seat while a mirror multiplies the chandeliers and balconies. Cassatt fuses <strong>intimacy</strong> and <strong>public display</strong>, using luminous brushwork to place her sitter within the social theater of Parisian leisure <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.
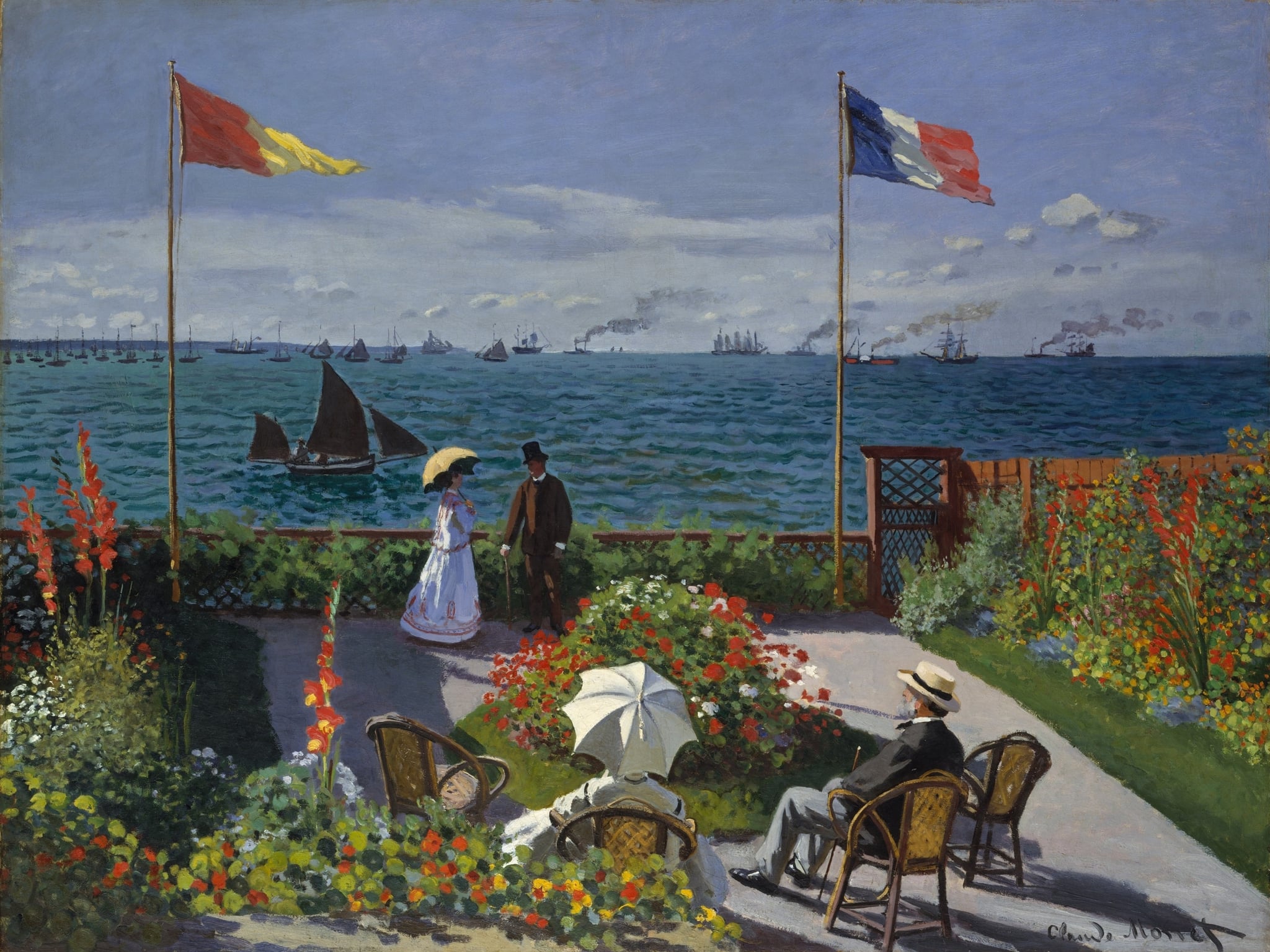

The Terrace at Sainte-Adresse
Claude Monet (1867)
Claude Monet’s The Terrace at Sainte-Adresse stages a sunlit garden against the Channel, where <strong>bourgeois leisure</strong> unfolds between two wind-whipped flags and a horizon shared by <strong>sail and steam</strong>. Bright flowers, wicker chairs, and a white parasol form an ordered foreground, while the busy harbor and snapping tricolor project a confident, modern nation. The banded design—garden, sea, sky—reveals Monet’s early <strong>Japonisme</strong> and his drive to fuse fleeting light with a consciously structured composition <sup>[1]</sup>.
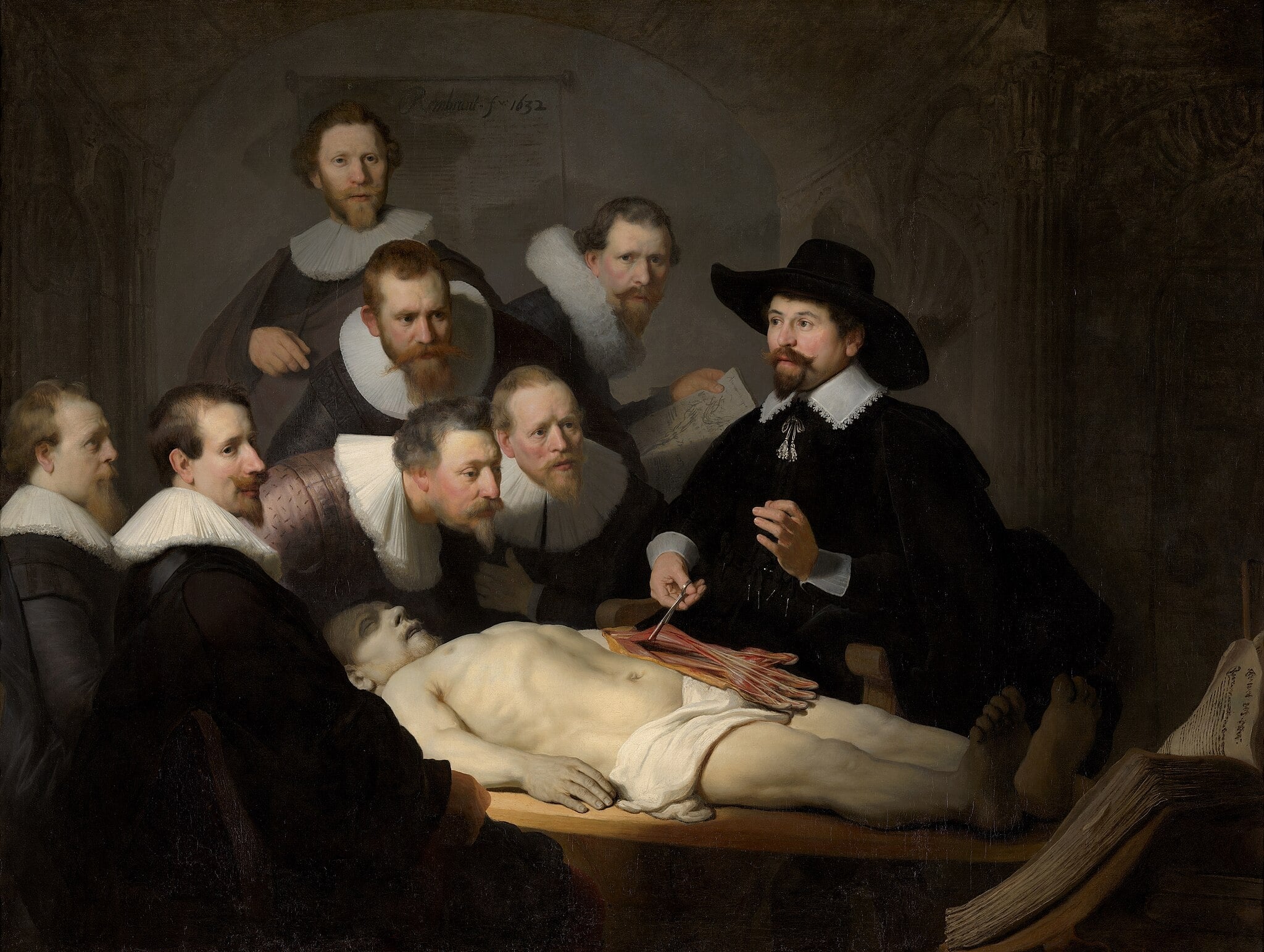

The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp
Rembrandt van Rijn (1632)
Rembrandt van Rijn turns a civic commission into a drama of <strong>knowledge made visible</strong>. A cone of light binds the ruff‑collared surgeons, the pale cadaver, and Dr. Tulp’s forceps as he raises the <strong>forearm tendons</strong> to explain the hand. Book and body face each other across the table, staging the tension—and alliance—between <strong>textual authority</strong> and <strong>empirical observation</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Boulevard des Capucines
Claude Monet (1873–1874)
From a high perch above Paris, Claude Monet turns the Haussmann boulevard into a living current of <strong>light, weather, and motion</strong>. Leafless trees web the view, crowds dissolve into <strong>flickering strokes</strong>, and a sudden <strong>pink cluster of balloons</strong> pierces the cool winter scale <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Lady at the Tea Table
Mary Cassatt (1883–85 (signed 1885))
Mary Cassatt’s Lady at the Tea Table distills a domestic rite into a scene of <strong>quiet authority</strong>. The sitter’s black silhouette, lace cap, and poised hand marshal a regiment of <strong>cobalt‑and‑gold Canton porcelain</strong>, while tight cropping and planar light convert hospitality into <strong>modern self‑possession</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The Theater Box
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1874)
Renoir’s The Theater Box turns a plush loge into a stage where seeing becomes the performance. A luminous woman—pearls, pale gloves, black‑and‑white stripes—faces us, while her companion scans the auditorium through opera glasses. The painting crystallizes Parisian <strong>modernity</strong> and the choreography of the <strong>gaze</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The Piazza San Marco, Venice
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1881)
Renoir’s The Piazza San Marco, Venice redefines St. Mark’s Basilica as <strong>atmosphere</strong> rather than architecture, fusing domes, mosaics, and crowd into vibrating color. Blue‑violet shadows sweep the square while pigeons and passersby resolve into <strong>daubs of light</strong>, declaring modern vision as the true subject <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
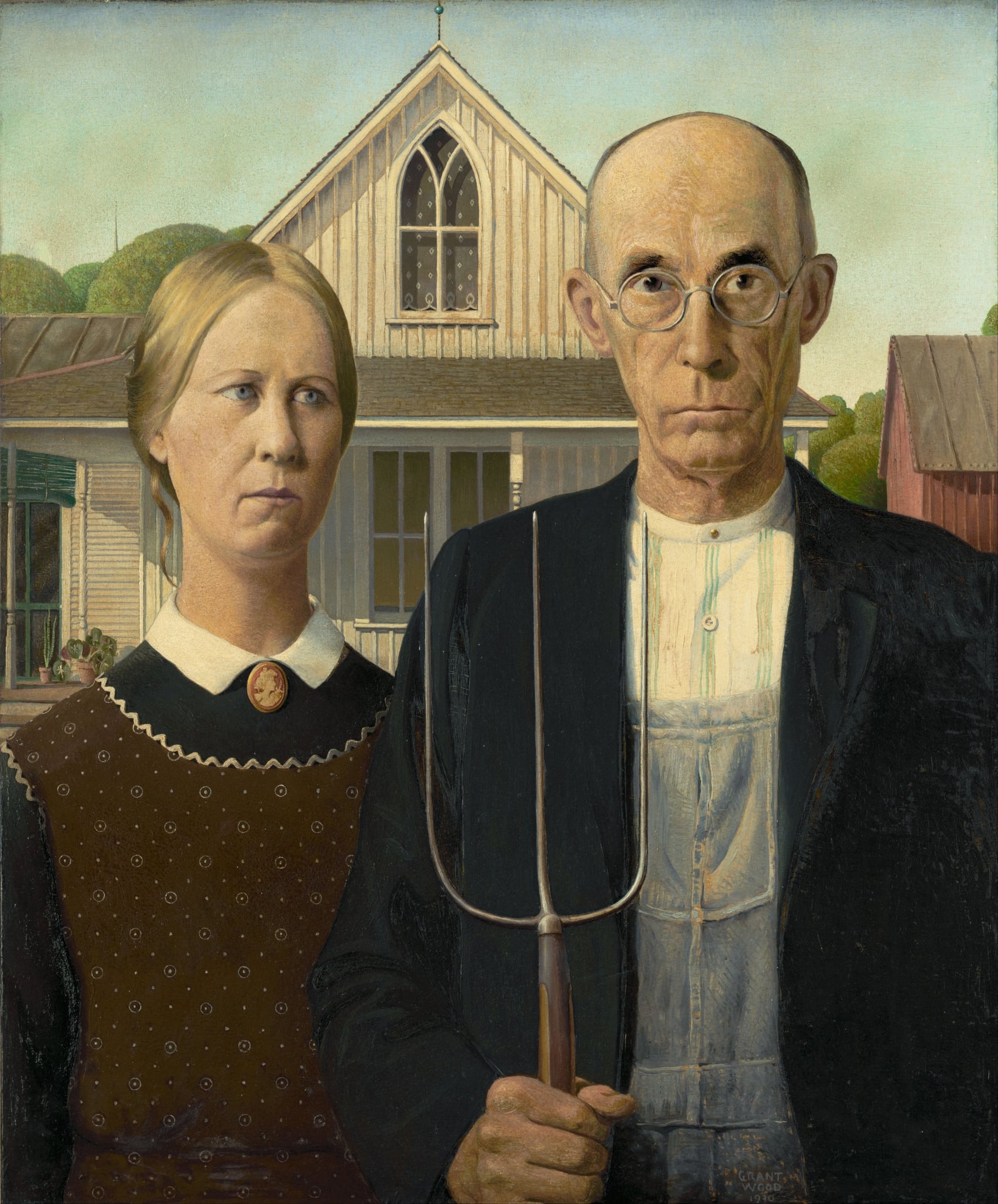

American Gothic
Grant Wood (1930)
Grant Wood’s American Gothic (1930) turns a plain Midwestern homestead into a <strong>moral emblem</strong> by binding two flinty figures to the strict geometry of a Carpenter Gothic gable and a three‑tined pitchfork. The painting’s cool precision and echoing verticals create a <strong>compressed ethic of work, order, and restraint</strong> that can read as both tribute and critique <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>.
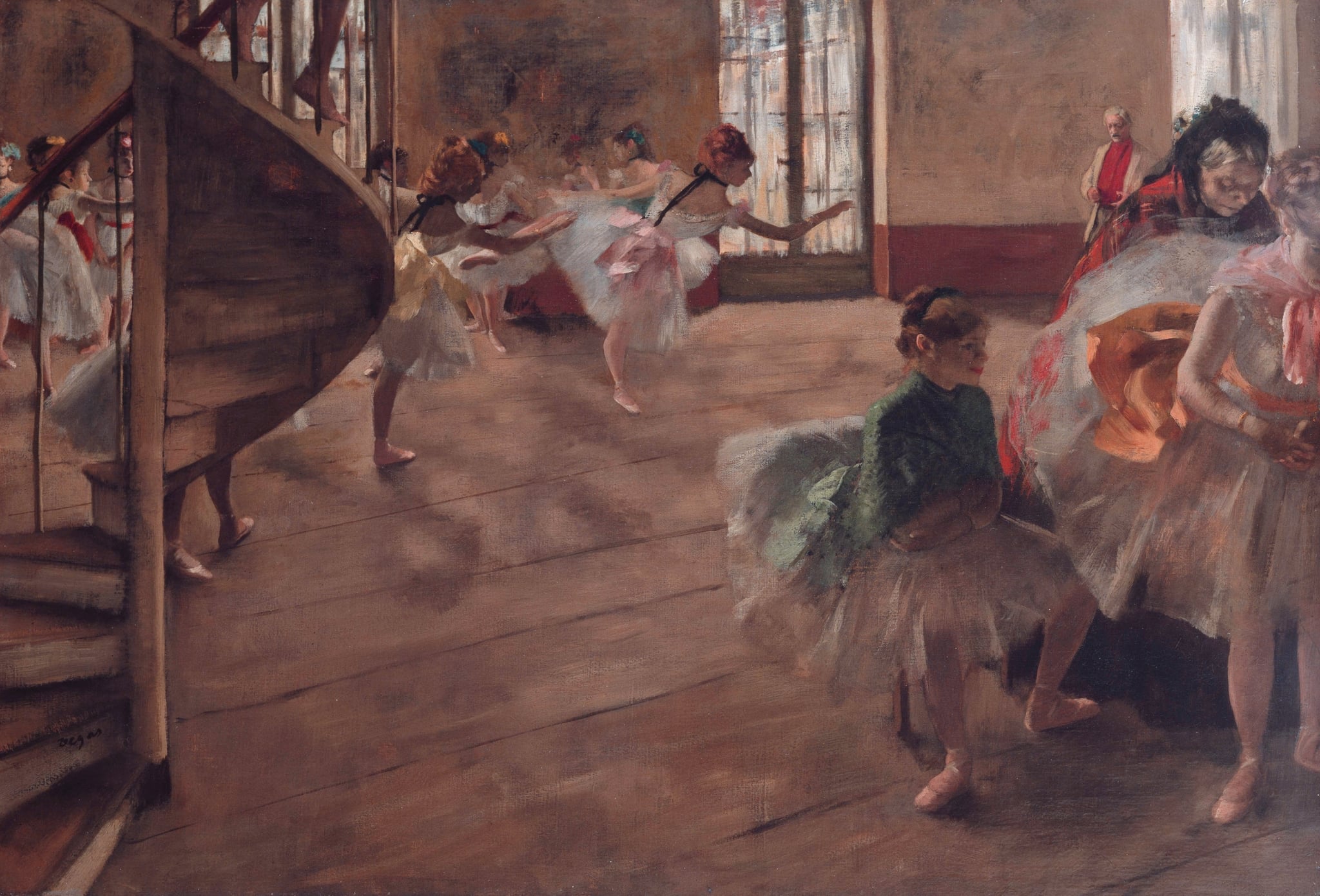

The Ballet Rehearsal
Edgar Degas (c. 1874)
In The Ballet Rehearsal, Edgar Degas turns a practice room into a modern drama where <strong>discipline and desire</strong> collide. A dark <strong>spiral staircase</strong> slices the space, scuffed floorboards yawn open, and clusters of dancers oscillate between poised effort and weary waiting <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[4]</sup>.
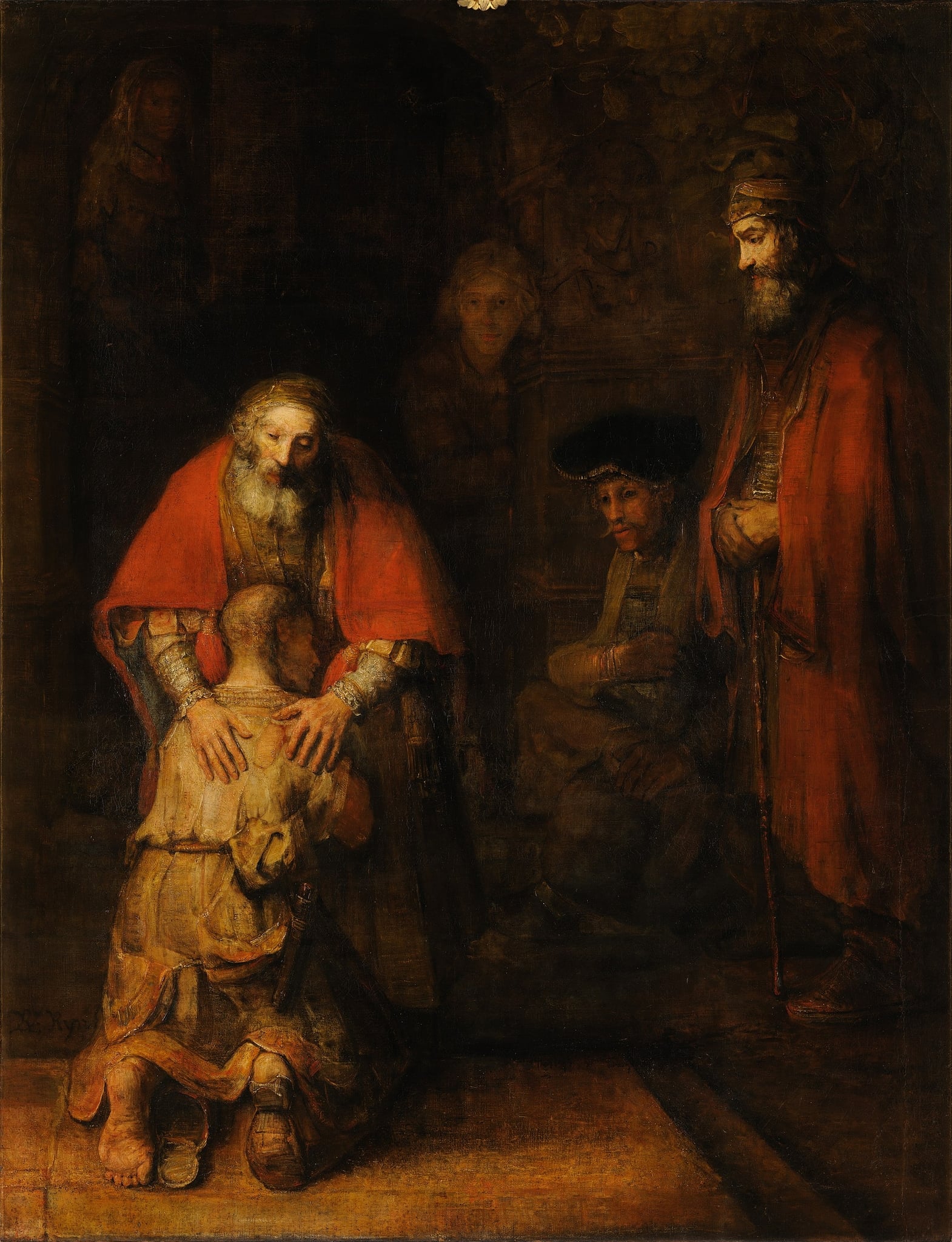

The Return of the Prodigal Son
Rembrandt van Rijn (c. 1661–1669 (probably completed by 1669))
Rembrandt van Rijn’s The Return of the Prodigal Son is a late-life meditation on <strong>mercy</strong>, <strong>homecoming</strong>, and <strong>restored dignity</strong>. In a hush of dusk-like light, a ragged son kneels into his father’s <strong>embrace</strong>, while an upright elder brother holds back in shadow. The image concentrates meaning in illuminated <strong>faces, hands, and feet</strong>, turning a parable into a timeless human reckoning. <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>

Las Meninas
Diego Velazquez (1656)
In Las Meninas, a luminous Infanta anchors a shadowed studio where the painter pauses at a vast easel and a small wall mirror reflects the monarchs. The scene folds artist, sitters, and viewer into one reflexive tableau, turning court protocol into a meditation on <strong>seeing and being seen</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[3]</sup>. A bright doorway at the rear deepens space and time, as if someone has just entered—or is leaving—the picture we occupy <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[5]</sup>.

The Third of May 1808
Francisco Goya (1814)
Francisco Goya’s The Third of May 1808 turns a specific reprisal after Madrid’s uprising into a universal indictment of <strong>state violence</strong>. A lantern’s harsh glare isolates a civilian who raises his arms in a <strong>cruciform</strong> gesture as a faceless firing squad executes prisoners, transforming reportage into <strong>modern anti-war testimony</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Arnolfini Portrait
Jan van Eyck (1434)
In The Arnolfini Portrait, Jan van Eyck stages a poised encounter between a richly dressed couple whose joined hands, a single burning candle, and a convex mirror transform a domestic interior into a scene of <strong>status and sanctity</strong>. The painting asserts the artist’s own <strong>presence</strong>—"Johannes de eyck fuit hic 1434"—as if to validate the moment while showcasing oil painting’s power to make belief tangible through light, texture, and reflection <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

The Son of Man
Rene Magritte (1964)
Rene Magritte’s The Son of Man stages a crisp <strong>everyman</strong> in bowler hat and overcoat before a sea horizon while a <strong>green apple</strong> hovers to block his face. The tiny glimpse of one eye above the fruit turns a straightforward portrait into a <strong>riddle about seeing and knowing</strong> <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Self-Portrait
Mary Cassatt (1878)
In Self-Portrait, Mary Cassatt presents a poised, <strong>modern woman</strong> angled diagonally across a striped chair, her gaze turned away in <strong>thoughtful reserve</strong>. A <strong>sage-olive ground</strong> and tight crop strip away setting, while the <strong>white dress</strong> flickers with lilacs and blues against a <strong>decisive red ribbon</strong> and floral bonnet. The image asserts <strong>professional selfhood</strong> through restraint, asymmetry, and broken color.<sup>[1]</sup>

Liberty Leading the People
Eugene Delacroix (1830)
<strong>Liberty Leading the People</strong> turns a real street uprising into a modern myth: a bare‑breasted Liberty in a <strong>Phrygian cap</strong> thrusts the <strong>tricolor</strong> forward as Parisians of different classes surge over corpses and rubble. Delacroix binds allegory to eyewitness detail—Notre‑Dame flickers through smoke, a bourgeois in a top hat shoulders a musket, and a pistol‑waving boy keeps pace—so that freedom appears as both idea and action <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. After its 2024 cleaning, sharper blues, whites, and reds re‑ignite the painting’s charged color drama <sup>[4]</sup>.

The Gleaners
Jean-Francois Millet (1857)
Three peasant women bend in a solemn rhythm, gleaning leftover stalks under a dry, late-afternoon light. In the far distance, tiny carts, haystacks, and an overseer on horseback signal abundance and authority, while the foreground figures loom with <strong>monumental gravity</strong>, asserting the dignity of labor amid inequality <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.

Mother About to Wash Her Sleepy Child
Mary Cassatt (1880)
Mary Cassatt’s Mother About to Wash Her Sleepy Child (1880) turns an ordinary bedtime ritual into a scene of <strong>caregiving, labor, and modern intimacy</strong>. Cropped close, with the child’s legs diagonally splayed and a tilted washbowl at the mother’s knee, the picture translates domestic routine into a <strong>modern Madonna</strong> for the bourgeois interior. Its flickering blues and milky whites, plus patterned upholstery and wallpaper, signal Cassatt’s <strong>Impressionist</strong> and japonisme-inflected design sense <sup>[2]</sup>.
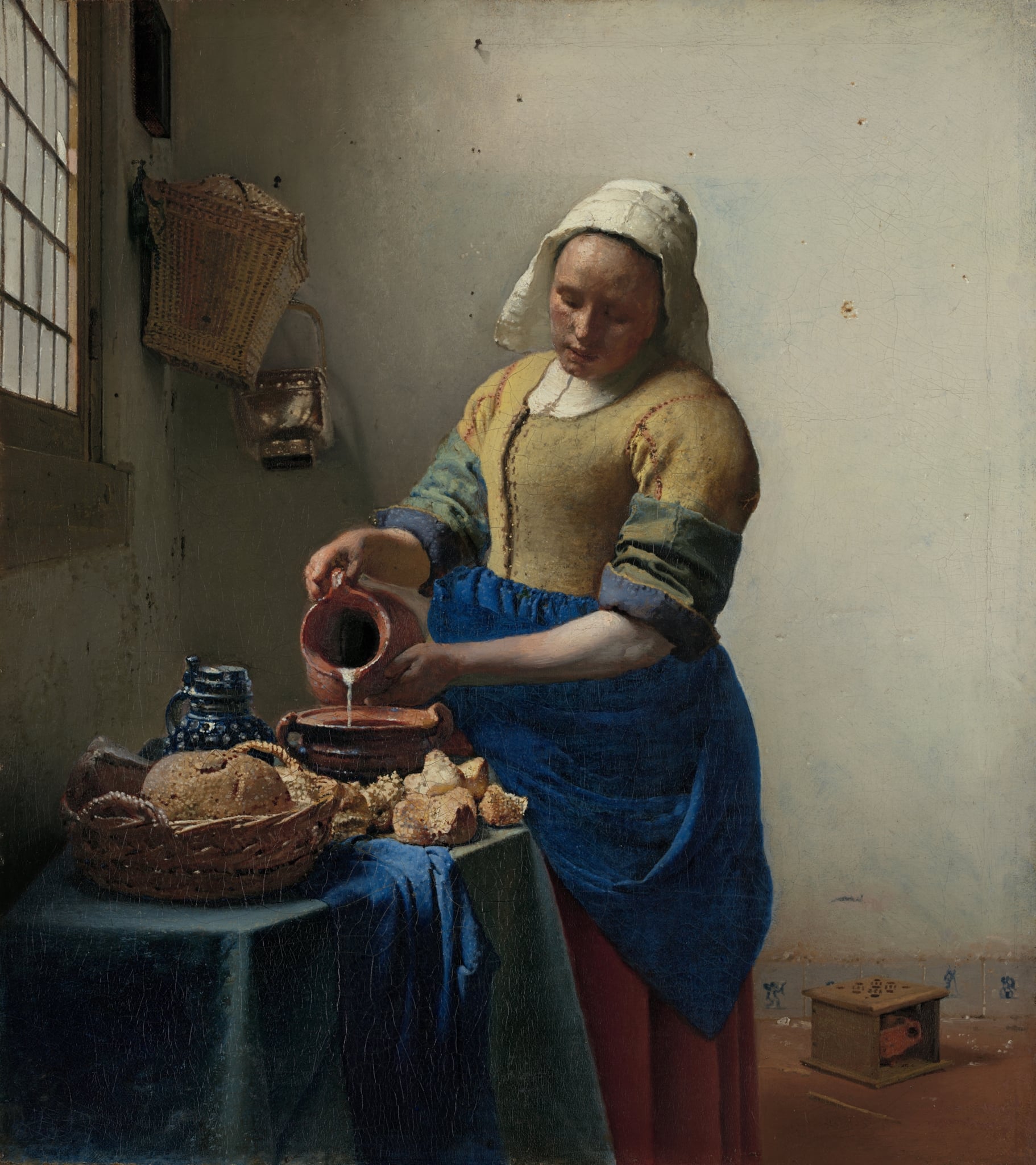

The Milkmaid
Johannes Vermeer (c. 1660)
In The Milkmaid, Vermeer turns an ordinary act—pouring milk—into a scene of <strong>quiet monumentality</strong>. Light from the left fixes the maid’s absorbed attention and ignites the <strong>saturated yellow and blue</strong> of her dress, while the slow thread of milk becomes the image’s pulse <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>. Bread, a Delft jug, nail holes, and a small <strong>foot warmer</strong> anchor a world where humble work is endowed with dignity and latent meaning <sup>[1]</sup><sup>[2]</sup>.